Abstract.
Rationale: Poor specificity of face-value endpoints and the poor sensitivity of gross clinical examination may have militated against demonstrating prophylaxis by selegiline.
Methods:
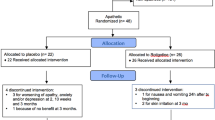
Objective measures of the four cardinal signs were used as primary outcome criteria in a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group study of selegiline monotherapy in 25 newly diagnosed elderly sufferers from idiopathic parkinsonism, stratified for sex and Hoehn and Yahr functional staging.
Results:
There was a significant interaction between time and nature of treatment with respect to rigidity. The effect of time during active treatment was highly significant: rigidity decreased by 1.3 % per week. The worsening of rigidity on placebo was not statistically significant. Neuronal rescue is a possible explanation for the long term, progressive improvement produced by selegiline.
No significant treatment effect was seen on the other cardinal signs. However, there was a significant quadratic time trend for arousal on active treatment suggesting tolerance to this effect.
Conclusion:
The difference in time course between the psychostimulant and physical effects suggests more than one mode of action.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 7 December 1994 /Accepted in revised form: 12 September 1995
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirollos, C., Charlett, A., Bowes, S. et al. Time course of physical and psychological responses to selegiline monotherapy in newly diagnosed, idiopathic parkinosonism. E J Clin Pharmacol 50, 7–18 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280050062
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280050062