Abstract
Purpose
What is the level of knowledge of pharmacists concerning pain management and the use of opioids at the end of life, and how do they cooperate with physicians?
Methods
A written questionnaire was sent to a sample of community and hospital pharmacists in the Netherlands. The questionnaire was completed by 182 pharmacists (response rate 45%).
Results
Pharmacists were aware of the most basic knowledge about opioids. Among the respondents, 29% erroneously thought that life-threatening respiratory depression was a danger with pain control, and 38% erroneously believed that opioids were the preferred drug for palliative sedation. One in three responding pharmacists did not think his/her theoretical knowledge was sufficient to provide advice on pain control. Most pharmacists had working agreements with physicians on euthanasia (81%), but fewer had working agreements on palliative sedation (46%) or opioid therapy (25%). Based on the experience of most of responding pharmacists (93%), physicians were open to unsolicited advice on opioid prescriptions. The majority of community pharmacists (94%) checked opioid prescriptions most often only after dispensing, while it was not a common practice among the majority of hospital pharmacists (68%) to check prescriptions at all.
Conclusions
Although the basic knowledge of most pharmacists was adequate, based on the responses to the questionnaire, there seems to be a lack of knowledge in several areas, which may hamper pharmacists in improving the quality of care when giving advice to physicians and preventing or correcting mistakes if necessary. If education is improved, a more active role of the pharmacist may improve the quality of end-of-life pharmacotherapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Pain is one of the symptoms most frequently encountered at the end of life [1, 2], although it can be controlled satisfactorily in most cases if health care professionals are adequately informed [3]. Possibilities to manage pain in patients at the end of life have increased in the past decade, and these possibilities have been incorporated into handbooks and practice guidelines that were developed to support professionals in evidence-based practice [4–6]. However, the existence of professional guidelines does not guarantee that this knowledge is optimally used in daily practice.
Several barriers have been identified concerning the prescribing and use of opioids that hamper the quality of pain management. First, there is still a lack of theoretical knowledge about opioids among practicing physicians and nurses [4, 7–9]. A systematic review of obstacles hindering cancer pain management found that inadequate knowledge was one of the most reported barriers among physicians for adequate pain management [10]. The most reported misconceptions were the likelihood of opioid addiction and the belief that morphine dosage had an upper limit. Lack of theoretical knowledge also includes rare effects of opioids such as opioid-induced hyperalgesia [11]. Secondly, even when health care professionals do have sufficient theoretical knowledge about pain management guidelines, there is no guarantee of adherence to these guidelines in daily practice. For example, patients who clearly need opioids for pain frequently receive dosages that are too low [12, 13]. Another example is the prescribing of laxatives concomitantly with opioids, a clinical guideline that has been recommended in the World Health Organization’s (WHO) pain ladder [6] and almost all guidelines about pain management [4, 5, 14]. However, in daily practice, only about half of the patients are prescribed a laxative concomitantly [15–17]. Nearing end-of-life constipation can still be a problem, although the patient’s deteriorating functional status can mean management of constipation has a lower priority. In the last days of life, when patients are no longer able to receive oral treatment and consciousness diminishes, oral laxatives should be discontinued [18].
Compared to physicians and nurses, surprisingly few studies have been aimed at assessing the knowledge and experiences of pharmacists on pain management and opioid use. The responsibilities of pharmacists in terms of providing pharmaceutical care vary among countries, and hence their role in pain management may differ. In the Netherlands, in contrast with other countries [19], pharmacists are not allowed to prescribe; their primary task is to control the quality of prescribing, check for potential interactions and support prescribers and patients with optimal medication use [20]. Dutch hospital pharmacists frequently contact and advise clinicians, and an increasing number of hospital pharmacists are present in the wards for consultation and patient education [21]. In community pharmacy, patient education is common, and there are regular pharmacotherapeutic audit meetings between pharmacists and general practitioners [22]. Characteristic of the Netherlands health care system is that euthanasia and palliative sedation are legal options when suffering is unbearable and hopeless [23], and most pharmacies are prepared to fill prescriptions for euthanasia [24].
A number of studies have investigated pharmacists’ knowledge and attitudes, although none of these have been carried out in the Netherlands. These studies have identified a general need for more knowledge and education in pain management [25, 26]. Misconceptions were not only prevalent among physicians[10], but also among pharmacists [27]. Risk of addiction was no barrier to most pharmacists to dispense opioids, but conservative physicians and nurses and the concerns of pharmacists for adverse effects were reported as barriers to opioid dispensing [28]. Consequently, the results of these studies on pharmacists do not support the possible assumption that pharmacists’ knowledge is sufficient for achieving optimal pharmacotherapy at the end of life. On the contrary, they suggest that the pharmacist may actually be a limiting factor in achieving optimal pharmacotherapy at the end of life. However, note should be made of the fact that there have not been any recent surveys performed among pharmacists, and the previous studies were all performed in the USA and had relatively low response rates [27, 28].
In end-of-life care, interdisciplinary cooperation among professionals is essential [29], and within this team approach the pharmacist has the responsibility to maintain and optimize the quality of pharmacotherapy. Hence, it is important that the pharmacist has an adequate and up-to-date knowledge of pain management and the medication involved. The aim of the study reported here was to study the level of knowledge of pharmacists in the Netherlands on pain management and the use of opioids at the end of life, how they cooperate with physicians and what barriers to good end-of-life care pharmacists experience.
Methods
Design and population
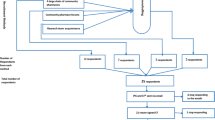
Pharmacists working as health care providers in the Netherlands can specialize in community pharmacy or hospital pharmacy. Both community pharmacists and hospital pharmacists were approached to participate in this study. Names of potential participants were retrieved randomly from a national medical address book (BSL) that is publicly available and contains the addresses and basic professional qualifications of professionals working in Dutch health care. It is updated on a yearly basis. The random sample was taken per specialism: community pharmacists and hospital pharmacists. Inclusion criteria were: working in the Netherlands as a community or hospital pharmacist and not being in training. All the names were first ordered by postal code (region), and then every Nth case was sampled, with N being the number in the sample frame divided by the desired number in the sample. The samples were representative of the Netherlands.
The questionnaire was sent out in January 2009 followed by two reminders. A non-response questionnaire was enclosed with the second reminder for use in the non-response analysis. Respondents could complete the questionnaire on paper or online. The written questionnaire was anonymous. A separate answer card with the personal data of the respondent could be returned to prevent further reminders. The online questionnaire was not anonymous because it would otherwise not be possible to exclude the possibility that individuals who were not in the sample would complete the questionnaire. However, when the database was closed, the questionnaires were anonymized.
A total of 412 pharmacists were sent a questionnaire. Of these, seven envelopes were returned to sender (respondent had moved in the case of a private address or was no longer working at the institution in the case of a work address). Of the 322 community pharmacists, 147 completed the entire questionnaire (response rate 46%). Of the 83 hospital pharmacists, 35 completed the full questionnaire (response rate 42%). The total overall response rate was 45%. Of the completed questionnaires, 70% were completed in writing and 30% were completed online. The non-response questionnaire was completed by 35 community pharmacists and seven hospital pharmacists.
After the closing of the data collection, a document with the correct answers to the knowledge statements was sent by e-mail to those who had indicated they were interested in receiving this.
Developing the questionnaire and the pilot study
The questionnaire was developed by the authors who have expertise in end-of-life care, pharmacy, medicine, epidemiology and the development of questionnaires. Previous studies of the knowledge or attitude concerning opioids and pain management at the end of life were used as a reference material [8, 30]. Questions were adapted and added with the aim of satisfying the aims of the study and to fit the specific situation in the Netherlands. To this end, we used inter alia Dutch guidelines, original articles and review articles [8, 11, 14, 31–36]. The pilot questionnaire was tested among general practitioners (GPs) in training, elderly care physicians in training and pharmacists. Opinions differed on the difficulty level of the knowledge statements in the questionnaire, but most respondents did not think the statements were unclear or too difficult; they sometimes even thought they were (too) easy.
The questionnaire consisted of three types of questions: (1) knowledge statements with three options as answers: “true”, “false” and “don’t know”; (2) experience and attitude questions, with five options as answers: “completely agree”, “agree more than disagree”, “neutral”, “disagree more than agree” and “completely disagree”; (3) other questions, partly structured with four options as answers: “often”, “sometimes”, “seldom” and “never”, and partly semi-structured. Several questions on background were asked, inter alia to grade one’s own knowledge about opioids and pain management on a score of 1–10.
Analysis
We calculated descriptive statistics for the comparisons between community pharmacists and hospital pharmacists. Chi-square tests were used for comparing proportions between respondents and non-respondents, using linear-by-linear association for ordinal variables. Student’s t tests were used for comparing means. For all tests p values are presented. In Table 3, the categories “completely agree” and “agree more than disagree” were merged to the category “agree” versus the categories “neutral”, and “(completely) disagree”.
Results
Background characteristics
In Table 1, the background characteristics of the respondents are shown per specialty. Hospital pharmacists were responsible for more patients to whom opioids were dispensed compared to community pharmacists. They also graded their own knowledge concerning opioids and pain management higher.
There was one significant difference in the background characteristics between pharmacists who completed the non-response questionnaire (n = 44) and those who completed the full questionnaire (n = 182). Non-responders were more often fulltime employed (93%) than responders (74%, data not shown). The most important reasons for non-response were no time, too high a workload and understaffing.
Knowledge statements
In Table 2, the answers to the knowledge statements are shown per specialty. Of the 14 statements on knowledge included in the questionnaire, community pharmacists gave, on average, correct answers to between nine and ten of these. Hospital pharmacists answered more statements correctly (between 10 and 11). Knowledge questions for which the number of correct answers was low were “opioids may cause or worsen pain” (statement is true, 11% correct answers), “drug management of nausea in treatment with opioids is evidence-based” (statement is false, 19% correct answers), “simultaneous prescription of a weak opioid (e.g. tramadol) and a strong opioid (e.g. morphine) is contra-indicated” (statement is true, 49% correct answers), “opioids are the favoured drugs for palliative sedation” (statement is false, 61% correct answers) and “life-threatening respiratory depression is a real danger when titrating morphine to control pain” (statement is false, 71% correct answers). Of the responding pharmacists, 74% knew that decreased renal function could raise the plasma concentration of morphine and its active metabolite (morphine 6-glucuronide), and 82% calculated an example of opioid rotation correctly.
Attitudes, experiences and barriers on pain management
Pharmacists did not think that patients always indicate their pain to their physician (Table 3). The majority of the pharmacists (81%) stated that an opioid prescription should consist of both maintenance and medication as needed. Barriers to prescribing opioids experienced by the responding pharmacists were opioid fear by the patient (79%) and family (72%), underreporting of pain by patients (77%) and insufficient information about the pain (60%). Practical/logistic issues, such as problems with manufacturing/availability and with reimbursement, were not often experienced as obstacles to prescribing.
Attitudes and experiences on opioid rotation, tolerance, addiction and checking prescriptions
Table 4 shows that almost 39% of the responding pharmacists found it difficult to calculate opioid dosages in the case of opioid rotation. Fear of addiction was seen as a limiting factor for opioid use in daily practice (78%). The majority of the community pharmacists (94%) checked opioid prescriptions most often after dispensing, while the majority of the hospital pharmacists (68%) did not check opioid prescriptions personally. Community pharmacists were more frequently personally involved compared to their clinical colleagues; 15% of the community pharmacists and none of the hospital pharmacists reported often having personal contact with the patient/caregiver.
Cooperation with physicians through working agreements, advice and contact over prescriptions
Table 5 shows the types of cooperation between pharmacists and physicians. Working arrangements with physicians regarding euthanasia were more frequently reported by hospital pharmacists (97%) than by community pharmacists (77%). Working agreements concerning palliative sedation and opioid usage were less frequent. Community pharmacist were more often consulted by GPs, and hospital pharmacists by nursing home physicians and clinical specialists. Most pharmacists (93%) reported that physicians were open to unsolicited advice concerning the opioids prescribed by the physician. Almost all pharmacists (97%) would contact the physician if there was something wrong with the prescription, with the most reported reasons for contacting a physician being laxatives not prescribed (77%), administrative incompleteness (53%) and drug–drug interactions (52%). Most pharmacists contacted the physician when an opioid was prescribed without a laxative (63%). Reasons for not contacting the physician were that he/she might have had a good reason for not prescribing a laxative or that a laxative was not needed as the patient was terminal or being sedated. Other pharmacists dispensed a laxative to the patient according to working agreements, and some did not contact physicians about laxatives. Most pharmacists (96%) did not contact the physician when an opioid was prescribed without a prescription for an anti-emetic drug.
Additional education
About three-quarters of the responding pharmacists (76%) indicated that they had enough options for additional education in subjects related to opioids and pain and symptom management at the end of life (data not given). Others were very adamant that there were not enough options—neither in their region, nor non-commercial—or information they could use in their daily practice to support physicians.
The subjects most often mentioned in which further education was warranted were opioid rotation (59%), pain and symptom management in general (52%), and palliative sedation (49%). The preferred methods to receive further education were literature in Dutch journals (65%), conferences (47%), courses on the Internet (44%) and literature in international journals (41%).
Discussion
Although the knowledge of the majority of the respondents was adequate on many points, by means of the questionnaire, we were able to identify gaps in knowledge on some aspects of opioid use in a considerable number of the responding pharmacists. Pharmacists answered 71% of the knowledge questions correctly (10/14). In a number of published studies, physicians answered between 31 and 68% questions correctly [37–39], while in a single previous study, pharmacists answered 46% of the questions correctly [25]. The overall scores in different studies cannot be compared due to the variations in the statements included in the questionnaires.
A point of concern was that only one in nine pharmacists was aware that opioids may cause or worsen pain. This is a rare effect and has not been known for a long time, so it is understandable that many pharmacists are indeed unaware of this adverse effect. However, the clinical effects can be significant if the dose of opioids is increased instead of decreased when a patient suffers from opioid-induced pain sensitivity [11, 40, 41]. Although the majority of the pharmacists stated that life-threatening respiratory depression represent no real danger to the use of opioids for pain control [35], 25% thought it was a real danger. Many studies have shown that this is not the case when opioids are titrated [34], even in patients with end-of-life chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [42].
Pharmacists would be able to support physicians in preventing opioid over-dosage in patients with renal failure, if they were to be aware of the fact that half-life of morphine itself and of its active morphine 6-glucuronide is increased in the elderly and in patients with renal dysfunction [43]. However, only 74% of the responding pharmacists answered this statement correctly, and for those who did, it is not known if they actually used this knowledge for prevention in practice. Pharmacists could also have a role in supporting physicians with opioid rotation. Opioid rotation is a complex procedure in which the use of equianalgesic tables should always be accompanied by clinical judgement [44]. Half of the responding pharmacists have been occasionally/often consulted by physicians with questions relating to opioid rotation, and the majority of pharmacists occasionally/often advice physicians to rotate when pain control is inadequate or when there are side effects. However, 40% of the pharmacists indicated they found it difficult to calculate the correct dosage, and 18% were not able to calculate the correct dosage when asked to do so. Opioid rotation was also the subject that was most often mentioned by pharmacists as an area in which they would like to receive further education (59%).
It is crucial that pharmacists involved in end-of-life care are aware that opioids are not the drug of choice for palliative sedation. Approximately one in three of the responding pharmacists thought that opioids are the favoured drugs for palliative sedation. According to Dutch guidelines for palliative sedation, sedation with opioids should be considered malpractice [31]. Sedation was mentioned by half of the pharmacists as a subject in which they would like to receive further education.
Co-prescribing of laxatives is the most reported reason given in this study for physician–pharmacist contact, and 63% of the pharmacists reported that not prescribing a laxative when an opioid is prescribed is a reason for contact. Although laxatives should not be prescribed in the last days of life, it is important that physicians should combine opioids with laxatives in most patients receiving palliative care [18]. Studies have found that many patients who are being prescribed opioids are not prescribed laxatives concomitantly [15, 16]. Although more evidence for the most effective laxative therapy in end-of-life care is needed [45], checking on the concomitant use of laxatives can improve the quality of pain management. The pharmacists participating in our study seldom contact physicians on the co-prescribing of anti-emetics for the treatment or prevention of nausea during opioid therapy. Although nausea occurs in 15–30% of the patients receiving morphine for cancer, this approach is understandable as it is difficult to give advice when data on the superiority of one anti-emetic drug over another are lacking [14]. As nausea is common at the start of opioid therapy [46], pharmacist–physician contact on nausea control is most relevant at the initiation of opioid therapy.
Studies have shown that patients have serious concerns regarding the use of opioids for pain relief and that these concerns may interfere with adherence to analgesic regimens [47]. The pharmacists in our study reported opioid fear by the patient is a barrier to good pharmacotherapy, and they also identified this fear among family members of patients prescribed opioids. In most people with an incurable disease preferring to remain at home during the last stage of their lives [48], education on pain management should not only be communicated to the patient but also to family caregivers [49]. Financial issues were seldom seen as a barrier, although they were acknowledged to be important consideration during end-of-life treatment in a previous study performed in different Western countries [50]. In this respect, cost is not an issue in the Netherlands as the costs of opioids are fully reimbursed by the health care system. Given the rather good coverage of pharmaceuticals, availability and logistics are seldom experienced as problematic.
Most pharmacists had working agreements with physicians on euthanasia (81%); among hospital pharmacists, the 97% reporting “yes” to this question on our questionnaire was substantially higher than 71% responding positively in 1994 [51], reflecting the practical incorporation of euthanasia in the Netherlands health system. Working agreements were less common for palliative sedation (46%) and/or opioid prescribing (25%), and were more common in hospital pharmacy than in community pharmacy. In hospital as well as community settings, specific interventions of pharmacists have shown to contribute to the quality of care of patients at the end of their life [52–54]. As physicians are generally open to receiving unsolicited advice from the pharmacist regarding opioid prescribing (93%), specific interventions can also be developed in the Netherlands. The open attitude of physicians might also be the first step towards developing local working agreements between pharmacists and physicians for palliative sedation and pain management.
The usual practice in the Netherlands is that community pharmacists check all prescriptions after dispensing, whereas hospital pharmacists often only check prescriptions “at risk”, for example, in the case of drug–drug interactions. Our results show, however, that one might question whether current hospital practice is adequate given the number of issues that warrant attention.
Strengths and limitations of this study
A major strength of this study is that it is one of the first studies which maps the knowledge level of pharmacists regarding the use of opioids and pain management at the end of life. Such studies are necessary to map strengths and weaknesses in the knowledge levels and experiences of pharmacists and subsequently improve/add to the pharmacist’s level of knowledge of pharmacotherapy in end-of-life patients. A limitation of this study is that only a limited number of themes were assessed in which pharmacists should have adequate knowledge, and within those themes, not all aspects were studied. Another limitation is the relatively poor response rate of 45%, with other pharmacy studies reporting higher response rates [55, 56]. Our initial sample was representative of pharmacists in the Netherlands, and the characteristics of responders and non-responders were comparable, except for those in full-time employment. This may have biased our results: full-time pharmacists may have more experience and knowledge as they work more hours, and the actual knowledge in this population may be higher.
Another limitation is that some knowledge statements and their answer categories (true or false) leave room for interpretation. In retrospect, the statement that “simultaneous prescription of a weak opioid (e.g. tramadol) and a strong opioid (e.g. morphine) is contra-indicated” may have been more ambiguous than we intended it to be. Technically speaking, this is not a true contra-indication as it is not a medical condition increasing the risk of a serious adverse drug reaction. However, the addition of tramadol to morphine is not a preferable treatment option, since it does not reduce pain and increases side effects [57]. The question of whether the management of nausea in treatment with opioids is evidence based is also open to interpretation. Anti-emetics are not licensed for opioid-induced nausea, and there is a lack of knowledge about their efficacy in end-of-life patients [58], but there are best practices for opioid-induced nausea [59]. We do not know how pharmacists interpreted “evidence based”. Although respondents of the pilot study did not make remarks with respect to interpretation, open interpretability is relevant to all questions—possibly most to those with a low score. In summary, the questions have not been validated, and this leaves room open to interpretation. However, we believe these results do provide a good indication of the knowledge level of pharmacists.
Conclusion
Although the effects of gaps in the knowledge of pharmacists on opioids in clinical practice differ per subject, we can conclude that most of the knowledge tested in our study should be part of the basic knowledge pharmacists should have acquired and that a gap in this knowledge can be a barrier to providing adequate care to the end-of-life patients. One in three pharmacists did not think they had sufficient knowledge to advise on pain control, but most were willing to follow additional education. Physicians were open to unsolicited advice from the pharmacist regarding opioid prescriptions. If education is improved, pharmacists could claim a more active role in communication with patients, caregivers and physicians to improve the quality in end-of-life pharmacotherapy.
References
Potter J, Hami F, Bryan T, Quigley C (2003) Symptoms in 400 patients referred to palliative care services: prevalence and patterns. Palliat Med 17:310–314
Borgsteede SD, Deliens L, Beentjes B, Schellevis F, Stalman WA, van Eijk JT, van der Wal G (2007) Symptoms in patients receiving palliative care: a study on patient-physician encounters in general practice. Palliat Med 21:417–423
Teno JM, Clarridge BR, Casey V, Welch LC, Wetle T, Shield R, Mor V (2004) Family perspectives on end-of-life care at the last place of care. JAMA 291:88–93
Hanks GW, Conno F, Cherny N, Hanna M, Kalso E, McQuay HJ, Mercadante S, Meynadier J, Poulain P, Ripamonti C, Radbruch L, Casas JR, Sawe J, Twycross RG, Ventafridda V (2001) Morphine and alternative opioids in cancer pain: the EAPC recommendations. Br J Cancer 84:587–593
Gordon DB, Dahl JL, Miaskowski C, McCarberg B, Todd KH, Paice JA, Lipman AG, Bookbinder M, Sanders SH, Turk DC, Carr DB (2005) American pain society recommendations for improving the quality of acute and cancer pain management: American Pain Society Quality of Care Task Force. Arch Intern Med 165:1574–1580
World Health Organization (2002) National cancer control programmes: policies and managerial guidelines. Geneva, World Health Organization
Estfan B, Mahmoud F, Shaheen P, Davis MP, Lasheen W, Rivera N, Legrand SB, Lagman RL, Walsh D, Rybicki L (2007) Respiratory function during parenteral opioid titration for cancer pain. Palliat Med 21:81–86
Elliott TE, Elliott BA (1992) Physician attitudes and beliefs about use of morphine for cancer pain. J Pain Symptom Manage 7:141–148
Gallagher R, Hawley P, Yeomans W (2004) A survey of cancer pain management knowledge and attitudes of British Columbian physicians. Pain Res Manag 9:188–194
Oldenmenger WH, Sillevis Smitt PA, van, DS, Stoter G, van der Rijt CC (2009) A systematic review on barriers hindering adequate cancer pain management and interventions to reduce them: a critical appraisal. Eur J Cancer 45, 1370-1380
Mercadante S, Ferrera P, Villari P, Arcuri E (2003) Hyperalgesia: an emerging iatrogenic syndrome. J Pain Symptom Manage 26:769–775
Von Roenn JH, Cleeland CS, Gonin R, Hatfield AK, Pandya KJ (1993) Physician attitudes and practice in cancer pain management. A survey from the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Ann Intern Med 119:121–126
Morley-Forster PK, Clark AJ, Speechley M, Moulin DE (2003) Attitudes toward opioid use for chronic pain: a Canadian physician survey. Pain Res Manag 8:189–194
Cherny N, Ripamonti C, Pereira J, Davis C, Fallon M, McQuay H, Mercadante S, Pasternak G, Ventafridda V (2001) Strategies to manage the adverse effects of oral morphine: an evidence-based report. J Clin Oncol 19:2542–2554
Borgsteede SD, Deliens L, Zuurmond WW, Schellevis FG, Willems DL, van der Wal G, van Eijk JT (2009) Prescribing of pain medication in palliative care. A survey in general practice. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 18, 16-23
Davies EC, Green CF, Taylor S, Williamson PR, Mottram DR, Pirmohamed M (2009) Adverse drug reactions in hospital in-patients: a prospective analysis of 3695 patient-episodes. PLoS ONE 4:e4439
Max EK, Hernandez JJ, Sturpe DA, Zuckerman IH (2007) Prophylaxis for opioid-induced constipation in elderly long-term care residents: a cross-sectional study of Medicare beneficiaries. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother 5:129–136
Larkin PJ, Sykes NP, Centeno C, Ellershaw JE, Elsner F, Eugene B, Gootjes JR, Nabal M, Noguera A, Ripamonti C, Zucco F, Zuurmond WW (2008) The management of constipation in palliative care: clinical practice recommendations. Palliat Med 22:796–807
Tonna AP, Stewart D, West B, McCaig D (2007) Pharmacist prescribing in the UK—a literature review of current practice and research. J Clin Pharm Ther 32:545–556
de Gier JJ (2000) Clinical pharmacy in primary care and community pharmacy. Pharmacotherapy 20:278S–281S
Dutch Association of Hospital Pharmacists (2003) Hospital pharmacy in the Netherlands. An overview provided by the Dutch Association of Hospital Pharmacists. EJHP (2003):43-45
van Mil JW (2005) Pharmaceutical care in community pharmacy: practice and research in the Netherlands. Ann Pharmacother 39:1720–1725
van der Heide A, Onwuteaka-Philipsen BD, Rurup ML, Buiting HM, van Delden JJ, Hanssen-de Wolf JE, Janssen AG, Pasman HR, Rietjens JA, Prins CJ, Deerenberg IM, Gevers JK, van der Maas PJ, van der Wal G (2007) End-of-life practices in the Netherlands under the Euthanasia Act. N Engl J Med 356:1957–1965
Lau HS, Riezebos J, Abas V, Porsius AJ, de Boer A (2000) A nation-wide study on the practice of euthanasia and physician-assisted suicide in community and hospital pharmacies in The Netherlands. Pharm World Sci 22:3–9
McIntyre W, Hopkins D, Wolfe J (2000) Assessing pharmacists’ knowledge of cancer pain. J Pharm Care Pain Symptom Control 8:75–83
Furstenberg CT, Ahles TA, Whedon MB, Pierce KL, Dolan M, Roberts L, Silberfarb PM (1998) Knowledge and attitudes of health-care providers toward cancer pain management: a comparison of physicians, nurses, and pharmacists in the state of New Hampshire. J Pain Symptom Manage 15:335–349
Greenwald BD, Narcessian EJ (1999) Opioids for managing patients with chronic pain: community pharmacists’ perspectives and concerns. J Pain Symptom Manage 17:369–375
Krick SE, Lindley CM, Bennett M (1994) Pharmacy-perceived barriers to cancer pain control: results of the North Carolina Cancer Pain Initiative Pharmacist Survey. Ann Pharmacother 28:857–862
Crawford GB, Price SD (2003) Team working: palliative care as a model of interdisciplinary practice. Med J Aust 179:S32–S34
Potter M, Schafer S, Gonzalez-Mendez E, Gjeltema K, Lopez A, Wu J, Pedrin R, Cozen M, Wilson R, Thom D, Croughan-Minihane M (2001) Opioids for chronic nonmalignant pain. Attitudes and practices of primary care physicians in the UCSF/Stanford Collaborative Research Network. University of California, San Francisco. J Fam Pract 50:145–151
Commissie Landelijke Richtlijn Palliatieve Sedatie (2009). KNMG richtlijn "Palliatieve sedatie". KNMG (Royal Dutch Medical Association), Utrecht. Issued: 1 March 2010
Glare P, Pereira G, Kristjanson LJ, Stockler M, Tattersall M (2004) Systematic review of the efficacy of antiemetics in the treatment of nausea in patients with far-advanced cancer. Support Care Cancer 12:432–440
Thorns A, Sykes N (2000) Opioid use in last week of life and implications for end-of-life decision-making. Lancet 356:398–399
Morita T, Tsunoda J, Inoue S, Chihara S (2001) Effects of high dose opioids and sedatives on survival in terminally ill cancer patients. J Pain Symptom Manage 21:282–289
Good PD, Ravenscroft PJ, Cavenagh J (2005) Effects of opioids and sedatives on survival in an Australian inpatient palliative care population. Intern Med J 35:512–517
Mercadante S, Arcuri E (2004) Opioids and renal function. J Pain 5:2–19
Elliott TE, Murray DM, Elliott BA, Braun B, Oken MM, Johnson KM, Post-White J, Lichtblau L (1995) Physician knowledge and attitudes about cancer pain management: a survey from the Minnesota cancer pain project. J Pain Symptom Manage 10:494–504
Lambert K, Oxberry S, Hulme CW, Saharia K, Rigby AS, Johnson MJ (2007) Knowledge of attitudes to opioids in palliative care patients. Palliat Med 21:721–722
Vallerand AH, Collins-Bohler D, Templin T, Hasenau SM (2007) Knowledge of and barriers to pain management in caregivers of cancer patients receiving homecare. Cancer Nurs 30:31–37
Mao J (2002) Opioid-induced abnormal pain sensitivity: implications in clinical opioid therapy. Pain 100:213–217
Davis MP, Shaiova LA, Angst MS (2007) When opioids cause pain. J Clin Oncol 25:4497–4498
O’Donnell DE, Aaron S, Bourbeau J, Hernandez P, Marciniuk D, Balter M, Ford G, Gervais A, Goldstein R, Hodder R, Maltais F, Road J, McKay V, Schenkel J, Ariel A, Day A, Lacasse Y, Levy R, Lien D, Miller J, Rocker G, Sinuff T, Stewart P, Voduc N, Abboud R, Ariel A, Becklake M, Borycki E, Brooks D, Bryan S, Calcutt L, Chapman K, Choudry N, Couet A, Coyle S, Craig A, Crawford I, Dean M, Grossman R, Haffner J, Heyland D, Hogg D, Holroyde M, Kaplan A, Kayser J, Lein D, Lowry J, McDonald L, MacFarlane A, McIvor A, Rea J, Reid D, Rouleau M, Samis L, Sin D, Vandemheen K, Wedzicha JA, Weiss K (2004) State of the Art Compendium: Canadian Thoracic Society recommendations for the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Can Respir J 11[Suppl B]:7B–59B
Pergolizzi J, Boger RH, Budd K, Dahan A, Erdine S, Hans G, Kress HG, Langford R, Likar R, Raffa RB, Sacerdote P (2008) Opioids and the management of chronic severe pain in the elderly: consensus statement of an International Expert Panel with focus on the six clinically most often used World Health Organization Step III opioids (buprenorphine, fentanyl, hydromorphone, methadone, morphine, oxycodone). Pain Pract 8:287–313
Shaheen PE, Walsh D, Lasheen W, Davis MP, Lagman RL (2009) Opioid equianalgesic tables: are they all equally dangerous? J Pain Symptom Manage 38:409–417
Miles CL, Fellowes D, Goodman ML, Wilkinson S (2006) Laxatives for the management of constipation in palliative care patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev CD003448
Leppert W, Luczak J (2005) The role of tramadol in cancer pain treatment—a review. Support Care Cancer 13:5–17
Dawson R, Sellers DE, Spross JA, Jablonski ES, Hoyer DR, Solomon MZ (2005) Do patients’ beliefs act as barriers to effective pain management behaviors and outcomes in patients with cancer-related or noncancer-related pain? Oncol Nurs Forum 32:363–374
Townsend J, Frank AO, Fermont D, Dyer S, Karran O, Walgrove A, Piper M (1990) Terminal cancer care and patients’ preference for place of death: a prospective study. Br Med J 301:415–417
Aranda S, Yates P, Edwards H, Nash R, Skerman H, McCarthy A (2004) Barriers to effective cancer pain management: a survey of Australian family caregivers. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl) 13:336–343
Hanratty B, Holland P, Jacoby A, Whitehead M (2007) Financial stress and strain associated with terminal cancer—a review of the evidence. Palliat Med 21:595–607
de Boer A, Sang LH, Porsius A (1997) Physician-assisted death and pharmacy practice in the Netherlands. N Engl J Med 337:1091–1092
Lee J, McPherson ML (2006) Outcomes of recommendations by hospice pharmacists. Am J Health–Syst Pharm 63:2235–2239
Needham DS, Wong IC, Campion PD (2002) Evaluation of the effectiveness of UK community pharmacists’ interventions in community palliative care. Palliat Med 16:219–225
Hill RR (2007) Clinical pharmacy services in a home-based palliative care program. Am J Health Syst Pharm 64, 806, 808, 810
Cameron I, Matheson C, Bond C (2006) A survey of community pharmacist’s training needs in the management of opioid dependent clients in Grampian Scotland. Pharm J 276:601–603
Porteous T, Bond C, Robertson R, Hannaford P, Reiter E (2003) Electronic transfer of prescription-related information: comparing views of patients, general practitioners, and pharmacists. Br J Gen Pract 53:204–209
Marcou TA, Marque S, Mazoit JX, Benhamou D (2005) The median effective dose of tramadol and morphine for postoperative patients: a study of interactions. Anesth Analg 100:469–474
Porreca F, Ossipov MH (2009) Nausea and vomiting side effects with opioid analgesics during treatment of chronic pain: mechanisms, implications, and management options. Pain Med 10:654–662
Herndon CM, Jackson KC, Hallin PA (2002) Management of opioid-induced gastrointestinal effects in patients receiving palliative care. Pharmacotherapy 22:240–250
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the Platform Palliative Care from the Dutch Ministry of Health, the Comprehensive Cancer Centre Amsterdam (IKA) and the Arijan Porsius Fund
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.0), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Borgsteede, S.D., Rhodius, C.A., De Smet, P.A.G.M. et al. The use of opioids at the end of life: knowledge level of pharmacists and cooperation with physicians. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 67, 79–89 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-010-0901-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-010-0901-7