Abstract
Purpose
Codeine is an analgesic drug acting on μ-opioid receptors predominantly via its metabolite morphine formed almost exclusively by CYP2D6. Genetic polymorphisms in CYP2D6 are associated with diminished pain relief and/or severe opioid side effects. In Chinese individuals, CYP2D6*10 is the most common allele with reduced enzyme activity. In this study, we investigated the effect of this allele on the pharmacokinetics of codeine and its metabolites.
Method
A blood sample was collected from healthy Mongolian volunteers for CYP2D6 genotyping using a PCR-RFLP assay. A pharmacokinetic study was then carried out in three groups with CYP2D6*1/*1 (n = 10), CYP2D6*1/*10 (n = 10) and CYP2D6*10/*10 (n = 9) genotypes by collecting serial blood samples for determination of plasma levels of codeine and its metabolites, morphine, morphine 3-glucuronide (M3G) and morphine 6-glucuronide (M6G) before and after a single 30-mg oral dose of codeine phosphate. Codeine and its metabolites were measured by LC-MS/MS.
Results
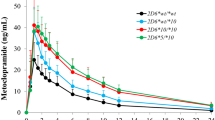
No significant differences were observed in the pharmacokinetic parameters of codeine in the three genotype groups. However, the C max and AUC0-∞ of morphine, M3G and M6G were significantly different between the study groups (P < 0.05). Compared with the *1/*1 group, the AUC0-∞ for morphine in the *1/*10 and *10/*10 groups decreased by ratios (95 % CI) of 0.93 (0.26–1.59) and 0.494 (0.135–0.853) respectively. Corresponding ratios for M3G were 0.791 (0.294–1.288) and 0.615 (0.412–0.818) and for M6G were 0.643 (0.39–0.957) and 0.423 (0.267–0.579).
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that the CYP2D6*10 allele plays an important role in the pharmacokinetics of the O-demethylated metabolites of codeine after oral administration.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora S, Herbert ME (2001) Myth: codeine is a powerful and effective analgesic. West J Med 174:428
Thorn CF, Klein TE, Altman RB (2009) Codeine and morphine pathway. Pharmacogenet Genomics 19:556–558
Mortimer O, Persson K, Ladona MG, Spalding D, Zanger UM, Meyer UA, Rane A (1990) Polymorphic formation of morphine from codeine in poor and extensive metabolizers of dextromethorphan: relationship to the presence of immunoidentified cytochrome P-450IID1. Clin Pharmacol Ther 47:27–35
Gasche Y, Daali Y, Fathi M, Chiappe A, Cottini S, Dayer P, Desmeules J (2004) Codeine intoxication associated with ultrarapid CYP2D6 metabolism. N Engl J Med 351:2827–2831
Persson K, Sjöström S, Sigurdardottir I, Molnár V, Hammarlund-Udenaes M, Rane A (1995) Patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) with codeine for postoperative pain relief in ten extensive metabolisers and one poor metaboliser of dextromethorphan. Br J Clin Pharmacol 39:182–186
Zuo LJ, Guo T, Xia DY, Jia LH (2012) Allele and genotype frequencies of CYP3A4, CYP2C19, and CYP2D6 in Han, Uighur, Hui, and Mongolian Chinese populations. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers 16:102–108
Bradford LD (2002) CYP2D6 allele frequency in European Caucasians, Asians, Africans and their descendants. Pharmacogenomics 3:229–243
Ozawa S, Soyama A, Saeki M, Fukushima-Uesaka H, Itoda M, Koyano S, Sai K, Ohno Y, Saito Y, Sawada J (2004) Ethnic differences in genetic polymorphisms of CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP3As and MDR1/ABCB1. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 19:83–95
Nishida Y, Fukuda T, Yamamoto I, Azuma J (2000) CYP2D6 genotypes in a Japanese population: low frequencies of CYP2D6 gene duplication but high frequency of CYP2D6*10. Pharmacogenetics 10:567–570
Teh LK, Bertilsson L (2012) Pharmacogenomics of CYP2D6: molecular genetics, interethnic differences and clinical importance. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 27:55–67
Shen H, He MM, Liu H, Wrighton SA, Wang L, Guo B, Li C (2007) Comparative metabolic capabilities and inhibitory profiles of CYP2D6.1, CYP2D6.10, and CYP2D6.17. Drug Metab Dispos 35:1292–1300
Wu X, Zhang W, Bai Y, Guo T, Gu J (2013) Simultaneous analysis of codeine and its active metabolites in human plasma using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: application to a pharmacokinetic study after oral administration of codeine. J Pharm Biomed Anal 78-79C:261–268
Kirchheiner J, Schmidt H, Tzvetkov M, Keulen JT, Lötsch J, Roots I, Brockmöller J (2007) Pharmacokinetics of codeine and its metabolite morphine in ultra-rapid metabolizers due to CYP2D6 duplication. Pharmacogenomics J 7:257–265
Tseng CY, Wang SL, Lai MD, Lai ML, Huang JD (1996) Formation of morphine from codeine in Chinese subjects of different CYP2D6 genotypes. Clin Pharmacol Ther 60:177–182
Halling J, Weihe P, Brosen K (2008) CYP2D6 polymorphism in relation to tramadol metabolism: a study of faroese patients. Ther Drug Monit 30:271–275
Susce MT, Murray-Carmichael E, de Leon J (2006) Response to hydrocodone, codeine and oxycodone in a CYP2D6 poor metabolizer. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 30:1356–1358
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to the study participants, to Professor J. Paul Fawcett of University of Otago and to Professor Jingkai Gu of Jilin University for their excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Yuan, L., Zuo, J. et al. The impact of CYP2D6 polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of codeine and its metabolites in Mongolian Chinese subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 70, 57–63 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-013-1573-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-013-1573-x