Abstract
Objectives: To assess the effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of the antimalarial mefloquine and its major plasma metabolite in healthy volunteers.
Methods: In an open, two-way cross-over study, 20 healthy male volunteers who had fasted overnight were randomised to receive a single oral dose of 750 mg mefloquine in the absence or presence of a standardised, high-fat breakfast, administered 30 min before drug administration. Blood samples were taken at specific times over an 8-week period. Plasma concentrations of mefloquine and its carboxylic acid metabolite were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography for pharmacokinetic evaluation.
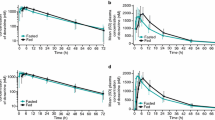
Results: The parameters Cmax and AUC of both mefloquine and its metabolite were significantly (P < 0.05) higher under post-prandial conditions than under fasting conditions (mefloquine: mean Cmax 1500 vs 868 μg · l−1, mean AUC 645 vs 461 mg l−1 · h; metabolite: Cmax 1662 vs 1231 μg · l−1, AUC 1740 vs 1310 mg l−1 · h). The intersubject variability in Cmax and AUC of mefloquine was less than 30% (coefficient of variation). The time to peak plasma concentration of mefloquine was significantly shorter after food intake (17 vs 36 h). Compared with absorption in volunteers who had fasted, food did not alter t1/2 (mefloquine and its metabolite) and tmax (metabolite).
Conclusion: Under the conditions of this study, food increases the rate and the extent of mefloquine absorption. It is reasonable to recommend that mefloquine be administered with food in travellers receiving chemoprophylaxis and in patients on recovery receiving curative treatment. In acutely ill patients, mefloquine should be taken as soon as possible and administration with or shortly after meals should be attempted as soon as feasible.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 10 February 1997 / Accepted in revised form: 16 June 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crevoisier, C., Handschin, J., Barré, J. et al. Food increases the bioavailability of mefloquine. E J Clin Pharmacol 53, 135–139 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280050351
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280050351