Abstract
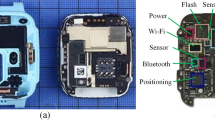
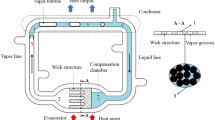
In recent years, heat pipes have been widely used in various hand held mobile electronic devices such as smart phones, tablet PCs, digital cameras. With the development of technology these devices have different user friendly features and applications; which require very high clock speeds of the processor. In general, a high clock speed generates a lot of heat, which needs to be spreaded or removed to eliminate the hot spot on the processor surface. However, it is a challenging task to achieve proper cooling of such electronic devices mentioned above because of their confined spaces and concentrated heat sources. Regarding this challenge, we introduced an ultra-thin heat pipe; this heat pipe consists of a special fiber wick structure named as “Center Fiber Wick” which can provide sufficient vapor space on the both sides of the wick structure. We also developed a cooling module that uses this kind of ultra-thin heat pipe to eliminate the hot spot issue. This cooling module consists of an ultra-thin heat pipe and a metal plate. By changing the width, the flattened thickness and the effective length of the ultra-thin heat pipe, several experiments have been conducted to characterize the thermal properties of the developed cooling module. In addition, other experiments were also conducted to determine the effects of changes in the number of heat pipes in a single module. Characterization and comparison of the module have also been conducted both experimentally and theoretically.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Cross-sectional area (m2)
- H :
-
Height (mm)
- K :
-
Permeability (m2)
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity (W/m K)
- L:
-
Length (m)
- Q :
-
Heat input (W)
- R :
-
Thermal resistance (K/W)
- r :
-
Radius (m)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- X :
-
Distance (m)
Distance (mm)
- amb:
-
Ambient
- avg:
-
Average
- cross:
-
Cross-sectional
- eff:
-
Effective
- HP:
-
Heat pipe
- h:
-
Heater
- IN:
-
Input
- p:
-
Pore
References
Ponnapan R (2002) Novel grooved-shaped screen-wick miniature heat pipe. AIAA J Thermo Phys Heat Transf 16(1):17–21
Maidanik YF (2005) Loop heat pipes. Appl Therm Eng 25:635–657
Vasilev LL (2005) Heat pipes in modern heat exchangers. Appl Therm Eng 25:1–9
Vasilev LL (2008) Micro and miniature heat pipes—electronic component coolers. Appl Therm Eng 28:266–273
Mochizuki M, Nguyen T, Mashiko M, Saito Y (2004) Update cooling technology for personal computers using heat pipes and vapor chamber. In: 1st international seminar on heat pipes and heat recovery system, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 8–9 Dec 2004
Jalilvand A, Mochizuki M, Saito Y, Kawahara Y, Nguyen T, Wuttijumnong V (2011) Thinner thermal solution module by combination of thin heat pipe and piezo fan. In: InterPACK 2011 6–8 July 2011, Portland, Oregon, USA
Faghri A (1995) Heat pipe science and technology. Taylor and Francis, London
Ahamed MS, Mochizuki M, Saito Y, Mashiko K, Kawahara Y, Tahara Y (2011) Investigation of thermal performance of thin heat pipe with fiber wick structure. In: 48th national heat transfer symposium, Okayama, Japan, 01–03 Jun 2011
Ahamed MS, Mochizuki M, Saito Y (2012) Experimental & theoretical study of the dominant limiting factors in thin heat pipe with fiber wick structure. In: Thermal engineering conference, Kumamoto, Japan, 17–18 Nov 2012
Ahamed MS, Mochizuki M, Saito Y, Mashiko M (2015) Hot spot elimination by thin and smart heat spreader. In: InterPACK 2015 & ICNMM2015, San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–9 July 2015
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahamed, M.S., Saito, Y., Mashiko, K. et al. Characterization of a high performance ultra-thin heat pipe cooling module for mobile hand held electronic devices. Heat Mass Transfer 53, 3241–3247 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-017-2022-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-017-2022-7