Abstract
Purpose
Ezetimibe is the first lipid-lowering drug that inhibits the intestinal uptake of dietary and biliary cholesterol without affecting the absorption of fat-soluble nutrients. Ezetimibe is readily absorbed, and undergoes rapid and almost complete glucuronidation by UGT, particularly UGT1A1, in enterocytes during its first pass. Genetic polymorphisms of UGT1A1 may decrease ezetimibe glucuronidation. Therefore, we tested the effects of the UGT1A1*6 and *28 alleles on the pharmacokinetics of ezetimibe.
Methods
Three hundred and ninety healthy Korean subjects (347 male and 43 female) were recruited and genotyped for UGT1A1 (*6 and *28 variants). Forty-three subjects among them participated in a pharmacokinetic study of ezetimibe. These 43 subjects were divided into three groups (UGT1A1*1/*1, UGT1A1*1/*X, and UGT1A1*X/*X; where *X = *6 or *28) according to the number of UGT1A1 variant alleles. All received a single 10-mg oral dose of ezetimibe. The concentrations of unchanged ezetimibe and ezetimibe–glucuronide in plasma were determined by LC-MS/MS.
Results
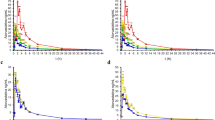
The frequencies of the UGT1A1 genotypes were 47.69%, 23.85%, 19.49%, 3.33%, 3.33%, and 2.31% for the *1/*1, *1/*6, *1/*28, *6/*6, *6/*28, and *28/*28 genotypes respectively. Besides the Cmax of unchanged ezetimibe, no significant difference was found in any other pharmacokinetic parameter of unchanged ezetimibe or ezetimibe–glucuronide in the three groups. Cmax and AUC0–48 in subjects with UGT1A1*28/*28 in the UGT1A1*X/*X group were significantly different from those in the wild-type.
Conclusions
The UGT1A1*6 allele was not found to significantly affect the pharmacokinetics of ezetimibe, but the UGT1A1*28 allele might.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- UGT1A1:
-
UDP-glucuronosyltransferases 1A1
References
Patrick JE, Kosoglou T, Stauber KL, Alton KB, Maxwell SE, Zhu Y, Statkevich P, Iannucci R, Chowdhury S, Affrime M, Cayen MN (2002) Disposition of the selective cholesterol absorption inhibitor ezetimibe in healthy male subjects. Drug Metab Dispos 30:430–437
Kosoglou T, Statkevich P, Johnson-Levonas AO, Paolini JF, Bergman AJ, Alton KB (2005) Ezetimibe: a review of its metabolism, pharmacokinetics and drug interactions. Clin Pharmacokinet 44:467–494
Jeu L, Cheng JW (2003) Pharmacology and therapeutics of ezetimibe (SCH 58235), a cholesterol-absorption inhibitor. Clin Ther 25:2352–2387
Nutescu EA, Shapiro NL (2003) Ezetimibe: a selective cholesterol absorption inhibitor. Pharmacotherapy 23:1463–1474
Van Heek M, Farley C, Compton DS, Hoos L, Alton KB, Sybertz EJ, Davis HR Jr (2000) Comparison of the activity and disposition of the novel cholesterol absorption inhibitor, SCH58235, and its glucuronide, SCH60663. Br J Pharmacol 129:1748–1754
Ghosal A, Hapangama N, Yuan Y, Achanfuo-Yeboah J, Iannucci R, Chowdhury S, Alton K, Patrick JE, Zbaida S (2004) Identification of human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzyme(s) responsible for the glucuronidation of ezetimibe (Zetia). Drug Metab Dispos 32:314–320
Ezzet F, Krishna G, Wexler DB, Statkevich P, Kosoglou T, Batra VK (2001) A population pharmacokinetic model that describes multiple peaks due to enterohepatic recirculation of ezetimibe. Clin Ther 23:871–885
Nagar S, Remmel RP (2006) Uridine diphosphoglucuronosyltransferase pharmacogenetics and cancer. Oncogene 25:1659–1672
Tukey RH, Strassburg CP (2000) Human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases: metabolism, expression, and disease. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 40:581–616
UGT1A1 allele nomenclature. In: UDP Glucuronosyltransferase Homepage. http://www.pharmacogenomics.pha.ulaval.ca/webdav/site/pharmacogenomics/shared/Nomenclature/UGT1A/UGT1A1.htm. Accessed 15 April 2009
Liu JY, Qu K, Sferruzza AD, Bender RA (2007) Distribution of the UGT1A1*28 polymorphism in Caucasian and Asian populations in the US: a genomic analysis of 138 healthy individuals. Anticancer Drugs 18:693–696
Minami H, Sai K, Saeki M, Saito Y, Ozawa S, Suzuki K, Kaniwa N, Sawada J, Hamaguchi T, Yamamoto N, Shirao K, Yamada Y, Ohmatsu H, Kubota K, Yoshida T, Ohtsu A, Saijo N (2007) Irinotecan pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics and UGT1A genetic polymorphisms in Japanese: roles of UGT1A1*6 and *28. Pharmacogenet Genomics 17:497–504
Bosma PJ, Chowdhury JR, Bakker C, Gantla S, de Boer A, Oostra BA, Lindhout D, Tytgat GN, Jansen PL, Oude Elferink RP, Chowdhury NR (1995) The genetic basis of the reduced expression of bilirubin UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1 in Gilbert’s syndrome. N Engl J Med 333:1171–1175
Maruo Y, D’Addario C, Mori A, Iwai M, Takahashi H, Sato H, Takeuchi Y (2004) Two linked polymorphic mutations (A(TA)7TAA and T-3279G) of UGT1A1 as the principal cause of Gilbert syndrome. Hum Genet 115:525–526
Iyer L, Das S, Janisch L, Wen M, Ramírez J, Karrison T, Fleming GF, Vokes EE, Schilsky RL, Ratain MJ (2002) UGT1A1*28 polymorphism as a determinant of irinotecan disposition and toxicity. Pharmacogenomics J 2:43–47
Ando Y, Saka H, Ando M, Sawa T, Muro K, Ueoka H, Yokoyama A, Saitoh S, Shimokata K, Hasegawa Y (2000) Polymorphisms of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase gene and irinotecan toxicity: a pharmacogenetic analysis. Cancer Res 60:6921–6926
Yamamoto K, Sato H, Fujiyama Y, Doida Y, Bamba T (1998) Contribution of two missense mutations (G71R and Y486D) of the bilirubin UDP glycosyltransferase (UGT1A1) gene of phenotypes of Gilbert’s syndrome and Crigler-Najjar syndrome type II. Biochim Biophys Acta 1406:267–273
Udomuksorn W, Elliot DJ, Lewis BC, Mackenzie PI, Yoovathaworn K, Miners JO (2007) Influence of mutations associated with Gilbert and Crigler-Najjar type II syndromes on the glucuronidation kinetics of bilirubin and other UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A substrates. Pharmacogenet Genom 17:1017–1029
Huang MJ, Kua KE, Teng HC, Tang KS, Weng HW, Huang CS (2004) Risk factors for severe hyperbilirubinemia in neonates. Pediatr Res 56:682–689
Oswald S, Scheuch E, Cascorbi I, Siegmund W (2006) A LC-MS/MS method to quantify the novel cholesterol lowering drug ezetimibe in human serum, urine and feces in healthy subjects genotyped for SLCO1B1. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 830:143–150
Li S, Liu G, Jia J, Li X, Yu C (2006) Liquid chromatography-negative ion electrospray tandem mass spectrometry method for the quantification of ezetimibe in human plasma. J Pharm Biomed Anal 40:987–992
Guillemette C (2003) Pharmacogenomics of human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzymes. Pharmacogenomics J 3:136–158
Araki K, Fujita K, Ando Y, Nagashima F, Yamamoto W, Endo H, Miya T, Kodama K, Narabayashi M, Sasaki Y (2006) Pharmacogenetic impact of polymorphisms in the coding region of the UGT1A1 gene on SN-38 glucuronidation in Japanese patients with cancer. Cancer Sci 97:1255–1259
Sai K, Saeki M, Saito Y, Ozawa S, Katori N, Jinno H, Hasegawa R, Kaniwa N, Sawada J, Komamura K, Ueno K, Kamakura S, Kitakaze M, Kitamura Y, Kamatani N, Minami H, Ohtsu A, Shirao K, Yoshida T, Saijo N (2004) UGT1A1 haplotypes associated with reduced glucuronidation and increased serum bilirubin in irinotecan-administered Japanese patients with cancer. Clin Pharmacol Ther 75:501–515
Cai H, Nguyen N, Peterkin V, Yang YS, Hotz K, Beaton La Placa D, Chen S, Tukey RH, Stevens JC (2010) A humanized UGT1 mouse model expressing the UGT1A1*28 allele for assessing drug clearance by UGT1A1 dependent glucuronidation. Drug Metab Dispos 38:879–886
Yamamoto T, Ito K, Honma M, Takada T, Suzuki H (2007) Cholesterol-lowering effect of ezetimibe in uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A-deficient (Gunn) rats. Drug Metab Dispos 35:1455–1458
Oswald S, Westrup S, Grube M, Kroemer HK, Weitschies W, Siegmund W (2006) Disposition and sterol-lowering effect of ezetimibe in multidrug resistance-associated protein 2-deficient rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 318:1293–1299
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
This study was supported by the Samsung Research Fund at Sungkyunkwan University, 2007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bae, JW., Choi, CI., Lee, JH. et al. Effects of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of ezetimibe in healthy subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 67, 39–45 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-010-0899-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-010-0899-x