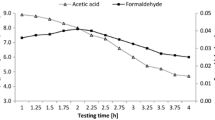
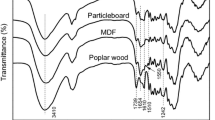
Abstract
This work examines the performance of three formaldehyde scavengers in wood-based panels. Sodium metabisulfite, ammonium bisulfite and urea were applied in different physical forms during particleboard production, and the resulting physico-mechanical properties (internal bond strength, thickness swelling, density and moisture content) and formaldehyde emission levels were compared. Formaldehyde content was measured using the perforator method, and formaldehyde emission was evaluated both by desiccator and gas analysis methods. The chemical reactions involved in each formaldehyde scavenging process are proposed and discussed. The tested scavengers showed distinct performances under the different emission testing conditions, which were interpreted in terms of the stability of the chemical compounds formed upon formaldehyde capture. Sodium metabisulfite proved to be an excellent scavenger for all formaldehyde methods allowing the production of particleboard panels with zero formaldehyde emission.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amazio P, Avella M, Errico ME, Gentile G, Balducci F, Gnaccarini A, Moratalla J, Belanche M (2011) Low formaldehyde emission particleboard panels realized through a new acrylic binder. J Appl Polym Sci 122(4):2779–2788
Barberá JJ, Metzger A, Wolf M (2000) Sulfites, thiosulfates, and dithionites. Ullmann’s encyclopedia of industrial chemistry. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim
Boran S, Usta M, Gümüskaya E (2011) Decreasing formaldehyde emission from medium density fiberboard panels produced by adding different amine compounds to urea formaldehyde resin. Int J Adhes Adhes 31(7):674–678
Carvalho L, Martins J, Costa C (2010) Transport phenomena. In: Thoemen H, Irle M, Sernek M (eds) Wood-based panels: an introduction for specialists. Brunel University Press, London, pp 123–176
Costa N, Pereira J, Martins D, Martins J, Ferra J, Cruz P, Magalhães F, Mendes A, Carvalho L (2011) Innovative catalysts for urea-formaldehyde resins. In: Caldeira F (ed) Minimizing the environmental impact of the forest products industries. University Fernando Pessoa, Porto
Costa N, Pereira J, Ferra J, Cruz P, Martins J, Magalhães F, Mendes A, Carvalho L (2012a) Sodium metabisulfite as scavenger of air pollutants in wood based building materials. Int Wood Prod J. doi:10.1179/2042645313Y.0000000037
Costa N, Pereira J, Martins J, Ferra J, Cruz P, Magalhães F, Mendes A, Carvalho L (2012b) Alternative to latent catalysts for curing UF resins used in the production of low formaldehyde emission wood-based panels. Int J Adhes Adhes 33:56–60
Despres A, Pizzi A, Vu C, Delmotte L (2010) Colourless formaldehyde-free urea resin adhesives for wood panels. Eur J Wood Prod 68(1):13–20
Dongbin F, Jianzhang L, An M (2006) Curing characteristics of low molar ratio urea-formaldehyde resin. J Adhes Interface 7(4):45–52
Dreyfors JM, Jones SB, Sayed Y (1989) Hexamethylenetetramine—a review. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 50(11):579–585
Dunky M (1998) Urea-formaldehyde (UF) adhesive resins for wood. Int J Adhes Adhes 18(2):95–107
Dunky M, Grunwald D, Haelvoet W (2001) Emission. In: Johansson C-J, Pizzi T, Leemput MV (eds) COST action E13: wood adhesion and glued products, working group 2: glued wood products, state of the art report
Eom Y-G, Kim J-S, Kim S, Kim J-A, Kim H-J (2006) reduction of formaldehyde emission from particleboards by bio-scavengers. Mokchae Konghak 34:29–41
Gerrans GC, Hartmann-Petersen P, Hartmann-Petersen R (2004) Encyclopaedia of science and technology, New Africa Books, South Africa, p 129
Gunnells D, Griffin K (1998) Catalyst systems. In: Bradfield J (ed) Resin and blending seminar proceedings, Portland, Oregon and Charlotte, North Carolina. For Prod Soc, p 176
IARC (2006) Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risk to humans, vol 88. World Health Organization—International Agency For Research On Cancer
Kim S (2009) The reduction of indoor air pollutant from wood-based composite by adding pozzolan for building materials. Constr Build Mater 23(6):2319–2323
Kim S, Kim HJ (2005) Comparison of standard methods and gas chromatography method in determination of formaldehyde emission from MDF bonded with formaldehyde-based resins. Bioresour Technol 96(13):1457–1464
Kim S, Kim HJ, Kim HS, Lee HH (2006) Effect of bio-scavengers on the curing behavior and bonding properties of melamine-formaldehyde resins. Macromol Mater Eng 291(9):1027–1034
Lehmann WF (1983) Method and composition for reduction of formaldehyde emission in wood composite panels. US patent 4397756
Meyer B, Boehme C (1997) Formaldehyde emission from solid wood. Forest Prod J 47(5):45–48
Miller FP, Vandome AF, McBrewster J (2009) Kraft process. VDM Publishing House Ltd, Germany, pp 1–72
Myers GE (1984) How mole ratio of uf resin affects formaldehyde emission and other properties—a literature critique. For Prod J 34(5):35–41
Park BD, Kang EC, Park JY (2008) Thermal curing behavior of modified urea-formaldehyde resin adhesives with two formaldehyde scavengers and their influence on adhesion performance. J Appl Polym Sci 110(3):1573–1580
Park B-D, Kang E-C, Park S-B, Park J (2011) Empirical correlations between test methods of measuring formaldehyde emission of plywood, particleboard and medium density fiberboard. Eur J Wood Prod 69(2):311–316
Pizzi A, Mittal KL (1994) Handbook of adhesive technology. M. Dekker, New York
Que Z, Furuno T (2007) Formaldehyde emission from wood products: relationship between the values by the chamber method and those by the desiccator test. Wood Sci Technol 41(3):267–279
Risholm-Sundman M, Larsen A, Vestin E, Weibull A (2007) Formaldehyde emission—comparison of different standard methods. Atmos Environ 41(15):3193–3202
Salem MZM, Bohm M, Barcik S, Berankova J (2011a) Formaldehyde emission from wood-based panels bonded with different formaldehyde-based resins. Drvna Ind 62(3):177–183
Salem MZM, Böhm M, Beránková J, Srba J (2011b) Effect of some manufacturing variables on formaldehyde release from particleboard: relationship between different test methods. Build Environ 46(10):1946–1953
Salem MZM, Böhm M, Srba J, Beránková J (2012) Evaluation of formaldehyde emission from different types of wood-based panels and flooring materials using different standard test methods. Build Environ 49:86–96
Tang L, Zhang ZG, Qi J, Zhao JR, Feng Y (2011) The preparation and application of a new formaldehyde-free adhesive for plywood. Int J Adhes Adhes 31(6):507–512
Walker JF (1944) Formaldehyde. American Chemical Society monograph series. Waverly Press, New York
Acknowledgments
This work is co-founded by FEDER (Fundo Europeu de Desenvolvimento Regional)/QREN (E0_formaldehyde project with reference FCOMP010202FEDER005347) and national funds through FCT (project PTDC/EQU–EQU/111571/2009) under the framework of COMPETE-Programa Operacional Factor de Competitividade (POFC). The authors wish to thank Euroresinas and Sonae Indústria PCDM for providing the equipment and raw materials needed for this work. Nuno Costa wishes to thank FCT/MCTES for PhD grant SFRH/BDE/33655/2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa, N.A., Pereira, J., Ferra, J. et al. Scavengers for achieving zero formaldehyde emission of wood-based panels. Wood Sci Technol 47, 1261–1272 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-013-0573-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-013-0573-4