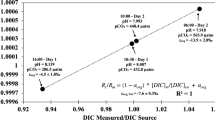
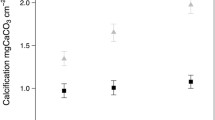
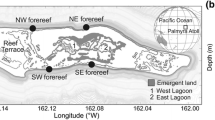
Abstract
Benthic marine primary producers affect the chemistry of their surrounding environment through metabolic processes. Photosynthesis and respiration will elevate or depress the concentration of oxygen in the diffusive boundary layer. Likewise, acid–base regulation and biomineralization/dissolution for calcifying species can alter the relative concentration of inorganic carbon species and thus pH. Here, we measured the relative ability of several common benthic primary producers from coral reef systems of the central Pacific and the Caribbean to simultaneously affect seawater oxygen concentration and pH values. Repeated measurements over a diel cycle confirmed that several primary producers substantially alter surrounding seawater chemistry over time. The majority of fleshy algae exhibited a stoichiometric ratio of oxygen to hydrogen ions not significantly different from one during daylight hours. In contrast, calcifiers exhibited significantly lower oxygen to hydrogen ion ratios that were unique for each species and were inversely correlated with known rates of calcification. These data provide the first quantitative estimates of the simultaneous influence of several species of benthic primary producers on water column oxygen concentrations and pH across different tropical reef systems. Finally, because more productive fleshy taxa have the potential to raise both oxygen and pH during the day to a greater extent than calcified species, our results suggest that some fleshy taxa may provide a buffering capacity to future ocean acidification scenarios.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen ED, Spence DHN (1981) The differential ability of aquatic plants to utilize the inorganic carbon supply in fresh waters. New Phytol 87:269–283
Anderson LA, Sarmiento JL (1994) Redfield ratios of remineralization determined by nutrient data analysis. Global Biogeochem Cycles 8:65–80. doi:10.1029/93gb03318
Anthony KRN, Kline DI, Diaz-Pulido G, Dove S, Hoegh-Guldberg O (2008) Ocean acidification causes bleaching and productivity loss in coral reef builders. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:17442–17446. doi:10.1073/pnas.0804478105
Anthony KRN, Kleypas JA, Gattuso JP (2011) Coral reefs modify their seawater carbon chemistry—implications for impacts of ocean acidification. Global Change Biol 17:3655–3666. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2011.02510.x
Axelsson L (1988) Changes in pH as a measure of photosynthesis by marine macroalgae. Mar Biol 97:287–294
Barnes DJ (1983) Profiling coral reef productivity and calcification using pH and oxygen electrodes. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 66:149–161. doi:10.1016/0022-0981(83)90036-9
Barnes DJ, Devereux MJ (1984) Productivity and calcification on a coral reef: a survey using pH and oxygen electrode techniques. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 79:213–231. doi:10.1016/0022-0981(84)90196-5
Barnes DJ, Lazar B (1993) Metabolic performance of a shallow reef patch near Eilat on the Red sea. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 174:1–13
Bates NR, Amat A, Andersson AJ (2009) The interaction of ocean acidification and carbonate chemistry on coral reef calcification: evaluating the carbonate chemistry coral reef ecosystem feedback (CREF) hypothesis on the Bermuda coral reef. Biogeosci Discuss 6:7627–7672
Bellwood DR, Hughes TP, Folke C, Nystrom M (2004) Confronting the coral reef crisis. Nature 429:827–833
Borowitzka MA, Larkum AWD (1976) Calcification in the green alga Halimeda IV: action of metabolic inhibitors on photosynthesis and calcification. J Exp Bot 27:894–907
Borowitzka MA, Larkum AWD (1987) Calcification in algae: mechanisms and the role of metabolism. Crit Rev Plant Sci 6:1–45
Bruno JF, Edmunds PJ (1998) Metabolic consequences of phenotypic plasticity in the coral Madracis mirabilis: the effect of morphology and water flow on aggregate respiration. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 229:187–195. doi:10.1016/s0022-0981(98)00050-1
Bruno JF, Selig ER (2007) Regional decline of coral cover in the Indo-Pacific: timing, extent, and subregional comparisons. PLoS ONE 2:e711
Carpenter RC, Hackney JM, Adey WH (1991) Measurements of primary productivity and nitrogenase activity of coral reef algae in a chamber incorporating oscillatory flow. Limnol Oceanogr 36:40–49
Coles SL, Jokiel P (1977) Effects of temperature on photosynthesis and respiration in hermatypic corals. Mar Biol (Berl) 43:209–216
Cook CM, Lanaras T, Roubelakis-Angelakis KA (1988) Bicarbonate transport and alkalization of the medium by four species of Rhodophyta. J Exp Bot 39:1185–1198
Cooper TF, De’Ath G, Fabricius KE, Lough JM (2008) Declining coral calcification in massive Porites in two nearshore regions of the northern great barrier reef. Global Change Biol 14:529–538. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2007.01520.x
Dennison WC, Barnes DJ (1988) Effect of water motion on coral photosynthesis and calcification. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 115:167–177
Edmunds PJ, Putnam HM, Nisbet RM, Muller EB (2011) Benchmarks in organism performance and their use in comparative analyses. Oecologia 167:379–390. doi:10.1007/s00442-011-2004-2
Frankignoulle M, Gattuso JP, Biondo R, Bourge I, CopinMontegut G, Pichon M (1996) Carbon fluxes in coral reefs II: eulerian study of inorganic carbon dynamics and measurement of air-sea CO2 exchanges. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 145:123–132. doi:10.3354/meps145123
Galzin R, Pointier JP (1985) Moorea Island, society archipelago 5th int coral reef congress. Tahiti, pp 73–101
Gates RD, Edmunds PJ (1999) The physiological mechanisms of acclimatization in tropical reef corals. Am Zool 39:30–43
Gattuso JP, Pichon M, Delesalle B, Canon C, Frankignoulle M (1996) Carbon fluxes in coral reefs I: lagrangian measurement of community metabolism and resulting air-sea CO2 disequilibrium. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 145:109–121. doi:10.3354/meps145109
Gattuso JP, Payri CE, Pichon M, Delesalle B, Frankignoulle M (1997) Primary production, calcification, and air-sea CO2 fluxes of a macroalgal-dominated coral reef community (Moorea, French Polynesia). J Phycol 33:729–738
Gattuso JP, Allemand D, Frankignoulle M (1999a) Photosynthesis and calcification at cellular, organismal and community levels in coral reefs: a review on interactions and control by carbonate chemistry. Am Zool 39:160–183
Gattuso JP, Frankignoulle M, Smith SV (1999b) Measurement of community metabolism and significance in the coral reef CO2 source-sink debate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13017–13022. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.23.13017
Gattuso JP, Pichon M, Jaubert J, Marchioretti M, Frankignoulle M (1996b) Primary production, calcification and air-sea CO2 fluxes in coral reefs: organism, ecosystem and global scales. Bull Inst Oceanogr (Monaco) 14(4):39–46
Haas AF, Wild C (2010) Composition analysis of organic matter released by cosmopolitan coral reef-associated green algae. Aquat Biol 10:131–138. doi:10.3354/ab00271
Haas AF, Nelson CE, Wegley Kelly L, Carlson CA, Rohwer F, Leichter JJ, Wyatt A, Smith JE (2011) Effects of coral reef benthic primary producers on dissolved organic carbon and microbial activity. PLoS One 6:e27973. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0027973
Hench JL, Leichter JJ, Monismith SG (2008) Episodic circulation and exchange in a wave-driven coral reef and lagoon system. Limnol Oceanogr 53:2681–2694
Hendriks IE, Duarte CM, Alvarez M (2010) Vulnerability of marine biodiversity to ocean acidification: a meta-analysis. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 86:157–164. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2009.11.022
Hoegh-Guldberg O, Mumby PJ, Hooten AJ, Steneck RS, Greenfield P, Gomez E, Harvell CD, Sale PF, Edwards AJ, Caldeira K, Knowlton N, Eakin CM, Iglesias-Prieto R, Muthiga N, Bradbury RH, Dubi A, Hatziolos ME (2007) Coral reefs under rapid climate change and ocean acidification. Science 318:1737–1742
Hofmann GE, Smith JE, Johnson KS, Send U, Levin LA, Micheli F, Paytan A, Price NN, Peterson B, Takeshita Y, Matson PG, Crook ED, Kroeker KJ, Gambi MC, Rivest EB, Frieder CA, Yu PC, Martz T (2011) High-frequency dynamics of ocean pH: a multi-ecosystem comparison. PLoS ONE 6:e28983. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0028983
Hughes TP, Baird AH, Bellwood DR, Card M, Connolly SR, Folke C, Grosberg R, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Jackson JB, Kleypas J, Lough JM, Marshall P, Nystrom M, Palumbi SR, Pandolfi JM, Rosen B, Roughgarden J (2003) Climate change, human impacts, and the resilience of coral reefs. Science 301:929–933
Hurd CL, Cornwall CE, Currie K, Hepburn CD, McGraw CM, Hunter KA, Boyd PW (2011) Metabolically induced pH fluctuations by some coastal calcifiers exceed projected 22nd century ocean acidification: a mechanism for differential susceptibility? Global Change Biol 17:3254–3262. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2011.02473.x
Israel A, Beer S (1992) Photosynthetic carbon acquisition in the red alga Gracilaria conferta. Mar Biol 112:697–700. doi:10.1007/bf00346189
Johannes RE, Alberts J, D’Elia C, Kinzie RA, Pomeroy LR, Sottile W, Wiebe W, Marsh JA Jr, Helfrich P, Maragos J, Meyer J, Smith S, Crabtree D, Roth A, McCloskey LR, Betzer S, Marshall N, Pilson MEQ, Telek G, Clutter RI, DuPaul WD, Webb KL, Wells JM Jr (1972) The metabolism of some coral reef communities: a team study of nutrient and energy flux at Eniwetok. Bioscience 22:541–543
Jokiel PL (2011) Ocean acidification and control of reef coral calcification by boundary layer limitation of proton flux. Bull Mar Sci 87:639–657. doi:10.5343/bms.2010.1107
Jokiel PL, Morrissey JI (1986) Influence of size on primary production in the reef coral Pocillopora damicornis and the macroalga Acanthophora spicifera. Mar Biol 91:15–26. doi:10.1007/bf00397566
Jokiel P, Rodgers K, Kuffner I, Andersson A, Cox E, Mackenzie F (2008) Ocean acidification and calcifying reef organisms: a mesocosm investigation. Coral Reefs 27:473–483. doi:10.1007/s00338-008-0380-9
Kaspar HF (1992) Oxygen conditions on surfaces of coralline red algae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 81:97–100
Kleypas JA, Anthony KRN, Gattuso JP (2011) Coral reefs modify their seawater carbon chemistry—case study from a barrier reef (Moorea, French Polynesia). Global Change Biol 17:3667–3678
Kroeker KJ, Kordas RL, Crim RN, Singh GG (2010) Meta-analysis reveals negative yet variable effects of ocean acidification on marine organisms. Ecol Lett 13:1419–1434. doi:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2010.01518.x
Lesser MP, Weis VM, Patterson MR, Jokiel PL (1994) Effects of morphology and water motion on carbon delivery and productivity in the reef coral, Pocillopora damicornis: diffusion barriers, inorganic carbon limitation, and biochemical plasticity. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 178:153–179. doi:10.1016/0022-0981(94)90034-5
Lindahl PEB (1963) The inhibition of the photosynthesis of aquatic plants by tetramethylthiuram disulphide. Symbolae Botanicae Upsaliensis 17:1–47
Littler MM, Arnold KE (1982) Primary productivity of marine macroalgal functional-form groups from southwestern North America. J Phycol 18:307–311. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8817.1982.tb03188.x
Littler MM, Littler DS (1980) The evolution of thallus form and survival strategies in benthic marine macroalgae: field and laboratory tests of a functional form model. Am Nat 116:25–44
Lough JM, Barnes DJ (2000) Environmental controls on growth of the massive coral Porites. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 245:225–243. doi:10.1016/s0022-0981(99)00168-9
Lucas WJ (1983) Photosynthetic assimilation of exogenous HCO3 by aquatic plants. Annu Rev of Plant Physiol 34:71–104. doi:10.1146/annurev.pp.34.060183.000443
Maberly SC, Spence DHN (1983) Photosynthetic inorganic carbon use by freshwater plants. J Ecol 71:705–724
Marsh JA Jr (1970) Primary productivity of reef-building calcareous red algae. Ecology 51:255–263
Mass T, Genin A, Shavit U, Grinstein M, Tchernov D (2010) Flow enhances photosynthesis in marine benthic autotrophs by increasing the efflux of oxygen from the organism to the water. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:2527–2531. doi:10.1073/pnas.0912348107
McCloskey LR, Muscatine L (1984) Production and respiration in the Red Sea coral Stylophora pistillata as a function of depth. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol 222:215–230. doi:10.1098/rspb.1984.0060
McCook LJ, Jompa J, Diaz-Pulido G (2001) Competition between corals and algae on coral reefs: a review of evidence and mechanisms. Coral Reefs 19:400–417
Miller RJ, Reed DC, Brzezinski MA (2009) Community structure and productivity of subtidal turf and foliose algal assemblages. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 388:1–11. doi:10.3354/meps08131
Muller EB, Kooijman S, Edmunds PJ, Doyle FJ, Nisbet RM (2009) Dynamic energy budgets in syntrophic symbiotic relationships between heterotrophic hosts and photoautotrophic symbionts. J Theor Biol 259:44–57. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2009.03.004
Murphy S, Gardner FH (1975) Platelet storage at 22 degrees C: role of gas transport across plastic containers in maintenance of viability. Blood 46:209–218
Murru M, Sandgren CD (2004) Habitat matters for inorganic carbon acquisition in 38 species of red macroalgae (Rhodophyta) from Puget Sound, Washingto, USA. J Phycol 40:837–845. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8817.2004.03182.x
Naumann M, Niggl W, Laforsch C, Glaser C, Wild C (2009) Coral surface area quantification–evaluation of established techniques by comparison with computer tomography. Coral Reefs 28:109–117. doi:10.1007/s00338-008-0459-3
Naumann M, Haas A, Struck U, Mayr C, el-Zibdah M, Wild C (2010) Organic matter release by dominant hermatypic corals of the Northern Red Sea. Coral Reefs 29:649–659. doi:10.1007/s00338-010-0612-7
Niggel W, Haas AF, Wild C (2010) Benthic community composition affects O2 availability and variability in a Northern Red Sea fringing reef. Hydrobiologia 644:401–405
Nyström M, Folke C, Moberg F (2000) Coral reef disturbance and resilience in a human-dominated environment. Trends Ecol Evol 15:413–417. doi:10.1016/s0169-5347(00)01948-0
Ohde S, van Woesik R (1999) Carbon dioxide flux and metabolic processes of a coral reef, Okinawa. Bull Mar Sci 65:559–576
Price NN, Hamilton SL, Tootell JS, Smith JE (2011) Species-specific consequences of ocean acidification for the calcareous tropical green algae Halimeda. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 440:67–78. doi:10.3354/meps09309
Price NN, Martz TR, Brainard RE, Smith JE (2012) Diel variability in seawater pH relates to calcification and benthic community structure on coral reefs. PLoS One 7. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0043843
Prins HBA, Elzenga JTM (1989) Bicarbonate utilization: function and mechanism. Aquat Bot 34:59–83. doi:10.1016/0304-3770(89)90050-8
Raven JA (1997) Inorganic carbon acquisition by marine autotrophs. In: Callow JA (ed) Advances in botanical research. Academic Press, New York, pp 85–209
Roffman B (1968) Patterns of oxygen exchange in some Pacific corals. Comp Biochem Physiol 27:405–418. doi:10.1016/0010-406x(68)90239-9
Russo AR (1990) The role of seaweed complexity in structuring Hawaiian epiphytal amphipod communities. Hydrobiologia 194:1–12. doi:10.1007/bf00012107
Shamberger KEF, Feely RA, Sabine CL, Atkinson MJ, DeCarlo EH, Mackenzie FT, Drupp PS, Butterfield DA (2011) Calcification and organic production on a Hawaiian coral reef. Mar Chem 127:64–75. doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2011.08.003
Shashar N, Cohen Y, Loya Y (1993) Extreme diel fluctuations of oxygen in diffusive boundary layers surrounding stony corals. Biol Bull 185:455–461
Shashar N, Kinane S, Jokiel PJ, Patterson MR (1996) Hydromechanical boundary layers over a coral reef. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 199:17–28
Smith SV (1973) Carbon dioxide dynamics: a record of organic carbon production, respiration, and calcification in the Eniwetok reef flat community. Limnol Oceanogr 18:106–120
Valiela I (1984) Marine ecological processes. Springer, New York
van Duyl FC, Scheffers SR, Thomas FIM, Driscoll M (2006) The effect of water exchange on bacterioplankton depletion and inorganic nutrient dynamics in coral reef cavities. Coral Reefs 25:23–36
Wild C, Niggel W, Naumann MS, Haas AF (2010) Organic matter release by Red Sea coral reef organisms—potential effects on microbial activity and in situ O2 availability. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 411:61–71. doi:10.3354/meps08653
Wilkinson C (2008) Status of coral reefs of the world: 2008. In: Wilkinson C (ed) Coral reefs. Global Coral Reef Monitoring Network and Reef and Rainforest Research Centre, Townsville, Australia p 296
Wu EY, Barazanji KW, Johnson RLJ (1997) Sources of error in Α-aD-O2 calculated from blood stored in plastic and glass syringes. J Appl Physiol 82:196–202
Zeebe RE, Wolf-Gladrow DA, Jansen H (1999) On the time required to establish chemical and isotopic equilibrium in the carbon dioxide system in seawater. Mar Chem 65:135–153
Acknowledgments
We thank the entire staff of the Richard B. Gump South Pacific Research Station in Moorea. The Moorea Coral Reef Long-Term Ecological Research (MCR-LTER) project (US NSF OCE-0417412) provided field and laboratory logistical support. We further thank the entire staff of the CARMABI research station in Curaçao and especially Dr. M. Vermeij for logistical support. We would like to specifically thank A. Gregg, F. L Rohwer and L. Wegley Kelly for their help during the field research and the Smith and Sandin laboratories at SIO for comments on the manuscript. This research was supported by the United States National Science Foundation (NSF) awards OCE-0927415 to F. Rohwer, OCE-0927411 to C. A. Carlson, and OCE-0927448 to J. E. Smith and J. J. Leichter and grants from the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation to J. E. Smith, T. R. Martz, and R. Dunbar.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by R. Hill.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, J.E., Price, N.N., Nelson, C.E. et al. Coupled changes in oxygen concentration and pH caused by metabolism of benthic coral reef organisms. Mar Biol 160, 2437–2447 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-013-2239-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-013-2239-z