Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of the study is to conduct a systematic review of studies examining the association between anticholinergic burden and mortality in older individuals.
Methods
A literature search was performed to identify relevant studies, using MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsycINFO and CENTRAL, from January 1990 to December 2018. We included studies of patients with a mean age of 65 years or older where the anticholinergic burden was estimated using anticholinergic risk assessment tools, and associations between anticholinergic load and mortality were investigated. The primary outcome of interest was the association between anticholinergic burden and mortality.
Results
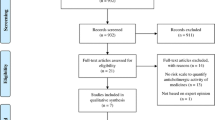
Twenty-seven studies were included. These were three cross-sectional, one nested case-control and 23 prospective or retrospective cohort studies. Most studies were determined to be of good quality. A total of 15 studies reported a positive correlation between anticholinergic burden and mortality, while the remaining 10 studies did not report a significant association. Eighteen out of 27 studies (80%) had a short follow-up period of 1 year or less. Among the five high-quality studies that met all the domains of the quality assessment criteria, four showed a positive association.
Conclusion
The variation in results could relate to the quality of the studies, follow-up period, anticholinergic risk assessment tool used and the study setting. Sixty-three percent (n = 17) of all the included studies, but almost all of the high-quality studies with an extended follow-up, reported a positive correlation between anticholinergic burden and mortality. Further high-quality research, using standardized measures and with adequate follow-up periods, is required to confirm the relationship between anticholinergic burden and mortality.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nishtala PS, Salahudeen MS, Hilmer SN (2016) Anticholinergics: theoretical and clinical overview. Expert Opin Drug Saf 15:753–768
Salahudeen MS, Duffull SB, Nishtala PS (2015) Anticholinergic burden quantified by anticholinergic risk scales and adverse outcomes in older people: a systematic review. BMC Geriatr 15:31
Salahudeen MS, Nishtala PS (2016) Examination and estimation of anticholinergic burden: current trends and implications for future research. Drugs Aging 33:305–313
Kouladjian O’Donnell L, Gnjidic D, Nahas R, Bell JS, Hilmer SN (2017) Anticholinergic burden: considerations for older adults. J Pharm Pract Res 47:67–77
Salahudeen MS, Nishtala PS, Duffull SB (2015) The influence of patient characteristics on anticholinergic events in older people. Dementia and geriatric cognitive disorders extra 5:530–541
Ruxton K, Woodman RJ, Mangoni AA (2015) Drugs with anticholinergic effects and cognitive impairment, falls and all-cause mortality in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol 80:209–220
Campbell N, Boustani M, Limbil T, Ott C, Fox C, Maidment I, Schubert CC, Munger S, Fick D, Miller D, Gulati R (2009) The cognitive impact of anticholinergics: a clinical review. Clin Interv Aging 4:225–233
Rudolph JL, Salow MJ, Angelini MC, McGlinchey RE (2008) The anticholinergic risk scale and anticholinergic adverse effects in older persons. Arch Intern Med 168:508–513
Fox C, Richardson K, Maidment ID, Savva GM, Matthews FE, Smithard D, Coulton S, Katona C, Boustani MA, Brayne C (2011) Anticholinergic medication use and cognitive impairment in the older population: the medical research council cognitive function and ageing study. J Am Geriatr Soc 59:1477–1483
Mulsant BH, Pollock BG, Kirshner M, Shen C, Dodge H, Ganguli M (2003) Serum anticholinergic activity in a community-based sample of older adults: relationship with cognitive performance. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60:198–203
Budnitz DS, Pollock DA, Weidenbach KN, Mendelsohn AB, Schroeder TJ, Annest JL (2006) National surveillance of emergency department visits for outpatient adverse drug events. Jama 296:1858–1866
Salahudeen MS, Hilmer SN, Nishtala PS (2015) Comparison of anticholinergic risk scales and associations with adverse health outcomes in older people. J Am Geriatr Soc 63:85–90
Kersten H, Wyller TB (2014) Anticholinergic drug burden in older people’s brain—how well is it measured? Basic & clinical pharmacology & toxicology 114:151–159
Wastesson JW, Morin L, Tan ECK, Johnell K (2018) An update on the clinical consequences of polypharmacy in older adults: a narrative review. Expert Opin Drug Saf 17:1185–1196
Welsh TJ, van der Wardt V, Ojo G, Gordon AL, Gladman JRF (2018) Anticholinergic drug burden tools/scales and adverse outcomes in different clinical settings: a systematic review of reviews. Drugs Aging 35:523–538
Crispo JA, Willis AW, Thibault DP, Fortin Y, Hays HD, McNair DS, Bjerre LM, Kohen DE, Perez-Lloret S, Mattison DR, Krewski D (2016) Associations between anticholinergic burden and adverse health outcomes in Parkinson disease. PLoS One 11:e0150621
Myint PK, Fox C, Kwok CS, Luben RN, Wareham NJ, Khaw KT (2015) Total anticholinergic burden and risk of mortality and cardiovascular disease over 10 years in 21,636 middle-aged and older men and women of EPIC-Norfolk prospective population study. Age Ageing 44:219–225
Nishtala PS, Narayan SW, Wang T, Hilmer SN (2014) Associations of drug burden index with falls, general practitioner visits, and mortality in older people. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 23:753–758
Mangoni AA, van Munster BC, Woodman RJ, de Rooij SE (2013) Measures of anticholinergic drug exposure, serum anticholinergic activity, and all-cause postdischarge mortality in older hospitalized patients with hip fractures. The American journal of geriatric psychiatry : official journal of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry 21:785–793
Lowry E, Woodman RJ, Soiza RL, Mangoni AA (2011) Associations between the anticholinergic risk scale score and physical function: potential implications for adverse outcomes in older hospitalized patients. J Am Med Dir Assoc 12:565–572
Kidd AC, Musonda P, Soiza RL, Butchart C, Lunt CJ, Pai Y, Hameed Y, Fox C, Potter JF, Myint PK (2014) The relationship between total anticholinergic burden (ACB) and early in-patient hospital mortality and length of stay in the oldest old aged 90 years and over admitted with an acute illness. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 59:155–161
Kumpula EK, Bell JS, Soini H, Pitkala KH (2011) Anticholinergic drug use and mortality among residents of long-term care facilities: a prospective cohort study. J Clin Pharmacol 51:256–263
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6:e1000097
Chew ML, Mulsant BH, Pollock BG, Lehman ME, Greenspan A, Mahmoud RA, Kirshner MA, Sorisio DA, Bies RR, Gharabawi G (2008) Anticholinergic activity of 107 medications commonly used by older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc 56:1333–1341
Klamer TT, Wauters M, Azermai M, Duran C, Christiaens T, Elseviers M, Vander Stichele R (2017) A novel scale linking potency and dosage to estimate anticholinergic exposure in older adults: the muscarinic acetylcholinergic receptor antagonist exposure scale. Basic & clinical pharmacology & toxicology 120:582–590
Duran CE, Azermai M, Vander Stichele RH (2013) Systematic review of anticholinergic risk scales in older adults. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 69:1485–1496
Boustani M, Campbell N, Munger S, Maidment I, Fox C (2008) Impact of anticholinergics on the aging brain: a review and practical application. Aging Health:311–320
Carnahan RM, Lund BC, Perry PJ, Pollock BG, Culp KR (2006) The anticholinergic drug scale as a measure of drug-related anticholinergic burden: associations with serum anticholinergic activity. J Clin Pharmacol 46:1481–1486
Ancelin ML, Artero S, Portet F, Dupuy AM, Touchon J, Ritchie K (2006) Non-degenerative mild cognitive impairment in elderly people and use of anticholinergic drugs: longitudinal cohort study. BMJ (Clinical research ed) 332:455–459
Ehrt U, Broich K, Larsen JP, Ballard C, Aarsland D (2010) Use of drugs with anticholinergic effect and impact on cognition in Parkinson’s disease: a cohort study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 81:160–165
Han L, Agostini JV, Allore HG (2008) Cumulative anticholinergic exposure is associated with poor memory and executive function in older men. J Am Geriatr Soc 56:2203–2210
Sittironnarit G, Ames D, Bush AI, Faux N, Flicker L, Foster J, Hilmer S, Lautenschlager NT, Maruff P, Masters CL, Martins RN, Rowe C, Szoeke C, Ellis KA (2011) Effects of anticholinergic drugs on cognitive function in older Australians: results from the AIBL study. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 31:173–178
Aizenberg D, Sigler M, Weizman A, Barak Y (2002) Anticholinergic burden and the risk of falls among elderly psychiatric inpatients: a 4-year case-control study. Int Psychogeriatr 14:307–310
Cancelli I, Valentinis L, Merlino G, Valente M, Gigli GL (2008) Drugs with anticholinergic properties as a risk factor for psychosis in patients affected by Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther 84:63–68
Minzenberg MJ, Poole JH, Benton C, Vinogradov S (2004) Association of anticholinergic load with impairment of complex attention and memory in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 161:116–124
Kiesel EK, Hopf YM, Drey M (2018) An anticholinergic burden score for German prescribers: score development. BMC Geriatr 18:239
Hilmer SN, Mager DE, Simonsick EM, Cao Y, Ling SM, Windham BG, Harris TB, Hanlon JT, Rubin SM, Shorr RI, Bauer DC, Abernethy DR (2007) A drug burden index to define the functional burden of medications in older people. Arch Intern Med 167:781–787
Higgins JPT, Altman DG (2011) Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (eds) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Wiley-Blackwell, Chichester, pp 187–242
GA Wells B Shea, D O’Connell, J Peterson, V Welch, M Losos, P Tugwell The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analysis www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp
Yeh YC, Liu CL, Peng LN, Lin MH, Chen LK (2013) Potential benefits of reducing medication-related anticholinergic burden for demented older adults: a prospective cohort study. Geriatr Gerontol Int 13:694–700
Jamieson HA, Nishtala PS, Scrase R, Deely JM, Abey-Nesbit R, Hilmer SN, Abernethy DR, Berry SD, Mor V, Lacey CJ, Schluter PJ (2018) Drug burden index and its association with hip fracture among older adults: a national population-based study. The journals of gerontology Series A, Biological sciences and medical sciences
Pasina L, Colzani L, Cortesi L, Tettamanti M, Zambon A, Nobili A, Mazzone A, Mazzola P, Annoni G, Bellelli G (2019) Relation between delirium and anticholinergic drug burden in a cohort of hospitalized older patients: an observational study. Drugs Aging 36:85–91
Boudreau DM, Yu O, Gray SL, Raebel MA, Johnson J, Larson EB (2011) Concomitant use of cholinesterase inhibitors and anticholinergics: prevalence and outcomes. J Am Geriatr Soc 59:2069–2076
Williams A, Sera L, McPherson ML (2018) Anticholinergic burden in hospice patients with dementia. The American journal of hospice & palliative care:1049909118800281
Gamble DT, Clark AB, Luben RN, Wareham NJ, Khaw KT, Myint PK (2018) Baseline anticholinergic burden from medications predicts incident fatal and non-fatal stroke in the EPIC-Norfolk general population. Int J Epidemiol 47:625–633
Uusvaara J, Pitkala KH, Kautiainen H, Tilvis RS, Strandberg TE (2011) Association of anticholinergic drugs with hospitalization and mortality among older cardiovascular patients: a prospective study. Drugs Aging 28:131–138
Ablett AD, Browning A, Quan V, Tay HS, McCormack C, Carter B, Hewitt J, Myint PK (2019) Anti-cholinergic burden and patient related clinical outcomes in an emergency general surgical setting. Asian Journal of Surgery 42:527–534
Panula J, Puustinen J, Jaatinen P, Vahlberg T, Aarnio P, Kivela SL (2009) Effects of potent anticholinergics, sedatives and antipsychotics on postoperative mortality in elderly patients with hip fracture: a retrospective, population-based study. Drugs Aging 26:963–971
Narbey D, Jolly D, Mahmoudi R, Trenque T, Blanchard F, Novella JL, Drame M (2013) Relationship between anticholinergic drug use and one-year outcome among elderly people hospitalised in medical wards via emergency department: the SAFES cohort study. J Nutr Health Aging 17:766–771
Ball PA, Morrissey H, Pilotto LSJ (2013) Anticholinergic burden assessed using general practice electronic records. J Pharm Pract Res 43:202–205
Aalto UL, Roitto HM, Finne-Soveri H, Kautiainen H, Pitkala K (2018) Use of anticholinergic drugs and its relationship with psychological well-being and mortality in long-term care facilities in Helsinki. J Am Med Dir Assoc 19:511–515
Luukkanen MJ, Uusvaara J, Laurila JV, Strandberg TE, Raivio MM, Tilvis RS, Pitkälä KH (2011) Anticholinergic drugs and their effects on delirium and mortality in the elderly. Dementia and geriatric cognitive disorders extra 1:43–50
Agar M, To T, Plummer J, Abernethy A, Currow D (2010) Anti-cholinergic load, health care utilization, and survival in people with advanced cancer: a pilot study. J Palliat Med 13:745–752
Corsonello A, Cozza A, D’Alia S, Onder G, Volpato S, Ruggiero C, Cherubini A, Di Rosa M, Fabbietti P, Lattanzio F (2019) The excess mortality risk associated with anticholinergic burden among older patients discharged from acute care hospital with depressive symptoms. European Journal of Internal Medicine 61:69–74
Lattanzio F, Corica F, Schepisi R, Amantea D, Bruno F, Cozza A, Onder G, Volpato S, Cherubini A, Ruggiero C, Maggio MG, Corsonello A (2018) Anticholinergic burden and 1-year mortality among older patients discharged from acute care hospital. Geriatr Gerontol Int 18:705–713
Gutierrez-Valencia M, Martinez-Velilla N, Vetrano DL, Corsonello A, Lattanzio F, Ladron-Arana S, Onder G (2017) Anticholinergic burden and health outcomes among older adults discharged from hospital: results from the CRIME study. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 73:1467–1474
Lattanzio F, Onder G, La Fauci MM, Volpato S, Cherubini A, Fabbietti P, Ruggiero C, Garasto S, Cozza A, Crescibene L, Tarsitano A, Corsonello A (2018) Anticholinergic burden is associated with increased mortality in older patients with dependency discharged from hospital. J Am Med Dir Assoc 19:942–947
Wauters M, Klamer T, Elseviers M, Vaes B, Dalleur O, Degryse J, Duran C, Christiaens T, Azermai M, Vander Stichele R (2017) Anticholinergic exposure in a cohort of adults aged 80 years and over: associations of the MARANTE scale with mortality and hospitalization. Basic & clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology 120:591–600
Vetrano DL, La Carpia D, Grande G, Casucci P, Bacelli T, Bernabei R, Onder G (2016) Anticholinergic medication burden and 5-year risk of hospitalization and death in nursing home elderly residents with coronary artery disease. J Am Med Dir Assoc 17:1056–1059
Wilson NM, Hilmer SN, March LM, Chen JS, Gnjidic D, Mason RS, Cameron ID, Sambrook PN (2012) Associations between drug burden index and mortality in older people in residential aged care facilities. Drugs Aging 29:157–165
Chatterjee S, Bali V, Carnahan RM, Chen H, Johnson ML, Aparasu RR (2017) Risk of mortality associated with anticholinergic use in elderly nursing home residents with depression. Drugs Aging 34:691–700
Sarbacker GB, Espino DV, Wood RC, Oakes SL, Anand D, Markides KA (2017) Total anticholinergic burden and survival within a cohort of elderly Mexican Americans. Geriatr Gerontol Int 17:1515–1521
Lowry E, Woodman RJ, Soiza RL, Hilmer SN, Mangoni AA (2012) Drug burden index, physical function, and adverse outcomes in older hospitalized patients. J Clin Pharmacol 52:1584–1591
Cross AJ, George J, Woodward MC, Ames D, Brodaty H, Wolfe R, Connors MH, Elliott RA (2017) Potentially inappropriate medication, anticholinergic burden, and mortality in people attending memory clinics. Journal of Alzheimer’s disease : JAD 60:349–358
Tan ECK, Eriksdotter M, Garcia-Ptacek S, Fastbom J, Johnell K (2018) Anticholinergic burden and risk of stroke and death in people with different types of dementia. Journal of Alzheimer’s disease : JAD 65:589–596
Gnjidic D, Hilmer SN, Hartikainen S, Tolppanen AM, Taipale H, Koponen M, Bell JS (2014) Impact of high risk drug use on hospitalization and mortality in older people with and without Alzheimer’s disease: a national population cohort study. PLoS One 9:e83224
Sevilla-Sanchez D, Molist-Brunet N, Gonzalez-Bueno J, Sola-Bonada N, Espaulella-Panicot J, Codina-Jane C (2018) Prevalence, risk factors and adverse outcomes of anticholinergic burden in patients with advanced chronic conditions at hospital admission. Geriatr Gerontol Int 18:1159–1165
Gutierrez-Valencia M, Izquierdo M, Malafarina V, Alonso-Renedo J, Gonzalez-Glaria B, Larrayoz-Sola B, Monforte-Gasque MP, Latasa-Zamalloa P, Martinez-Velilla N (2017) Impact of hospitalization in an acute geriatric unit on polypharmacy and potentially inappropriate prescriptions: a retrospective study. Geriatr Gerontol Int 17:2354–2360
Lu WH, Wen YW, Chen LK, Hsiao FY (2015) Effect of polypharmacy, potentially inappropriate medications and anticholinergic burden on clinical outcomes: a retrospective cohort study. CMAJ : Canadian Medical Association journal = journal de l’Association medicale canadienne 187:E130–E137
McIsaac DI, Wong CA, Diep D, van Walraven C (2018) Association of preoperative anticholinergic medication exposure with postoperative healthcare resource use and outcomes: a population-based cohort study. Ann Surg
Egberts A, van der Craats ST, van Wijk MD, Alkilabe S, van den Bemt P, Mattace-Raso FUS (2017) Anticholinergic drug exposure is associated with delirium and postdischarge institutionalization in acutely ill hospitalized older patients. Pharmacol Res Perspect 5:e00310
Dauphinot V, Faure R, Omrani S, Goutelle S, Bourguignon L, Krolak-Salmon P, Mouchoux C (2014) Exposure to anticholinergic and sedative drugs, risk of falls, and mortality: an elderly inpatient, multicenter cohort. J Clin Psychopharmacol 34:565–570
Landi F, Dell’Aquila G, Collamati A, Martone AM, Zuliani G, Gasperini B, Eusebi P, Lattanzio F, Cherubini A (2014) Anticholinergic drug use and negative outcomes among the frail elderly population living in a nursing home. J Am Med Dir Assoc 15:825–829
Naja M, Zmudka J, Hannat S, Liabeuf S, Serot JM, Jouanny P (2016) In geriatric patients, delirium symptoms are related to the anticholinergic burden. Geriatr Gerontol Int 16:424–431
Whalley LJ, Sharma S, Fox HC, Murray AD, Staff RT, Duthie AC, Deary IJ, Starr JM (2012) Anticholinergic drugs in late life: adverse effects on cognition but not on progress to dementia. Journal of Alzheimer’s disease : JAD 30:253–261
Fox C, Smith T, Maidment I, Chan WY, Bua N, Myint PK, Boustani M, Kwok CS, Glover M, Koopmans I, Campbell N (2014) Effect of medications with anti-cholinergic properties on cognitive function, delirium, physical function and mortality: a systematic review. Age Ageing 43:604–615
Villalba-Moreno AM, Alfaro-Lara ER, Santos-Ramos B (2015) Anticholinergic risk: use and limitations of anticholinergic scales. European journal of internal medicine 26:e65–e66
Shiloh R, Stryjer R, Weizman A, Nutt DJ (2000) Atlas of psychiatric pharmacotherapy. CRC Press
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MS, SA and GP designed the search strategy, extracted, analysed data and drafted the manuscript. LB assisted with analyses and drafting the manuscript. All authors contributed to data analyses and interpretation, critically commented on and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 125 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, S., Peterson, G.M., Bereznicki, L.R. et al. Association between anticholinergic drug burden and mortality in older people: a systematic review. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 76, 319–335 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-019-02795-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-019-02795-x