Abstract
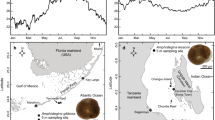
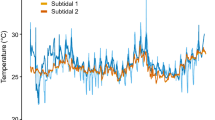
Invasive species allow an investigation of trait retention and adaptations after exposure to new habitats. Recent work on corals from the Gulf of Aqaba (GoA) shows that tolerance to high temperature persists thousands of years after invasion, without any apparent adaptive advantage. Here, we test whether thermal tolerance retention also occurs in another symbiont-bearing calcifying organism. To this end, we investigate the thermal tolerance of the benthic foraminifera Amphistegina lobifera from the GoA (29°30.14167 N, 34°55.085E) and compare it to a recent “Lessepsian invader population” from the Eastern Mediterranean (EaM) (32°37.386 N, 34°55.169E). We first established that the studied populations are genetically homogenous but distinct from a population in Australia and that they contain a similar consortium of diatom symbionts, confirming their recent common descent. Thereafter, we exposed specimens from GoA and EaM to elevated temperatures for three weeks and monitored survivorship, growth rates and photophysiology. Both populations exhibited a similar pattern of temperature tolerance. A consistent reduction of photosynthetic dark yields was observed at 34 °C and reduced growth was observed at 32 °C. The apparent tolerance to sustained exposure to high temperature cannot have a direct adaptive importance, as peak summer temperatures in both locations remain <32 °C. Instead, it seems that in the studied foraminifera, tolerance to high temperature is a conservative trait and the EaM population retained this trait since its recent invasion. Such pre-adaptation to higher temperatures confers A. lobifera a clear adaptive advantage in shallow and episodically high temperature environments in the Mediterranean under further warming.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alve E (1999) Colonization of new habitats by benthic foraminifera: a review. Earth Sci Rev 46:167–185. doi:10.1016/S0012-8252(99)00016-1
Amaral-Zettler LA, McCliment EA, Ducklow HW, Huse SM (2009) A method for studying protistan diversity using massively parallel sequencing of V9 hypervariable regions of small-subunit ribosomal RNA genes. PLoS ONE. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006372
André A, Quillévéré F, Morard R, Ujiié Y, Escarguel G, de Vargas C, de Garidel-Thoron T, Douady CJ, Ketmaier V (2014) SSU rDNA Divergence in Planktonic Foraminifera: molecular taxonomy and biogeographic implications. PLoS ONE 9:e104641. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0104641
Berkelmans R, Willis BL (1999) Seasonal and local spatial patterns in the upper thermal limits of corals on the inshore Central Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 18:219–228. doi:10.1007/s003380050186
Berkelmans R, De’ath G, Kininmonth S, Skirving WJ (2004) A comparison of the 1998 and 2002 coral bleaching events on the Great Barrier Reef: spatial correlation, patterns, and predictions. Coral Reefs 23:74–83. doi:10.1007/s00338-003-0353-y
Bernhard JM (2000) Distinguishing live from dead foraminifera: methods review and proper applications. Micropaleontology 46:38–46
Braithwaite CJR (1987) Geology and Paleogeography of the Red Sea region. In: Edwards AJ, Head SM (eds) Red Sea. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 22–44
Caruso A, Cosentino C (2014) The first colonization of the genus Amphistegina and other exotic benthic foraminifera of the Pelagian Islands and south-eastern Sicily (central Mediterranean Sea). Mar Micropaleontol 111:38–52. doi:10.1016/j.marmicro.2014.05.002
Chen IC, Hill JK, Ohlemuller R, Roy DB, Thomas CD (2011) Rapid range shifts of species associated with high levels of climate warming. Science 333:1024–1026. doi:10.1126/science.1206432
Coles SL, Riegl BM (2013) Thermal tolerances of reef corals in the Gulf: a review of the potential for increasing coral survival and adaptation to climate change through assisted translocation. Mar Pollut Bull 72:323–332. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.09.006
Darriba D, Taboada GL, Doallo R, Posada D (2012) jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat Methods 9:772
De’ath G, Fabricius KE, Sweatman H, Puotinen M (2012) The 27-year decline of coral cover on the Great Barrier Reef and its causes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:17995–17999. doi:10.1073/pnas.1208909109
deVargas C, Zaninetti L, Hilbrecht H, Pawlowski J (1997) Phylogeny and rates of molecular evolution of planktonic foraminifera: SSU rDNA sequences compared to the fossil record. J Mol Evol 45:285–294. doi:10.1007/pl00006232
Fine M, Gildor H, Genin A (2013) A coral reef refuge in the Red Sea. Glob Change Biol 19:3640–3647. doi:10.1111/gcb.12356
Grimm GW, Stögerer K, Topaç Ertan K, Kitazato H, Kučera M, Hemleben V, Hemleben C (2007) Diversity of rDNA in Chilostomella: molecular differentiation patterns and putative hermit types. Mar Micropaleontol 62:75–90. doi:10.1016/j.marmicro.2006.07.005
Gruber L, Almogi-Labin A, Sivan D, Herut B (2007) The life cycle of the symbiont-bearing larger foraminifera Amphistegina lobifera, a new arrival on the Israeli shelf. Rapports et procès-verbaux des réunions Commission Internationale pour l’exploration scientifique de la Mer Méditerranée 38:491
Guindon S, Dufayard J-F, Lefort V, Anisimova M, Hordijk W, Gascuel O (2010) New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst Biol 59:307–321
Hallock P (1979) Trends in test shape with depth in large, symbiont-bearing foraminifera. J Foraminifer Res 9:61–69
Hallock P (1981) Light dependence in Amphistegina. J Foraminifer Res 11:40–46. doi:10.2113/gsjfr.11.1.40
Hallock P (1981b) Production of carbonate sediments by selected large benthic foraminifera on two Pacific coral reefs. J Sediment Res 51:467–474
Hallock P (2000) Symbiont-bearing foraminifera: harbingers of global change? Micropalaeontology 46:95–104
Hallock P, Talge HK (1993) Symbiont loss (“bleaching”) in the reef-dwelling benthic foraminifer Amphistegina gibbosa in the Florida Keys in 1991–92. In: Ginsburg RN (ed) Proceedings of the colloquium on global aspects of coral reefs: health, hazards and history. University of Miami, Florida, pp 94–100
Hallock P, Talge HK, Smith KM, Cockey EM (1992) Bleaching in the reef-dwelling foraminifera Amphistegina gibbosa. In: Richmond RH (ed) Proceedings of the 7th international coral reef symposium. University of Guam Press, Mangilao, pp 44–49
Hammer, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electron 4:9. http://palaeo-electronica.org/2001_2001/past/issue2001_2001.htm
Hariri MS (2008) Effect of hydrographic conditions on the ecology of benthic foraminifera in two different hypersaline lagoons, eastern Red Sea coast, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Mar Sci 19:3–13
Herut B, Almogi-Labin A, Jannink N, Gertman I (2000) The seasonal dynamics of nutrient and chlorophyll a concentrations on the SE Mediterranean shelf-slope. Oceanol Acta 23:771–782. doi:10.1016/s0399-1784(00)01118-x
Hohenegger J (2006) The importance of symbiont-bearing benthic foraminifera for West Pacific carbonate beach environments. Mar Micropaleontol 61:4–39. doi:10.1016/j.marmicro.2006.05.007
Hyams O, Almogi-Labin A, Benjaminia C (2002) Larger foraminifera of the southeastern Mediterranean shallow continental shelf off Israel. Isr J Earth Sci 51:169–179. doi:10.1560/QAE1-KTEE-2K2L-QPCH
Hyams-Kaphzan O, Almogi-Labin A, Sivan D, Benjamini C (2008) Benthic foraminifera assemblage change along the southeastern Mediterranean inner shelf due to fall-off of Nile-derived siliciclastics. Neues Jahrbuch Fur Geologie Und Palaontologie-Abhandlungen 248:315–344. doi:10.1127/0077-7749/2008/0248-0315
Langer MR (2008) Foraminifera from the Mediterranean and the Red Sea. In: Por FD (ed) Aqaba-Eilat, the Improbable Gulf: Environment, Biodiversity and Preservation. Magnes Press, Jersusalem, pp 399–417
Langer MR, Hottinger L (2000) Biogeography of selected “larger” foraminifera. Micropaleontology 46:105–126. doi:10.2307/1486184
Langer MR, Silk MT, Lipps JH (1997) Global ocean carbonate and carbon dioxide production; the role of reef foraminifera. J Foraminifer Res 27:271–277. doi:10.2113/gsjfr.27.4.271
Langer MR, Weinmann AE, Lötters S, Rödder D (2012) “Strangers” in paradise: modeling the biogeographic range expansion of the foraminifera Amphistegina in the Mediterranean Sea. J Foraminifer Res 42:234–244. doi:10.2113/gsjfr.42.3.234
Lee J, Reimer C, McEnergy M (1980) The Identification of diatoms isolated as endosymbionts from larger foraminifera from the Gulf of Eilat (Red Sea) and the description of two new species, Fragilaria shiloi sp. nov. and Navicula reissii sp. nov. Bot Mar 23:41–48
Lee J, Erez J, McEnery M, Lagziel A, Xenophontos X (1986) Experiments on persistence of endosymbiotic diatoms in the larger foraminifer: Amphistegina lessonii. Symbiosis 1:211–226
Locarnini RA, Mishonov AV, Antonov JI, Boyer TP, Garcia HE, Baranova OK, Zweng MM, Paver CR, Reagan JR, Johnson DR, Hamilton M, Seidov D (2013) World Ocean Atlas 2013 temperature. In: AMTENAN (ed) National Centers for environmental information NOAA Atlas NESDIS 73. NOAA, USA, p 40
McKee ED, Chronic J, Leopold EB (1959) Sedimentary belts in lagoon of Kapingamarangi Atoll. AAPG Bull 43:501–562
Meric E, Avsar N, Yokes MB (2008) Some alien foraminifers along the Aegean and southwestern coasts of Turkey. Micropaleontology 54:307–349
Meriç E, Yokeş MB, Avşar N, Kıyak NG, Öner E, Nazik A, Demirtaşlı E, Dinçer F, Öztürk MZ (2015) Did Amphistegina lobifera Larsen reach the Mediterranean via the Suez Canal? Quatern Int. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2015.08.088
Merkado G, Holzmann M, Apotheloz-Perret-Gentil L, Pawlowski J, Abdu U, Almogi-Labin A, Hyams-Kaphzan O, Bakhrat A, Abramovich S (2013) Molecular evidence for Lessepsian invasion of Soritids (larger symbiont bearing benthic foraminifera). PLoS ONE. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0077725
Morard R, Quillevere F, Escarguel G, Ujiie Y, de Garidel-Thoron T, Norris RD, de Vargas C (2009) Morphological recognition of cryptic species in the planktonic foraminifer Orbulina universa. Mar Micropaleontol 71:148–165. doi:10.1016/j.marmicro.2009.03.001
Mouanga GH, Langer MR (2014) At the front of expanding ranges: shifting community structures at amphisteginid species range margins in the Mediterranean Sea. Neues Jb Geol Paläontol Abh 271:141–150. doi:10.1127/0077-7749/2014/0381
Muller PH (1974) Sediment production and population biology of the benthic foraminifer Amphistegina madagascariensis. Limnol Oceanogr 19:802–809
Occhipinti-Ambrogi A (2007) Global change and marine communities: alien species and climate change. Mar Pollut Bull 55:342–352. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2006.11.014
Paldor N, Anati DA (1979) Seasonal variations of temperature and salinity in the Gulf of Elat (Aqaba). Deep Sea Res Part A Oceanogr Res Papers 26:661–672. doi:10.1016/0198-0149(79)90039-6
Parker JH, Gischler E, Eisenhauer A (2012) Biodiversity of foraminifera from Late Pleistocene to Holocene coral reefs, South Sinai, Egypt. Mar Micropaleontol 86–87:59–75. doi:10.1016/j.marmicro.2012.02.002
Pawlowski J, Holzmann M, Berney C, Fahrni J, Cedhagen T, Bowser SS (2002) Phylogeny of allogromiid foraminifera inferred from SSU rRNA gene sequences. J Foraminifer Res 32:334–343. doi:10.2113/0320334
Pawlowski J, Fahrni J, Lecroq B, Longet D, Cornelius N, Excoffier L, Cedhagen T, Gooday AJ (2007) Bipolar gene flow in deep-sea benthic foraminifera. Mol Ecol 16:4089–4096. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2007.03465.x
Prazeres M, Uthicke S, Pandolfi J (2016a) Changing light levels induce photo-oxidative stress and alterations in shell density of Amphistegina lobifera (Foraminifera). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 549:69–78
Prazeres M, Uthicke S, Pandolfi JM (2016b) Influence of local habitat on the physiological responses of large benthic foraminifera to temperature and nutrient stress. Sci Rep UK 6:21936
Pruesse E, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2012) SINA: accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics 28:1823–1829
R Development Core Team (2014) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org/
Reiss Z, Hottinger L (1984) The Gulf of Aqaba: ecological micropaleontology. Springer, Berlin
SAS (2014) JMP statistics software, Version 11. SAS, Heidelberg
Schmidt C, Heinz P, Kucera M, Uthicke S (2011) Temperature-induced stress leads to bleaching in larger benthic foraminifera hosting endosymbiotic diatoms. Limnol Oceanogr 56:1587–1602. doi:10.4319/lo.2011.56.5.1587
Schmidt C, Kucera M, Uthicke S (2014) Combined effects of warming and ocean acidification on coral reef foraminifera Marginopora vertebralis and Heterostegina depressa. Coral Reefs 33:805–818. doi:10.1007/s00338-014-1151-4
Schmidt C, Morard R, Almogi-Labin A, Weinmann AE, Titelboim D, Abramovich S, Kucera M (2015) Recent invasion of the symbiont-bearing foraminifera Pararotalia into the Eastern Mediterranean facilitated by the ongoing warming trend. PLoS ONE 10:e0132917. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0132917
Schmidt C, Titelboim D, Brandt J, Herut B, Abramovich S, Almogi-Labin A, Kucera M (2016) Extremely heat tolerant photosymbiosis in a shallow marine benthic foraminifera. Sci Rep UK. doi:10.1038/srep30930
Shaltout M, Omstedt A (2014) Recent sea surface temperature trends and future scenarios for the Mediterranean Sea. Oceanologia 56:411–443. doi:10.5697/oc.56-3.411
Talge HK, Hallock P (1995) Cytological examination of symbiont loss in a benthic foraminifera, Amphistegina gibbosa. Mar Micropaleontol 26:107–113. doi:10.1016/0377-8398(95)00015-1
Talge HK, Hallock P (2003) Ultrastructural responses in field-bleached and experimentally stressed Amphistegina gibbosa (Class Foraminifera). J Eukaryot Microbiol 50:324–333. doi:10.1111/j.1550-7408.2003.tb00143.x
ter Kuile B, Erez J (1984) In situ growth rate experiments on the symbiont-bearing foraminifera Amphistegina lobifera and Amphisorus hemprichii. J Foraminifer Res 14:262–276. doi:10.2113/gsjfr.14.4.262
Titelboim D, Almogi-Labin A, Herut B, Kucera M, Schmidt C, Hyams-Kaphzan O, Ovadia O, Abramovich S (2016) Selective responses of benthic foraminifera to thermal pollution. Mar Pollut Bull. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.02.002
Triantaphyllou MV, Koukousioura O, Dimiza MD (2009) The presence of the Indo-Pacific symbiont-bearing foraminifer Amphistegina lobifera in Greek coastal ecosystems (Aegean Sea, Eastern Mediterranean). Mediterr Mar Sci 10:73–85
Triantaphyllou MV, Dimiza MD, Koukousioura O, Hallock P (2012) Observations of the life cycle of the symbiont-bearing foraminifer Amphistegina lobifera Larsen, an invasive species in coastal ecosystems of the Aegean Sea (Greece, E., Mediterranean). J Foraminifer Res 42:143–150
Tsuchiya M, Grimm GW, Heinz P, Stogerer K, Ertan KT, Collen J, Bruchert V, Hemleben C, Hemleben V, Kitazato H (2009) Ribosomal DNA shows extremely low genetic divergence in a world-wide distributed, but disjunct and highly adapted marine protozoan (Virgulinella fragilis, Foraminiferida). Mar Micropaleontol 70:8–19. doi:10.1016/j.marmicro.2008.10.001
Tsui CKM, Marshall W, Yokoyama R, Honda D, Lippmeier JC, Craven KD, Peterson PD, Berbee ML (2009) Labyrinthulomycetes phylogeny and its implications for the evolutionary loss of chloroplasts and gain of ectoplasmic gliding. Mol Phylogenet Evol 50:129–140
Uthicke S, Vogel N, Doyle J, Schmidt C, Humphrey C (2012) Interactive effects of climate change and eutrophication on the dinoflagellate-bearing benthic foraminifer Marginopora vertebralis. Coral Reefs 31:401–414. doi:10.1007/s00338-011-0851-2
van Dam JW, Negri AP, Mueller JF, Altenburger R, Uthicke S (2012) Additive pressures of elevated sea surface temperatures and herbicides on symbiont-bearing foraminifera. PLoS ONE 7:e33900. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0033900
Webster NS, Negri AP, Botté ES, Laffy PW, Flores F, Noonan S, Schmidt C, Uthicke S (2016) Host-associated coral reef microbes respond to the cumulative pressures of ocean warming and ocean acidification. Sci Rep UK 6:19324. http://www.nature.com/articles/srep19324#supplementary-information. doi:10.1038/srep19324
Weinmann AE, Rödder D, Lötters S, Langer MR (2013) Traveling through time: the past, present and future biogeographic range of the invasive foraminifera Amphistegina spp. in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar Micropaleontol 105:30–39. doi:10.1016/j.marmicro.2013.10.002
Weis VM (2010) The susceptibility and resilience of corals to thermal stress: adaptation, acclimatization or both? Mol Ecol 19:1515–1517. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2010.04575.x
Wickham H (2009) ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis. Springer, New York
Yilmaz P, Parfrey LW, Yarza P, Gerken J, Pruesse E, Quast C, Schweer T, Peplies J, Ludwig W, Glockner FO (2014) The SILVA and “all-species living tree project (LTP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D643–D648. doi:10.1093/nar/gkt1209
Yokes MB, Meric E, Avsa N (2007) On the presence of alien foraminifera Amphistegina lobifera Larsen on the coasts of the Maltese Islands. Aquat Invasions 2:439–441
Zenetos A, Gofas S, Morri C, Rosso A, Violanti D, Raso JEG, Cinar ME, Almogi-Labin A, Ates AS, Azzurro E, Ballesteros E, Bianchi CN, Bilecenoglu M, Gambi MC, Giangrande A, Gravili C, Hyams-Kaphzan O, Karachle PK, Katsanevakis S, Lipej L, Mastrototaro F, Mineur F, Pancucci-Papadopoulou MA, Espla AR, Salas C, San Martin G, Sfriso A, Streftaris N, Verlaque M (2012) Alien species in the Mediterranean Sea by 2012. A contribution to the application of European Union’s Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). Part 2. Introduction trends and pathways. Mediterr Mar Sci 13:328–352
Ziegler M, Uthicke S (2011) Photosynthetic plasticity of endosymbionts in larger benthic coral reef foraminifera. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 407:70–80. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2011.07.009
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the BMBF-MOST cooperation in Marine Sciences Grant No. 03F0639A, and the Ministry of Energy and Water Resources, Israel Grant No. 212-17-015 to MK; BH. The molecular work in the paper was supported by a grant of the Paul Brönnimann Foundation given to RM, MK, CS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors, CS, RM, MP, BH and MK, declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: F. T. Chan.
Reviewed by P. Hallock and an undisclosed expert.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Invasive Species.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, C., Morard, R., Prazeres, M. et al. Retention of high thermal tolerance in the invasive foraminifera Amphistegina lobifera from the Eastern Mediterranean and the Gulf of Aqaba. Mar Biol 163, 228 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-016-2998-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-016-2998-4