Abstract.
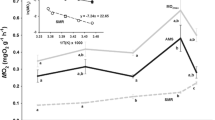
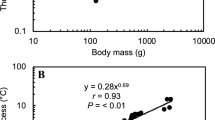
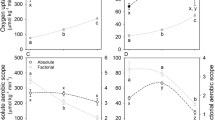
To evaluate the concept of metabolic cold adaptation (MCA) in fishes, we compared – in brain, red muscle, and white muscle of Antarctic notothenioid fishes and tropical/subtropical fishes – the activities of two enzymes of ATP-generating pathways, citrate synthase (CS), an indicator of citric acid cycle activity (aerobic metabolism), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), an indicator of potential for ATP production through anaerobic glycolysis. Brain was chosen because, unlike locomotory muscle, its metabolic activity is not likely to be influenced by a species' level of activity or nutritional status, so MCA should be readily observed if present. CS and LDH activities in brain exhibited a high level of MCA, but compensation to temperature was not complete (48% for CS; 46% for LDH). CS and LDH activities in red and white muscle varied widely among species, according to the general level of locomotory activity. The 'mode of life'-related enzymatic activities in locomotory muscle show that study of MCA at the level of whole organism metabolism is fraught with difficulties and experimental ambiguities. In contrast, the low variation among species within each group in enzymatic activities in brain, and the large differences between groups in CS and LDH activity, show that brain is an excellent study system for evaluating metabolic compensation to temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawall, .H., Torres, .J., Sidell, .B. et al. Metabolic cold adaptation in Antarctic fishes: evidence from enzymatic activities of brain. Marine Biology 140, 279–286 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270100695
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270100695