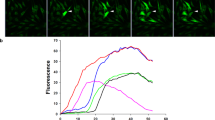
Abstract
In hypertonicity-stressed (i.e., 600 mOsm) SV40-immortalized rabbit and human corneal epithelial cell layers (RCEC and HCEC, respectively), we characterized the relationship between time-dependent changes in translayer resistance, relative cell volume and modulation of MAPK superfamily activities. Sulforhodamine B permeability initially increased by 1.4- and 2-fold in RCEC and HCEC, respectively. Subsequently, recovery to its isotonic level only occurred in RCEC. Light scattering revealed that in RCEC 1) regulatory volume increase (RVI) extent was 20% greater; 2) RVI half-time was 2.5-fold shorter. However, inhibition of Na-K-2Cl cotransporter and Na/K-ATPase activity suppressed the RVI response more in HCEC. MAPK activity changes were as follows: 1) p38 was wave-like and faster as well as larger in RCEC than in HCEC (90-and 18-fold, respectively); 2) increases in SAPK/JNK activity were negligible in comparison to those of p38; 3) Erk1/2 activity declined to 30–40% of their basal values. SB203580, a specific p38 inhibitor, dose de-pendently suppressed the RVI responses in both cell lines. However, neither U0126, which inhibits MEK, the kinase upstream of Erk, nor SP600125, inhibitor of SAPK/JNK, had any effect on this response. Taken together, sufficient activation of the p38 limb of the MAPK superfamily during a hypertonic challenge is essential for maintaining epithelial cell volume and translayer resistance. On the other hand, Erk1/2 activity restoration seems to be dependent on cell volume recovery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araie, M., Maurice, D. 1987. The rate of diffusion of fluorophores through the corneal epithelium and stroma. Exp. Eye. Res. 44:73–87
Araki, K., Ohashi, Y., Sasabe, T., Kinoshita, S., Hayashi, K., Yang, X.Z., Hosaka, Y., Aizawa, S., Handa, H. 1993. Immortalization of rabbit corneal epithelial cells by a recombinant SV40-adenovirus vector. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 34:2665–2671
Bildin, V.N., Yang, H., Crook, R.B., Fischbarg, J., Reinach, P.S. 2000. Adaptation by corneal epithelial cells to chronic hypertonic stress depends on upregulation of Na:K:2Cl cotransporter gene and protein expression and ion transport activity. J. Membrane Biol. 177:41–50
Bildin, V.N., Yang, H., Fischbarg, J., Reinach, P.S. 1998. Effects of chronic hypertonic stress on regulatory volume increase and Na-K-2C1 cotransporter expression in cultured corneal epithelial cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 438:637–642
Butterfield, L., Zentrich. E., Beekman, A., Heasley, L.E. 1999. Stress- and cell type-dependent regulation of transfected c-Jun N-terminal kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase isoforms. Biochem. J. 338:681–686
Candia, O.A., Patarca, R., Alvarez, L.J. 1998. Reduction of water permeability by anisotonic solutions in frog corneal epithelium. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 39:378–384
Cohen, D.M. 1999. Signalling and gene regulation by urea and NaCl in the renal medulla. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 26:69–73
Denkert, C., Warskulat, U., Hensel, F., Haussinger, D. 1998. Osmolyte strategy in human monocytes and macrophages: involvement of p38MAPK in hyperosmotic induction of betaine and myoinositol transporters. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 354: 172–180
Duzgun, S.A., Rasque, H., Kito, H., Azuma, N., Li, W., Basson, M.D., Gahtan, V., Dudrick, S.J., Sumpio, B.E. 2000. Mitogen-activated protein phosphorylation in endothelial cells exposed to hyperosmolar conditions. J. Cell Biochem. 76: 567–571
Fischbarg, J., Li, J., Kuang, K., Echevarria, M., Iserovich, P. 1993. Determination of volume and water permeability of plated cells from measurements of light scattering. Am. J. Physiol. 265: C1412–1423
Gillis, D., Shrode, L.D., Krump, E., Howard, CM., Rubie, E.A., Tibbies, L.A., Woodgett, J., Grinstein, S. 2001. Osmotic stimulation of the Na+/H+ exchanger NHE1: relationship to the activation of three MAPK pathways. J. Membrane Biol. 181:205–214
Goss, G.G., Jiang, L., Vandorpe, D.H., Kieller, D., Chernova, M.N., Robertson, M., Alper, S.L. 2001. Role of JNK in hypertonic activation of Cl--dependent Na+/H+ exchange in Xenopus oocytes. Am. J. Physiol. 281:1978–1990
Graf, J., Haussinger, D. 1996. Ion transport in hepatocytes: mechanisms and correlations to cell volume, hormone actions and metabolism. J. Hepatol. 24:53–77
Haas, M., McBrayer, D., Lytle, C. 1995. [Cl- i-dependent phosphorylation of the Na-K-Cl cotransport protein of dog tracheal epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 270:28955–28961
Hallows, K.R., Knauf, P.A. 1994. Regulatory volume decrease in HL-60 cells: importance of rapid changes in permeability of Cl- and organic solutes. Am. J. Physiol. 267:C1045–1056
Hoffert, J.D., Leitch, V., Agre, P., King, L.S. 2000. Hypertonic induction of aquaporin-5 expression through an ERK-dependent pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 275:9070–9077
Liedtke, CM., Cole, T.S. 2002. Activation of NKCC1 by hyperosmotic stress in human tracheal epithelial cells involves PKC-delta and ERK. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1589:77–88
Lu, L., Reinach, P.S., Kao, W.W. 2001. Corneal epithelial wound healing. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 226:653–664
Malek, A.M., Goss, G.G., Jiang, L., Izumo, S., Alper, S.L. 1998. Mannitol at clinical concentrations activates multiple signaling pathways and induces apoptosis in endothelial cells. Stroke 29:2631–2640
O’Neill, W.C. 1999. Physiological significance of volume-regulatory transporters. Am. J. Physiol. 276:C995-C1011
Palfrey, H.C., Pewitt, E.B. 1993. The ATP and Mg2+ dependence of Na+-K+-2Cl--cotransport reflects a requirement for protein phosphorylation: studies using calyculin A. Pfluegers Arch. 425:321–328
Pewitt, E.B., Hegde, R.S., Haas, M., Palfrey, H.C. 1990. The regulation of Na/K/2Cl cotransport and bumetanide binding in avian erythrocytes by protein phosphorylation and dephos-phorylation. Effects of kinase inhibitors and okadaic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 265:20747–20756
Reinach, P., Ganapathy, V., Torres-Zamorano, V. 1994. A Na:H exchanger subtype mediates volume regulation in bovine corneal epithelial cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 350:105–110
Roger, F., Martin, P.Y., Rousselot, M., Favre, H., Feraille, E. 1999. Cell shrinkage triggers the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases by hypertonicity in the rat kidney medullary thick ascending limb of the Henle’ s loop. Requirement of p38 kinase for the regulatory volume increase response. J. Biol. Chem. 274:34103–34110
Romio, L., Zegarra, M., Varesio, L., Galietta, L.J.V. 2001. Regulation of taurine transport in murine macrophages. Amino Acids. 21:151–160
Russell, J.M. 2000. Sodium-potassium-chloride cotransport. Physiol. Rev. 80:211–276
Sheikh-Hamad, D., Di Mari, J., Suki, W.N., Safirstein, R., Watts, B.A., 3rd, Rouse, D. 1998. p38 kinase activity is essential for osmotic induction of mRNAs for HSP70 and transporter for organic solute betaine in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J. Biol. Chem. 273:1832–1837
Sinning, R., Schliess, F., Kubitz, R., Haussinger, D. 1997. Osmo-signalling in C6 glioma cells. FEBS Lett. 400:163–167
Sun, D., O’Donnell, M.E. 1996. Astroglial-mediated phosphorylation of the Na-K-Cl cotransporter in brain microvessel endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 271:C620–627
Terada, Y., Tomita, K., Homma, M.K., Nonoguchi, H., Yang, T., Yamada, T., Yuasa, Y., Krebs, E.G., Sasaki, S., Marumo, F. 1994. Sequential activation of Raf-1 kinase, mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinase, MAP kinase, and S6 kinase by hyperosmolality in renal cells. J. Biol. Chem. 269:31296–31301
Watts, B.A., 3rd, Di Mari, J.F., Davis, R.J., Good, D.W. 1998. Hypertonicity activates MAP kinases and inhibits HCO-3 absorption via distinct pathways in thick ascending limb. Am. J. Physiol. 275:F478–486
Wojtaszek, P.A., Heasley, L.E., Siriwardana, G., Berl, T. 1998. Dominant-negative c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase 2 sensitizes renal inner medullary collecting duct cells to hypertonicity-induced lethality independent of organic osmolyte transport. J. Biol. Chem. 273:800–804
Zhuang, S., Hirai, S.I., Ohno, S. 2000. Hyperosmolality induces activation of cPKC and nPKC, a requirement for ERK1/2 activation in NIH/3T3 cells. Am. J. Physiol. 278:C102–109.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bildin, V.N., Wang, Z., Iserovich, P. et al. Hypertonicity-induced p38MAPK Activation Elicits Recovery of Corneal Epithelial Cell Volume and Layer Integrity. J. Membrain Biol. 193, 1–13 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-002-2002-8
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-002-2002-8