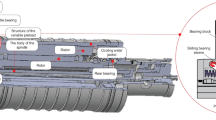
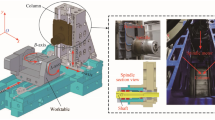
Abstract
The thermal deformation of motorized spindle has a great influence on the precision of numerical control (NC) machine tools. Thus, it is crucial to predict the thermal deformation in the design and operation control phase by numerical simulation and improve the precision of NC machine tools. In order to achieve this, an accurate thermal deformation prediction model for motorized spindle is required. In this paper, a model for predicting the thermal error of motorized spindle based on finite element method and parameter optimization is proposed. Levenberg-Marquardt (LM) method is applied to optimize the heat transfer coefficient of motorized spindle by using surface temperature data measured. The optimized heat transfer coefficient is then taken as one of the boundary condition of the finite element model. The boundary conditions about heat of the finite element model are obtained by energy loss experiment. The proposed model is validated by experimental results, and the results have shown well correlation.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bryan J (1990) International status of thermal error research (1990). CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 39(2):645–656
Liang RJ, Ye WH, Zhang HY, Yang QF (2012) The thermal error optimization models for CNC machine tools. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 63(9–12):1167–1176
Weck M, McKeown P, Bonse R, Herbst U (1995) Reduction and compensation of thermal errors in machine tools. CIRP Annals Manuf Technol 44(2):589–598
Creighton E, Honegger A, Tulsian A, Mukhopadhyay D (2010) Analysis of thermal errors in a high-speed micro-milling spindle. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 50(4):386–393
Barbin AY, Molodtsov VV (2013) Motorized spindles as primary drives in metal cutting machines. Russ Eng Res 33(8):481–485
Su H, Lu LH, Liang YC, Zhang Q, Sun YZ (2014) Thermal analysis of the hydrostatic spindle system by the finite volume element method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 71(9–12):1949–1959
Ma C, Yang J, Zhao L, Mei XS, Shi H (2015) Simulation and experimental study on the thermally induced deformations of high-speed spindle system. Appl Therm Eng 86:251–268
Liu ZF, Pan MH, Zhang AP, Zhao YS, Yang Y, Ma CY (2015) Thermal characteristic analysis of high-speed motorized spindle system based on thermal contact resistance and thermal-conduction resistance. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 76:1913–1926
Bossmanns B, Tu JF (1999) A thermal model for high speed spindles. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 39(9):1345–1346
Bossmanns B, Tu JF (2001) A power flow model for high speed motorized spindles—heat generation characterization. Trans ASME J Manuf Sci Eng 123(3):494–505
Liu JF, Chen XA (2014) Dynamic design for motorized spindles based on an integrated model. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 71(9–12):1961–1974
Zhang JF, Feng PF, Chen C, Yu DW, Wu ZJ (2013) A method for thermal performance modeling and simulation of machine tools. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 68(5–8):1517–1527
Holkup T, Cao H, Kolář P, Altintas Y, Zeleny J (2010) Thermo-mechanical model of spindles. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 59(1):365–368
Zhao HT, Yang JG, Shen JH (2007) Simulation of thermal behavior of a CNC machine tool spindle. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 47:1003–1010
Du ZC, Yao SY, Yang JG (2015) Thermal behavior analysis and thermal error compensation for motorized spindle of machine tools. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 16(7):1571–1581
Yang J, Shi H, Feng B, Zhao L, Ma C, Mei XS (2015) Thermal error modeling and compensation for a high-speed motorized spindle. Int J Adv Manuf Technol l77:1005–1017
Li DX, Feng PF, Zhang JF, Wu ZJ, Yu DW (2014) Calculation method of convective heat transfer coefficients for thermal simulation of a spindle system based on RBF neural network. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 70(5–8):1445–1454
Wang BM, Mei XS, Wu ZX, Zhu F (2015) Dynamic modeling for thermal error in motorized spindles. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 78:1141–1146
Huang YQ, Zhang J, Li X, Tian LJ (2014) Thermal error modeling by integrating GA and BP algorithms for the high-speed spindle. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 71(1):1669–1675
Li S, Zhang YA (1997) Study of pre-compensation for thermal errors of NC machine tools. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 37(12):1715–1719
Chena JS, Chiou G (1995) Quick testing and modeling of thermally induced errors of CNC machine tools. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 35(7):1063–1074
Yang H, Ni J (2003) Dynamic modeling for machine tool thermal error compensation. J Manuf Sci Eng 125(5):245–254
Wang YF, Sun QG, Lv HB (2014) The temperature field comparison between oil gas lubrication and oil injection lubrication of rolling bearing. Lubr Eng 39(2):66–70
Yang SY, Gao XH, Liu XX (2011) High-speed motorized spindle water-cooling system solid-liquid coupling heat transfer simulation analysis, Mach. Tool Hydr 39(11):102–104
Ludowski P, Taler D, Taler J (2013) Identification of thermal boundary conditions in heat exchangers of fluidized bed boilers. Appl Therm Eng 58:194–204
Taler J, Taler D, Ludowski P (2014) Measurements of local heat flux to membrane water walls of combustion chambers. Fuel 115(1):70–83
Gerlich V, Sulovská K, Zálešák M (2013) COMSOL multiphysics validation as simulation software for heat transfer calculation in buildings: Building simulation software validation. Measurement 46:2003–2012
Brito RF, Carvalho SR, Silva SMMLE (2015) Experimental investigation of thermal aspects in a cutting tool using comsol and inverse problem. Appl Therm Eng 86:60–68
Li YX, Yang JG, Gelvis T, Li YY (2008) Optimization of measuring points for machine tool thermal error based on grey system theory. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 35(7–8):745–775
Zhao HT, Yang JG, Shen JH (2006) Simulation of thermal behavior of a CNC machine tool spindle. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 46(6):1–8
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully wish to acknowledge the supports of the National Science Foundation (51375317), the National Science Foundation (51675353), Liaoning Province Science Foundation (2015020122), and National (local) Joint Engineering Laboratory for open funds (sjsc-2015-6).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Li, J., Wu, Y. et al. Prediction model and experimental validation for the thermal deformation of motorized spindle. Heat Mass Transfer 54, 2691–2704 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-018-2317-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-018-2317-3