Abstract
Purpose
The pharmacokinetics of orally administered immediate-release, twice-daily (BID) and modified-release, once-daily (QD) formulations of tacrolimus have high interindividual variability. We investigated factors affecting interindividual variability of tacrolimus bioavailability in renal transplant patients.
Methods
Ninety-seven Japanese renal transplant patients (47 patients on tacrolimus BID and 50 patients on tacrolimus QD) were enrolled in this study. The tacrolimus absolute bioavailability was calculated using the area under the concentration–time curve from 0 to 24 h (AUC0–24) after continuous intravenous infusion and oral formulations of tacrolimus in the same recipient.
Results
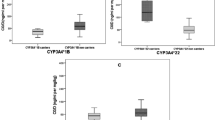
The median (quartile 1–quartile 3) tacrolimus relative bioavailability for recipients with the CYP3A5*1 or CYP3A5*3/*3 alleles was significantly lower for the tacrolimus QD group [9.1 % (6.3–10.7 %) and 15.4 % (11.5–18.7 %), respectively] than for the tacrolimus BID group [12.6 % (9.9–14.2 %) and 19.3 % (16.5–24.8 %), respectively] (P = 0.004 and 0.028, respectively). Consequently, tacrolimus absolute bioavailability was lowest for recipients with the CYP3A5*1 allele taking tacrolimus QD. The CYP3A5 polymorphism had no impact on the dose-adjusted AUC0–24 of tacrolimus in patients on continuous intravenous infusion (P = 0.906).
Conclusion
The larger interindividual variability of tacrolimus bioavailability for oral formulations appears to be due to the effects of the CYP3A5 polymorphism and the tacrolimus oral formulation. These factors should therefore be taken into account when determining individualized tacrolimus dosing.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scott LJ, McKeage K, Keam SJ, Plosker GL (2003) Tacrolimus: a further update of its use in the management of organ transplantation. Drugs 63:1247–1297
Staatz CE, Tett SE (2004) Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of tacrolimus in solid organ transplantation. Clin Pharmacokinet 43:623–653
Hesselink DA, van Schaik RH, van der Heiden IP, van der Werf M, Gregoor PJ, Lindemans J, Weimar W, van Gelder T (2003) Genetic polymorphisms of the CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and MDR-1 genes and pharmacokinetics of the calcineurin inhibitors cyclosporine and tacrolimus. Clin Pharmacol Ther 74:245–254
Tsuchiya N, Satoh S, Tada H, Li Z, Ohyama C, Sato K, Suzuki T, Habuchi T, Kato T (2004) Influence of CYP3A5 and MDR1 (ABCB1) polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation 78:1182–1187
Hesselink DA, van Gelder T, van Schaik RH (2005) The pharmacogenetics of calcineurin inhibitors: one step closer toward individualized immunosuppression? Pharmacogenomics 6:323–337
Hustert E, Haberl M, Burk O, Wolbold R, He YQ, Klein K, Nuessler AC, Neuhaus P, Klattig J, Eiselt R, Koch I, Zibat A, Brockmoller J, Halpert JR, Zanger UM, Wojnowski L (2001) The genetic determinants of the CYP3A5 polymorphism. Pharmacogenetics 11:773–779
Barraclough KA, Isbel NM, Johnson DW, Campbell SB, Staatz CE (2011) Once- versus twice-daily tacrolimus: are the formulations truly equivalent? Drugs 71:1561–1577
Hougardy JM, de Jonge H, Kuypers D, Abramowicz D (2012) The once-daily formulation of tacrolimus: a step forward in kidney transplantation? Transplantation 93:241–243
Crespo M, Mir M, Marin M, Hurtado S, Estadella C, Guri X, Rap O, Moral R, Puig JM, Lloveras J (2009) De novo kidney transplant recipients need higher doses of Advagraf compared with Prograf to get therapeutic levels. Transplant Proc 41:2115–2117
Wlodarczyk Z, Squifflet JP, Ostrowski M, Rigotti P, Stefoni S, Citterio F, Vanrenterghem Y, Kramer BK, Abramowicz D, Oppenheimer F, Pietruck F, Russ G, Karpf C, Undre N (2009) Pharmacokinetics for once- versus twice-daily tacrolimus formulations in de novo kidney transplantation: a randomized, open-label trial. Am J Transplant 9:2505–2513
Niioka T, Satoh S, Kagaya H, Numakura K, Inoue T, Saito M, Narita S, Tsuchiya N, Habuchi T, Miura M (2012) Comparison of pharmacokinetics and pharmacogentics of once and twice-daily tacrolimus in the early stage after renal transplantation. Transplantation 94:1013–1019
Fukuen S, Fukuda T, Maune H, Ikenaga Y, Yamamoto I, Inaba T, Azuma J (2002) Novel detection assay by PCR-RFLP and frequency of the CYP3A5 SNPs, CYP3A5*3 and *6, in a Japanese population. Pharmacogenetics 12:331–334
Cascorbi I, Gerloff T, Johne A, Meisel C, Hoffmeyer S, Schwab M, Schaeffeler E, Eichelbaum M, Brinkmann U, Roots I (2001) Frequency of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the P-glycoprotein drug transporter MDR1 gene in white subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther 69:169–174
Miura M, Satoh S, Kagaya H, Saito M, Numakura K, Tsuchiya N, Habuchi T (2011) Impact of the CYP3A4*1G polymorphism and its combination with CYP3A5 genotypes on tacrolimus pharmacokinetics in renal transplant patients. Pharmacogenomics 12:977–984
Miura M, Satoh S, Inoue K, Kagaya H, Saito M, Inoue T, Habuchi T, Suzuki T (2008) Influence of CYP3A5, ABCB1 and NR1I2 polymorphisms on prednisolone pharmacokinetics in renal transplant recipients. Steroids 73:1052–1059
Glowacki F, Lionet A, Hammelin JP, Labalette M, Provot F, Hazzan M, Broly F, Noel C, Cauffiez C (2011) Influence of cytochrome P450 3A5 (CYP3A5) genetic polymorphism on the pharmacokinetics of the prolonged-release, once-daily formulation of tacrolimus in stable renal transplant recipietns. Clin Pharmacokinet 50:451–459
Canaparo R, Finnstrom N, Serpe L, Nordmark A, Muntoni E, Eandi M, Rane A, Zara GP (2007) Expression of CYP3A isoforms and P-glycoprotein in human stomach, jejunum and ileum. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 34:1138–1144
Uesugi M, Masuda S, Katsura T, Oike F, Takada Y, Inui K (2006) Effect of intestinal CYP3A5 on postoperative tacrolimus trough levels in living-donor liver transplant recipients. Pharmacogenet Genomics 16:119–127
Lin YS, Dowling AL, Quigley SD, Farin FM, Zhang J, Lamba J, Schuetz EG, Thummel KE (2002) Co-regulation of CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 and contribution to hepatic and intestinal midazolam metabolism. Mol Pharmacol 62:162–172
Picard N, Rouguieg-Malki K, Kamar N, Rostaing L, Marquet P (2011) CYP3A5 genotype does not influence everolimus in vitro metabolism and clinical pharmacokinetics in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation 91:652–656
Dai Y, Hebert MF, Isoherranen N, Davis CL, Marsh C, Shen DD, Thummel KE (2006) Effect of CYP3A5 polymorphism on tacrolimus metabolic clearance in vitro. Drug Metab Dispos 34:836–847
De BK, Jimenez E, Sawyer JC, McMillin GA (2009) Analytical performance characteristics of the Abbott Architect i2000 Tacrolimus assay; comparisons with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and Abbott IMx methods. Clin Chim Acta 410:25–30
Wallemacq P, Goffinet JS, O’Morchoe S et al (2009) Multi-site analytical evaluation of the Abbott ARCHITECT tacrolimus assay. Ther Drug Monit 31:198–204
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant (No. 23592378 and No. 24927005) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Tokyo, Japan.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Takenori Niioka and Hideaki Kagaya contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niioka, T., Kagaya, H., Miura, M. et al. Pharmaceutical and genetic determinants for interindividual differences of tacrolimus bioavailability in renal transplant recipients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 69, 1659–1665 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-013-1514-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-013-1514-8