Abstract
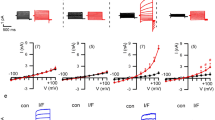
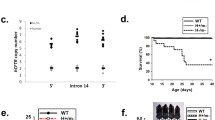
Trafficking of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) is central to its function, with the most common mutation, δF508, resulting in abnormal processing and trafficking. Therefore, there is a significant need to develop tools, which enable the trafficking of CFTR to be studied in vitro and in vivo. In previous studies it has been demonstrated that fusion of the green fluorescent protein (GFP) to the N-terminus of CFTR does lead to functional expression of CFTR chloride channels in epithelial cell lines. The aim of the present study was to examine whether it is possible to express GFP-tagged CFTR as a transgene in colonic and airway epithelial cells of cystic fibrosis (CF) mice and to correct the CF defect. Using the epithelial-specific human cytokeratin promoter K18, we generated bitransgenic mice cftr(551D/G551D) K18-GFP-CFTR+/-, designated GFP mice. Transcripts for GFP-CFTR could be detected in bitransgenic mice by use of RT-PCR techniques. Expression of GFP-CFTR protein was detected specifically in the colonic epithelium by both direct GFP fluorescence and the use of an anti-GFP antibody. Ussing chamber studies showed that the ion transport defect in colon and airways observed in cftr G551D/G5S1D mice was partially corrected in the bitransgenic animals. Thus, K18-GFP-CFTR is functionally expressed in transgenic mice, which will be a valuable tool in studies on CFTR synthesis, processing and ion transport in native epithelial tissues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alton, E.W., Middleton, P.G., Caplen, N.J., Smith, S.N., Steel, D.M., Munkonge, F.M., Jeffery, P.K., Geddes, D.M., Hart, S.L., Williamson, R. 1993. Non-invasive liposome-mediated gene delivery can correct the ion transport defect in cystic fibrosis mutant mice. Nat. Genet. 5:135–142
Biffi, A., Sersale, G., Cassetti, A., Villa, A., Bordignon, C., Assael, B.M., Conese, M. 1999. Restoration of bacterial killing activity of human respiratory cystic fibrosis cells through cationic vector-mediated cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene transfer. Hum. Gene Ther. 10:1923–1930
Chow, Y.H., Plumb, J., Wen, Y., Steer, B.M., Lu, Z., Buchwald, M., Hu, J. 2000. Targeting transgene expression to airway epithelia and submucosal glands, prominent sites of human CFTR expression. Mol. Ther. 2:359–367
Cuthbert, A.W., MacVinish, L.J., Hickman, M.E., Ratcliff, R., Colledge, W.H., Evans, M.J. 1994. Ion-transporting activity in the murine colonic epithelium of normal animals and animals with cystic fibrosis. Pflegers. Arch. 428:508–515
Delaney, S.J., Alton, E.W., Smith, S.N., Lunn, D.P., Farley, R., Lovelock, P.K., Thomson, S.A., Hume, D.A., Lamb, D., Porteous, D.J., Dorin, J.R., Wainwright, B.J. 1996. Cystic fibrosis mice carrying the missense mutation G551D replicate human genotype-phenotype correlations. EMBO J. 15:955–963
Drumm, M.L., Pope, H.A., Cliff, W.H., Rommens, J.M., Marvin, S.A., Tsui L.-C., Collins, F.S., Frizzell, R.A. Wilson, J.M. 1990. Correction of the cystic fibrosis defect in vitro by retrovirus-mediated gene transfer. Cell 62:1227–1233
Galietta, L.J., Haggie, P.M., Verkman, A.S. 2001. Green fluorescent protein-based halide indicators with improved chloride and iodide affinities. FEBS Lett. 499:220–224
Galietta, L.V., Springsteel, M.F., Eda, M., Niedzinski, E.J., By, K., Haddadin, M.J., Kurth, M.J., Nantz, M.H., Verkman, A.S. 2001. Novel CFTR chloride channel activators identified by screening of combinatorial libraries based on flavone and benzoquinolizinium lead compounds. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 19723–19728
Gerceker, A.A., Zaidi, T., Marks, P., Golan, D.E., Pier, G.B. 2000. Impact of heterogeneity within cultured cells on bacterial invasion: analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella enterica serovar typhi entry into MDCK cells by using a green fluorescent protein-labelled cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator receptor. Infect. Immun. 68:861–870
Gerdes, H.H., Kaether, C. 1996. Green fluorescent protein: applications in cell biology. FEBS Lett. 389:44–47
Grubb, B.R., Boucher, R.C. 1999. Pathophysiology of genetargeted mouse models for cystic fibrosis. Physiol. Rev. 79: S193-S214
Grubb, B.R., Gabriel, S.E. 1997. Intestinal physiology and pathology in gene-targeted mouse models of cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. 273:G258-G266
Grubb, B.R., Vick, R.N., Boucher, R.C. 1994. Hyperabsorption of Na+- and raised Ca2+-mediated Cl- secretion in nasal epithelia of CF mice. Am. J. Physiol. 266:C1478-C1483
Hall, R.A., Ostedgaard, L.S., Premont, R.T., Blitzer, J.T., Rahman, N., Welsh, M.J., Lefkowitz, R.J. 1998. A C-terminal motif found in the beta2-adrenergic receptor, P2Y1 receptor and cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator determines binding to the Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor family of PDZ proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:8496–8501
Hamosh, A., King, T.M., Rosenstein, B.J., Corey, M., Levison, H., Durie, P., Tsui, L.C., Mclntosh, I., Keston, M., Brock, DJ. 1992. Cystic fibrosis patients bearing both the common missense mutation Gly—Asp at codon 551 and the delta F508 mutation are clinically indistinguishable from delta F508 homozygotes, except for decreased risk of meconium ileus. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 51:245–250
Holt, J.R., Johns, D.C., Wang, S., Chen, Z.Y., Dunn, R.J., Marban, E., Corey, D.P. 1999. Functional expression of exogenous proteins in mammalian sensory hair cells infected with adenoviral vectors. J. Neurophysiol. 81:1881–1888
Hyde, S.C., Gill, D.R., Higgins, C.F., Trezise, A.E. 1993. Correction of the ion transport defect in cystic fibrosis transgenic mice by gene therapy. Nature 362:250–255
Koehler, D.R., Chow, Y.H., Plumb, J., Wen, Y., Rafii, B., Beicastro, R., Haardt, M., Lukacs, G.L., Post, M., Tanswell, A.K., Hu, J. 2000. A human epithelium specific vector optimized in rat pneumocytes for lung gene therapy. Pediatr. Res. 48:184–190
Kollen, W.J., Mulberg, A.E., Wei, X., Sugita, M., Raghuram, V., Wang, J., Foskett, J.K., Glick, M.C., Scanlin, T.F. 1999. High-efficiency transfer of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator cDNA into cystic fibrosis airway cells in culture using lactosylated polylysine as a vector. Hum. Gene Ther. 10:615–622
Kunzelmann, K. 1999. The Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator and its function in epithelial transport. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 137:1–70
Kunzelmann, K., Mall, M. 2002. Electrolyte transport in the colon: Mechanisms and implications for disease. Physiologkal Reviews 82:245–289
Kupper, J. 1998. Functional expression of GFP-tagged Kv1.3 and Kvl.4 channels in HEK 293 cells. Eur. J. Neurosci. 10:3908–3912
Li, H., Guo, W., Xu, H., Hood, R., Benedict, A.T., Nerbonne, J.M. 2001. Functional expression of a GFP-tagged Kvl.5 alpha-subunit in mouse ventricle. Am. J. Physiol. 281:H1955-H1967
Mall, M., Bleich, M., Greger, R., Schürlein, M., Kühr, J., Seydewitz, H.H., Brandis, M., Kunzelmann, K. 1998. Cholinergic ion secretion in human colon requires co-activation by cAMP. Am. J. Physiol. 275:G1274-G1281
Mall, M., Bleich, M., Kühr, J., Brandis, M., Greger, R., Kunzelmann, K. 1999. CFTR-mediated inhibition of amiloride-sensitive sodium conductance by CFTR in human colon is defective in cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. 277:G709-G716
Mall, M., Wissner, A., Seydewitz H.H., Kühr, J., Brandis, M., Greger, R., Kunzelmann, K. 2000. Defective cholinergic Cl- secretion and detection of K+ secretion in rectal biopsies from cystic fibrosis patients. Am. J. Physiol. 278:G617-G624
Meyer, E., Fromherz, P. 1999. Ca2+ activation of hSlo K+ channel is suppressed by N-terminal GFP tag. Eur. J. Neurosci. 11:1105–1108
Moyer, B.D., Denton, J., Karlson, K.H., Reynolds, D., Wang, S., Mickle, J.E., Milewski, M., Cutting, G.R., Guggino, W.B., Li, M., Stanton, B.A. 1999. A PDZ-interacting domain in CFTR is an apical membrane polarization signal. J. Clin. Invest. 104:1353–1361
Moyer, B.D., Loffing, J., Schwiebert, E.M., Loffing-Cueni, D., Halpin, P.A., Karlson, K.H., Ismailov, I.I., Guggino, W.B., Langford, G.M., Stanton, B.A. 1998. Membrane trafficking of the cystic fibrosis gene product, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator, tagged with green fluorescent protein in madin-darby canine kidney cells. J. Biol. Chem. 273:21759–21768
Oceandy, D., McMorran, B.J., Smith, S.N., Schreiber, R., Kunzelmann, K., Alten, E.W.F., Hume, D.A., Wainwright, B.J. 2002. Gene complementation of airway epithelium in the cystic fibrosis mouse is necessary and sufficient to correct the pathogen clearance and inflammatory abnormalities. Hum. Mol. Genet. 11:1059–1067
Pier, G.B., Grout, M., Zaidi, T.S. 1997. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator is an epithelial cell receptor for clearance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from the lung. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:12088–12093
Rich, DP., Anderson, M.P., Gregory, R.J., Cheng, S.H., Paul, S., Jefferson, D.M., McCann, J.D., Klinger, K.W., Smith, A.E., Welsh, M.J. 1990. Expression of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator corrects defective chloride channel regulation in cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells. Nature 347:358–363
Riordan, J.R., Rommens, J.M., Kerem, B.-S., Alon, N., Rozmahel, R., Grzelczak, Z., Zielenski, J., Plavsic, S.L.N., Chou, J.-L, Drumm, M.L., Iannuzzi, C.M., Collins, F.S., Tsui, L.-C. 1989. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science 245:1066–1072
Rochelle, L.G., Li, D.C., Ye, H., Lee, E., Talbot, C.R., Boucher, R.C. 2000. Distribution of ion transport mRNAs throughout murine nose and lung. Am. J. Physiol. 279:L14-L24
Schwiebert, E.M., Benos, D.J., Egan, M.E., Stutts, M.J., Guggino, W.B. 1999. CFTR is a conductance regulator as well as a chloride channel. Physiol. Rev. 79:S145-S166
Stutts, M.J., Canessa, C.M., Olsen, J.C., Hamrick, M., Cohn, J.A, Rossier, B.C., Boucher R.C. 1995. CFTR as a cAMP- dependent regulator of sodium channels. Science 269:847–850
Tarran, R., Grubb, B.R., Parsons, D., Picher, M., Hirsh A.J., Davis, C.W., Boucher, R.C. 2001. The CF salt controversy: in vivo observations and therapeutic approaches. Mol. Cell 8:149–158
Veeze, H.J., Halley, D.J., Bijman, J., De Jongste, J.C., De Jonge, H.R., Sinaasappel, M. 1994. Determinants of mild symptoms in cystic fibrosis patients — residual chloride secretion measured in rectal biopsies in relation to the genotype. J. Clin. Invest. 93:461–466
Veeze, H.J., Sinaasappel, M., Bijman, J., Bouquet, J., De Jonge, H.R. 1991. Ion transport abnormalities in rectal suction biopsies from children with cystic fibrosis. Gastroenterology 101:398–403
Wahlfors, J., Loimas, S., Pasanen, T., Hakkarainen, T. 2001. Green fluorescent protein (GFP) fusion constructs in gene therapy research. Histochem. Cell Biol. 115:59–65
Welsh, M.J. 1999. Gene transferor cystic fibrosis. J. Clin. Invest. 104:1165–1166
Zabner, J., Couture, L.A., Gregory, R.J., Graham, S.M., Smith, A.E., Welsh, M.J. 1993. Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer transiently corrects the chloride transport defect in nasal epithelia of patients with cystic fibrosis. Cell 75:207–216
Zdebik, A., Hug, M.J., Greger, R. 1997. Chloride channels in the luminal membrane of rat pancreatic acini. Pfuegers Arch 434:188–194
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oceandy, D., McMorran, B., Schreiber, R. et al. GFP-tagged CFTR transgene is functional in the G551D cystic fibrosis mouse colon. J. Membrane Biol. 192, 159–167 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-002-1072-y
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-002-1072-y