Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, and tolerability of escalating single oral doses of ACT-077825, a novel orally active renin inhibitor, in healthy male subjects.
Methods
In this single-center, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled (with enalapril) randomized study, 70 subjects received a single dose of ACT-077825 (1–1,000 mg), placebo, or enalapril 20 mg under fasted conditions. The main pharmacokinetic endpoints were area under the plasma ACT-077825 concentration–time curve from time zero to infinity and the terminal half-life (t1/2). The pharmacodynamic endpoints included immunoactive active renin (iAR) plasma concentrations and plasma renin activity (PRA). Standard laboratory and safety data were collected.
Results
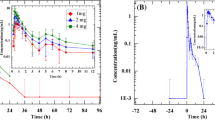
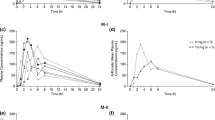
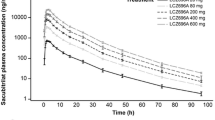
Of the few adverse events reported, diarrhea and headache were the most frequent. The pharmacokinetics of ACT-077825 were dose-proportional in the dose range 100 to 1,000 mg. Terminal t1/2, best characterized following a dose of 1,000 mg, was 41.6 h and tmax 4–5 h post-dose. ACT-077825 dose-dependently increased iAR and decreased PRA, effects that were associated with a decrease in blood pressure at 1,000 mg, similar to following treatment with enalapril.
Conclusion
The results provide evidence that ACT-077825, with a pharmacokinetic profile consistent with a once-a-day dosing regimen, may represent an effective antihypertensive agent and pave the way toward a multiple-ascending dose study.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma TK, Kam KK, Yan BP, Lam YY (2010) Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade for cardiovascular diseases: current status. Br J Pharmacol 160(6):1273–1292
Perret-Guillaume C, Joly L, Jankowski P, Benetos A (2009) Benefits of the RAS blockade: clinical evidence before the ONTARGET study. J Hypertens Suppl 27(2):S3–S7
Bing J (1973) Rapid marked increase in plasma renin in rats treated with inhibitors of the renin system. Effects of 1-sar-8-ala-angiotensin II and of a synthetic converting enzyme inhibitor (nonapeptide, SQ 20.881) on normal and adrenalectomized rats. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A 81(3):376–378
Doggrell SA, Wanstall JC (2004) Vascular chymase: pathophysiological role and therapeutic potential of inhibition. Cardiovasc Res 61(1):653–662
Nussberger J, Cugno M, Amstutz C, Cicardi M, Pellacani A, Agostoni A (1998) Plasma bradykinin in angio-oedema. Lancet 351:1693–1697
Siragy HM, Xue C, Abadir P, Carey RM (2005) Angiotensin subtype-2 receptors inhibit renin biosynthesis and angiotensin II formation. Hypertension 45(1):133–137
Zhang X, Lassila M, Cooper ME, Cao Z (2004) Retinal expression of vascular endothelial growth factor is mediated by angiotensin type 1 and type 2 receptors. Hypertension 432:276–281
Fisher ND, Hollenberg N (1995) Renal vascular responses to renin inhibition with zankiren in men. Clin Pharmacol Ther 57(3):342–348
Fisher ND, Hollenberg N (2001) Is there a future for renin inhibitors? Expert Opin Investig Drugs 10(3):417–426
Rongen GA, Lenders JW, Smits P, Thien T (1995) Clinical pharmacokinetics and efficacy of renin inhibitors. Clin Pharmacokinet 29(1):6–14
Azizi M, Webb R, Nussberger J, Hollenberg NK (2006) Renin inhibition with aliskiren: where are we now, and where are we going? J Hypertens 24(2):243–256
US prescribing information (2007) Tekturna®, aliskiren tablets. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, East Hanover, NJ
Bezencon O, Bur D, Weller T, Richard-Bildstein S, Remen L, Sifferlen T, Corminboeuf O, Grisostomi C, Boss C, Prade L, Delahaye S, Treiber A, Strickner P, Binkert C, Hess P, Steiner B, Fischli W (2009) Design and preparation of potent, nonpeptidic, bioavailable renin inhibitors. J Med Chem 52(12):3689–3702
Gough K (1995) Assessment of dose proportionality: reports from the statisticians in the pharmaceutical industry/pharmacokinetics UK joint working group. Drug Inform J 29:1039–1048
Daugherty KK (2008) Aliskiren. Am J Health Syst Pharm 65(14):1323–1332
Frampton JE, Curran MP (2007) Aliskiren: a review of its use in the management of hypertension. Drugs 67(12):1767–1792
Staessen JA, Li Y, Richart T (2006) Oral renin inhibitors. Lancet 368(9545):1449–1456
Nussberger J, Wuerzner G, Jensen C, Brunner HR (2002) Angiotensin II suppression in humans by the orally active renin inhibitor aliskiren (SPP100): comparison with enalapril. Hypertension 39(1):E1–E8
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by Actelion Pharmaceuticals Ltd. The authors acknowledge the contributions of all subjects, investigators, and study personnel, including staff from the bioanalytical laboratory, involved in this trial.
Conflict of interest
Laurent B. Nicolas, Marcelo M. Gutierrez, Christoph Binkert, and Jasper Dingemanse are full-time employees of Actelion Pharmaceuticals Ltd. This study was sponsored by Actelion Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nicolas, L.B., Gutierrez, M.M., Binkert, C. et al. Entry-into-humans study with a new direct renin inhibitor. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 68, 1257–1266 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-012-1253-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-012-1253-2