Abstract
Purpose
Systemic exposure to rosuvastatin in Asian subjects living in Japan or Singapore is approximately twice that observed in Caucasian subjects in Western countries or in Singapore. This study was conducted to determine whether pharmacokinetic differences exist among the most populous Asian subgroups and Caucasian subjects in the USA.
Method
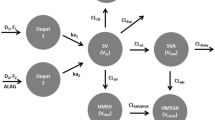
Rosuvastatin pharmacokinetics was studied in Chinese, Filipino, Asian-Indian, Korean, Vietnamese, Japanese and Caucasian subjects residing in California. Plasma concentrations of rosuvastatin and metabolites after a single 20-mg dose were determined by mass spectrometric detection. The influence of polymorphisms in SLCO1B1 (T521>C [Val174Ala] and A388>G [Asn130Asp]) and in ABCG2 (C421>A [Gln141Lys]) on exposure to rosuvastatin was also assessed.
Results
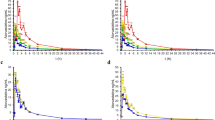
The average rosuvastatin area under the curve from time zero to time of last quantifiable concentration was between 64 and 84 % higher, and maximum drug concentration was between 70 and 98 % higher in East Asian subgroups compared with Caucasians. Data for Asian-Indians was intermediate to these two ethnic groups at 26 and 29 %, respectively. Similar increases in exposure to N-desmethyl rosuvastatin and rosuvastatin lactone were observed. Rosuvastatin exposure was higher in subjects carrying the SLCO1B1 521C allele compared with that in non-carriers of this allele. Similarly, exposure was higher in subjects carrying the ABCG2 421A allele compared with that in non-carriers.
Conclusion
Plasma exposure to rosuvastatin and its metabolites was significantly higher in Asian populations residing in the USA compared with Caucasian subjects living in the same environment. This study suggests that polymorphisms in the SLCO1B1 and ABCG2 genes contribute to the variability in rosuvastatin exposure.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Warwick MJ, Dane AL, Raza A, Schneck DW (2000) Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics and safety of the new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor ZD4522. Atherosclerosis 151:39
Martin PD, Mitchell PD, Schneck DW (2002) Pharmacodynamic effects and pharmacokinetics of a new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, rosuvastatin, after morning or evening administration in healthy volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 54:472–477
Sekino H, Onishi T (2005) Phase I study of ZD4522 (rosuvastatin), a new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor—evaluation of tolerance and pharmacokinetics in healthy adult male volunteers after single and repeated oral administration. J Clin Ther Med 21:187–203
Tzeng T-B, Schneck DW, Birmingham B, Mitchell PD, Zhang H, Martin PD, Kung L-P (2008) Population pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin: implications of renal impairment, race and dyslipidaemia. Curr Med Res Opin 24:2575–2585
Lee E, Ryan S, Birmingham B, Zalikowski J, March R, Ambrose H, Moore R, Lee C, Chen Y, Schneck D (2005) Rosuvastatin pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenetics in white and Asian subjects residing in the same environment. Clin Pharmacol Ther 78:330–341
Martin PD, Warwick MJ, Dane AL, Cantarini MV (2003) A double-blind, randomized, incomplete crossover trial to assess the dose proportionality of rosuvastatin in healthy volunteers. Clin Ther 25:2215–2224
Martin PD, Warwick MJ, Dane AL, Brindley C, Short T (2003) Absolute oral bioavailability of rosuvastatin in healthy white adult male volunteers. Clin Ther 25:2553–2563
Elsby R, Hilgendorf C, Fenner K (2012) Understanding the critical disposition pathways of statins to assess drug-drug interaction risk during drug development: it's not just about OATP1B1. Clin Pharmacol Ther 92:584–598
McCormick AD, McKillop D, Butters CJ, Miles GS, Baba T, Touchi A, Yamaguchi Y (2000) ZD4522—an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor free of metabolically mediated drug interactions: metabolic studies in human in vitro systems. J Clin Pharmacol 40:1055
Martin PD, Warwick MJ, Dane AL, Hill SJ, Giles PB, Phillips PJ, Lenz E (2003) Metabolism, excretion, and pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin in healthy adult male volunteers. Clin Ther 25:2822–2835
Cooper KJ, Martin PD, Dane AL, Warwick MJ, Schneck DW, Cantarini MV (2002) The effect of fluconazole on the pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 58:527–531
Tirona RG (2005) Ethic differences in statin disposition. Clin Pharmacol Ther 78:311–316
Choi JH, Lee MG, Cho JY, Lee JE, Kim KH, Park K (2008) Influence of OATP1B1 genotype on the pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin in Koreans. Clin Pharmacol Ther 83:251–257
Lee HK, Hu M, Lui SS, Ho CS, Wong CK, Tomlinson B (2013) Effects of polymorphisms in ABCG2, SLCO1B1, SLC10A1 and CYP2C9/19 on plasma concentrations of rosuvastatin and lipid response in Chinese patients. Pharmacogenomics 14:1283–1294
Zhang W, Yu BN, He YJ, Fan L, Li Q, Liu ZQ, Wang A, Liu YL, Tan ZR, Fen-Jiang, Huang YF, Zhou HH (2006) Role of BCRP 421C>A polymorphism on rosuvastatin pharmacokinetics in healthy Chinese males. Clin Chim Acta 373:99–103
Yamazaki M, Akiyama S, Nishigaki R, Sugiyama Y (1996) Uptake is the rate-limiting step in the overall hepatic elimination of pravastatin at steady-state in rats. Pharm Res 13:1559–1564
Ho RH, Tirona RG, Leake BF, Glaeser H, Lee W, Lemke CJ, Wang Y, Kim RB (2006) Drug and bile acid transporters in rosuvastatin hepatic uptake: function, expression and pharmacogenetics. Gastroenterology 130:1793–1806
Nishizato Y, Ieiri I, Suzuki H, Kimura M, Kawabata K, Hirota T, Takane H, Irie S, Kusuhara H, Urasaki Y, Urae A, Higuchi S, Otsubo K, Sugiyama Y (2003) Polymorphisms of OATP-C (SLC21A6) and OAT3 (SLC22A8) genes: consequences for pravastatin pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 73:554–565
Mwinyi J, Johne A, Bauer S, Roots I, Gerloff T (2004) Evidence for inverse effects of OATP-C (SLC21A6) 5 and 1b haplotypes on pravastatin kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 75:415–421
Niemi M, Schaeffeler E, Lang T, Fromm MF, Neuvonen M, Kyrklund C, Backman JT, Kerb R, Schwab M, Neuvonen PJ, Eichelbaum M, Kivistö KJ (2004) High plasma pravastatin concentrations are associated with single nucleotide polymorphisms and haplotypes of organic anion transporting polypeptide-C (OATP-C, SLCO1B1). Pharmacogenetics 14:429–440
Chung JY, Cho JY, Yu KS, Kim JR, Oh DS, Jung HR, Lim KS, Moon KH, Shin SG, Jang IJ (2005) Effect of OATP1B1 (SLCO1B1) variant alleles on the pharmacokinetics of pitavastatin in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther 78:342–350
Keskitalo JE, Zolk O, Fromm MF, Kurkinen KJ, Neuvonen PJ, Niemi M (2009) ABCG2 polymorphism markedly affects the pharmacokinetics of atorvastatin and rosuvastatin. Clin Pharmacol Ther 86:197–203
Martin PD, Dane AL, Nwose OM, Schneck DW, Warwick MJ (2002) No effect of age and gender on the pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin: a new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. J Clin Pharmacol 42:1116–1121
Yang CS, Pan E (2012) The effects of green tea polyphenols on drug metabolism. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 8:677–689
Gradhand U, Kim RB (2008) Pharmacogenomics of MRP transporters (ABCC1-5) and BCRP (ABCG2). Drug Metab Rev 40:317–354
Huang L, Wang Y, Grimm S (2006) ATP-dependent transport of rosuvastatin in membrane vesicles expressing breast cancer resistance protein. Drug Metab Dispos 34:738–742
Zamber CP, Lamba JK, Yasuda K, Farnum J, Thummel K, Schuetz JD, Schuetz EG (2003) Natural allelic variants of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) and their relationship to BCRP expression in human intestine. Pharmacogenetics 13:19–28
Lee SS, Jeong HE, Yi JM, Jung HJ, Jang JE, Kim EY, Lee SJ, Shin JG (2007) Identification and functional assessment of BCRP polymorphisms in a Korean population. Drug Metab Dispos 35:623–632
Birmingham BK, Bujac SR, Elsby R, Azumaya CT, Wei C, Chen Y, Mosqueda-Garcia R, Ambrose HJ (2015) Impact of ABCG2 and SLCO1B1 polymorphisms on pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin, atorvastatin and simvastatin acid in Caucasian and Asian subjects: a class effect?. Eur J Clin Pharmacol doi:10.1007/s00228-014-1801-z
Niemi M (2010) Transporter pharmacogenetics and statin toxicity. Clin Pharmacol Ther 87:130–133
Acknowledgments
Debra Ennis, an employee of AstraZeneca, performed the study analyses. Editorial support was provided by Kerry Knight and Valerie Moss of Prime Medica Ltd and Maren White of White Quill Ltd, supported by AstraZeneca.
Conflict of interest
B. Birmingham, S.R. Bujac, R. Elsby, C. Azumaya and H.J. Ambrose are employees of AstraZeneca. Y. Chen and J. Zalikowski are former employees of AstraZeneca. S.R. Bujac, R. Elsby, C. Azumaya, Y. Chen, J. Zalikowski and H.J. Ambrose all hold stock in AstraZeneca.
Responsibility for opinions, conclusions and interpretation of data lies with the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 613 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Birmingham, B.K., Bujac, S.R., Elsby, R. et al. Rosuvastatin pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenetics in Caucasian and Asian subjects residing in the United States. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 71, 329–340 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-014-1800-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-014-1800-0