Abstract
Objective
There is a perception that many drug usage evaluations do not widely influence prescribing behaviour. The aim of this study was to critically evaluate recent journal articles which fit the Medline definition for Drug Utilization Review (DUR) and which also cover multiple healthcare sites.
Methods
PubMed (National Library of Medicine, NLM) (2003, 2004) was searched using the MeSH topic ‘drug utilization’. Retrieved studies were evaluated to ascertain those describing a DUR (measuring drug use against specific criteria). These were subdivided according to whether the DUR was conducted at one site or across many. The multi-centre DURs were critically reviewed, including evaluating whether all phases of a quality cycle were completed and determining aspects of design such as whether the study was prospective or retrospective, any interventions conducted and provision of feedback.
Results
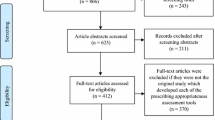
A total of 646 unique articles were retrieved. Of these, 495 (77%) did not meet the definition for DUR, while 151 (23%) articles did. Thirty-five (5%) described English language multi-centre DURs; ethics approval was obtained in ten of these and 18 were carried out retrospectively. In all 35 studies some comparator or standard was used, but only eight conducted an intervention and only three provided feedback to the prescribers.
Conclusion
Most DURs were not conducted across a number of centres. Of the recent published multi-centre DURs most presented only an initial audit and did not complete the quality cycle with feedback, intervention and re-audit. To widely influence prescribing behaviour, the full cycle is required with involvement of as many sites as possible to achieve improvements across many jurisdictions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sanz J (2005) Pharmacoepidemiology and the “Impact Factor”. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 60:765–772
Burk M, Furmaga E, Dong D, Cunningham F (2004) Multicenter drug use evaluation of tamsulosin and availability of guidance criteria for nonformulary use in the veterans affairs health system. J Manag Care Pharmacol 10:423–32
Butler J, Arbogast PG, Daugherty J, Jain MK, Ray WA, Griffin MR (2004) Outpatient utilization of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors among heart failure patients after hospital discharge. J Am Coll Cardiol 43:2036–43
Katzan IL, Hammer MD, Furlan AJ, Hixson ED, Nadzam DM (2003) Quality improvement and tissue-type plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke: a Cleveland update. Stroke 34:799–800
Keyserling HL, Sinkowitz-Cochran RL, Harris JM 2nd, Levine GL, Siegel JD, Stover BH, Lau SA, Jarvis WR (2003) Vancomycin use in hospitalized pediatric patients. Pediatrics 112:e104–11
Scott IA, Heath K, Harper C, Clough A (2003) An Australian comparison of specialist care of acute myocardial infarction. Int J Qual Health Care 15:155–61
Centres for Medicare and Medicaid (accessed July 11, 2005)http://www.cms.hhs.gov/quality/hospital/hqii.asp
Feucht CL, Rice LB (2003) An interventional program to improve antibiotic use. Ann Pharmacother 37:646–651
Landsberg PG, Pillans PI, Radford JM (2003) Evaluation of cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor use in patients admitted to a large teaching hospital. Intern Med J 33:225–8
Richards MJ, Robertson MB, Dartnell JG, Duarte MM, Jones NR, Kerr DA, Lim LL, Ritchie PD, Stanton GJ, Taylor SE (2003) Impact of a web-based antimicrobial approval system on broad-spectrum cephalosporin use at a teaching hospital. Med J Aust 178:386–90
Ritchie S, Scanlon N, Lewis M, Black PN (2004) Use of a preprinted sticker to improve the prescribing of prophylactic antibiotics for hip fracture surgery. Qual Saf Health Care 13:384–7
Potocki M, Goette J, Szucs TD, Nadal D (2003) Prospective survey of antibiotic utilization in pediatric hospitalized patients to identify targets for improvement of prescription. Infection 31:398–403
Soumerai SB, Avorn J (1990) Principles of educational outreach (‘academic detailing’) to improve clinical decision making. JAMA 263:549–56
Thomson O’Brien MA, Freemantle N, Oxman AD, Wolf F, Davis DA, Herrin J (2001) Continuing education meetings and workshops: effects on professional practice and health care outcomes. In: The Cochrane database of systematic reviews: reviews 2001, issue 1. Wiley & Sons, Chichester
Thamlikitkul V, Apisitwittaya W (2004) Implementation of clinical practice guidelines for upper respiratory infection in Thailand. Int J Infect Dis 8:47–51
Tamblyn R, Huang A, Perreault R, Jacques A, Roy D, Hanley J, McLeod P, Laprise R (2003) The medical office of the 21st century (MOXXI): effectiveness of computerized decision-making support in reducing inappropriate prescribing in primary care. CMAJ 169:549–56
Wright J, Warren E, Reeves J, Bibby J, Harrison S, Dowswell G, Russell I, Russell D (2003) Effectiveness of multifaceted implementation of guidelines in primary care. J Health Serv Res Policy 8:142–8
Lee R, Monteiro EF (2003) Third regional audit of antiretroviral prescribing in HIV patients. Int J STD AIDS 14:58–60
Antibiotic Writing Group (2003) Therapeutic Guidelines: antibiotic Version 12. Therapeutic Guidelines Limited, Melbourne
Gouws E, Bryce J, Habicht JP, Amaral J, Pariyo G, Schellenberg JA, Fontaine O (2004) Improving antimicrobial use among health workers in first-level facilities: results from the multi-country evaluation of the Integrated Management of Childhood Illness strategy. Bull World Health Organ 82:509–15
Bettinger TL, Crismon ML, Trivedi MH, Grannemann B, Shon SP (2004) Clinicians’ adherence to an algorithm for pharmacotherapy of depression in the Texas public mental health sector. Psychiatr Serv 55:703–5
Avorn J, Soumerai SB (1983) Improving drug-therapy decisions through educational outreach. A randomized controlled trial of academically based “detailing”. N Engl J Med 308:1457–63
Thomson O’Brien MA, Oxman AD, Davis DA, Haynes RB, Freemantle N, Harvey EL (1997) Educational outreach visits: effects on professional practice and health care outcomes. In: The Cochrane database of systematic reviews: reviews 1997, issue 4. Wiley & Sons, Chichester
Majumdar SR, Ross-Degnan D, Farraye FA, Lee M, Kemp JA, Lecates RF, Henning JM, Tunis SR, Schrammel P, Soumerai SB (2005) Controlled trial of interventions to increase testing and treatment for Helicobacter pylori and reduce medication use in patients with chronic acid-related symptoms. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 21:1029–39
Schmader KE, Hanlon JT, Pieper CF, Sloane R, Ruby CM, Twersky J, Francis SD, Branch LG, Lindblad CI, Artz M, Weinberger M, Feussner JR, Cohen HJ (2004) Effects of geriatric evaluation and management on adverse drug reactions and suboptimal prescribing in the frail elderly. Am J Med 116:394–401
Garbutt J, Jeffe DB, Shackelford P (2003) Diagnosis and treatment of acute otitis media: an assessment. Pediatrics 112:143–9
Lyons JS, MacIntyre JC, Lee ME, Carpinello S, Zuber MP, Fazio ML (2004) Psychotropic medications prescribing patterns for children and adolescents in New York’s public mental health system. Community Ment Health J 40:101–18
Roila F, Ballatori E, Patoia L, Palazzo S, Veronesi A., Frassoldati A, Cetto G, Cinieri S, Goldhirsch A (2003) Adjuvant systemic therapies in women with breast cancer: an audit of clinical practice in Italy. Ann Oncol 14:843–8
Nygaard HA, Naik M, Ruths S, Straand J (2003) Nursing-home residents and their drug use: a comparison between mentally intact and mentally impaired residents. The Bergen district nursing home (BEDNURS) study. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 59:463–9
Batty GM, Grant RL, Aggarwal R, Lowe D, Potter JM, Pearson MG, Jackson SH (2003) Using prescribing indicators to measure the quality of prescribing to elderly medical in-patients. Age Ageing 32:292–8
Bergman U, Risinggard H, Vlahovic-Palcevski V, Ericsson O (2004) Use of antibiotics at hospitals in Stockholm: a benchmarking project using internet. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 13:465–71
Ruths S, Straand J, Nygaard HA (2003) Multidisciplinary medication review in nursing home residents: what are the most significant drug-related problems? The Bergen District Nursing Home (BEDNURS) study. Qual Saf Health Care 12:176–80
Akter FU, Heller D, Smith A, Rahman MM, Milly AF (2004) Antimicrobial use in paediatric wards of teaching hospitals in Bangladesh. Mymensingh Med J 13:63–6
Bradley EH, Herrin J, Mattera JA, Holmboe ES, Wang Y, Frederick P, Roumanis SA, Radford MJ, Krumholz HM (2004) Hospital-level performance improvement: beta-blocker use after acute myocardial infarction. Med Care 42:591–9
Brotons C, Permanyer G, Pacheco V, Moral I, Ribera A, Cascant P, Pinar J (2003) Prophylactic treatment after myocardial infarction in primary care: how far can we go? Fam Pract 20:32–5
Bugnon-Reber A, de Torrente A, Troillet N, Genne D (2004) Antibiotic misuse in medium-sized Swiss hospitals. Swiss Med Wkly 134:481–5
Charbonneau A, Rosen AK, Ash AS, Owen RR, Kader B, Spiro A 3rd, Hankin C, Herz LR, Jo VPM, Kazis L, Miller DR, Berlowitz DR (2003) Measuring the quality of depression care in a large integrated health system. Med Care 41:669–80
Charbonneau A, Rosen AK, Owen RR, Spiro A 3rd, Ash AS, Miller DR, Kazis L, Kader B, Cunningham F, Berlowitz DR (2004) Monitoring depression care: in search of an accurate quality indicator. Med Care 42:522–31
Hanlon JT, Artz MB, Pieper CF, Lindblad CI, Sloane RJ, Ruby CM, Schmader KE (2004) Inappropriate medication use among frail elderly inpatients. Ann Pharmacother 38:9–14
Hanna K, Poulin-Costello M, Preston M, Maresky N (2003) Intravenous immune globulin use in Canada. Can J Clin Pharmacol 10:11–6
Harries AD, Gausi F, Salaniponi FM (2004) Prescriptions and dosages of anti-tuberculosis drugs in the National Tuberculosis Control Programme of Malawi. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 8:724–9
Humberstone V, Wheeler A, Lambert T (2004) An audit of outpatient antipsychotic usage in the three health sectors of Auckland, New Zealand. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 38:240–45
Laguna P, Martn A, del Arco C, Gargantilla P (2004) Risk factors for stroke and thromboprophylaxis in atrial fibrillation: what happens in daily clinical practice? The GEFAUR-1 study. Ann Emerg Med 44:3–11
Lloyd AJ, Harrison CL, Ferrier IN, Young AH (2003) The pharmacological treatment of bipolar affective disorder: practice is improving but could still be better. J Psychopharmacol 17:230–3
Loveland D, Boyle M, Godley M, Gillette C (2003) What happens to patients’ psychotropic prescriptions after discharge from a state psychiatric hospital? Adm Policy Ment Health 31:45–64
Mamun K, Lien CT, Goh-Tan CY, Ang WS (2004) Polypharmacy and inappropriate medication use in Singapore nursing homes. Ann Acad Med Singapore 33:49–52
Palmer NO, Batchelor PA (2004) An audit of antibiotic prescribing by vocational dental practitioners. Prim Dent Care 11:77–80
Paton C, Lelliott P, Harrington M, Okocha C, Sensky T, Duffett R (2003) Patterns of antipsychotic and anticholinergic prescribing for hospital inpatients. J Psychopharmacol 17:223–9
Trujillo JM, Gonyeau MJ, DiVall MV, Alexander SL (2004) Spironolactone use in patients with heart failure. J Clin Pharm Ther 29:165–70
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge CAPTION project teams in Queensland, NSW, Victoria, South Australia, Tasmania and the National Prescribing Service.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pulver, L.K., Tett, S.E. Drug utilization review across jurisdictions – a reality or still a distant dream?. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 62, 97–106 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-005-0087-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-005-0087-6