Abstract
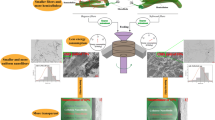
Nanofibers (NF) were isolated from bleached bagasse and rice straw pulps. The pulps were refined using high-shear ultrafine grinder and then homogenized using high-pressure homogenizer. The efficiency of the used isolation processes was studied by optical microscopy (OM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and testing the tensile properties (wet and dry) of nanopaper sheets made from the nanofibers. In addition, opacity and porosity of nanopaper sheets made after different processing steps were investigated. The microscopy studies showed that the processes used resulted in nanofibers with diameters ranging from 3.5 to 60 nm. The results indicated that main isolation of nanofibers took place during refining using the ultrafine grinding process, while high-pressure homogenization resulted in smaller and more homogeneous size of nanofibers. Nanopaper sheets made from bagasse showed better wet and dry tensile strength properties than those made of rice straw.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alemdar A, Sain M (2008) Isolation and characterization of nanofibers from agricultural residues–Wheat straw and soy hulls. Bioresources Technology 99:1664–1671
Bhatnagar A, Sain M (2005) Processing of cellulose nanofibers reinforced composites. J Reinf Plast Compos 24:1259–1268
Bondeson D, Mathew A, Oksman K (2006) Optimization of the isolation of nanocrystals from microcrystalline cellulose by acid hydrolysis. Cellulose 13:171–180
Chakraborty A, Sain M, Kortschot M (2005) Cellulose microfibrils: a novel method of preparation using high shear refining and cryocrushing. Holzforschung 59:102–107
Chen G, Liu G (2008) Electrospun cellulose nanofiber reinforced soybean protein isolate composite film. J Appl Polym Sci 110:641–646
Czaja WK, Young DJ, Kawecki M, Brown RM (2007) The future prospects of microbial cellulose in biomedical applications. Biomacromolecules 8:1–12
English B, Chow P, Bajwa DS (1997) Processing into composites. In: Rowell MR, Young RA, Rowell JK (eds) Paper and composites from agro-based resources. CRC Lewis Publishers, New York, pp 269–297
Fengel D, Wegener G (1989) Wood: Chemistry Ultrastructure Reactions. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin
Hans JS, Rowell JS (1997) Chemical composition of fibers. In: Rowell MR, Young RA, Rowell JK (eds) Paper and composites from agro-based resources. CRC Lewis Publishers, New York, pp 83–134
Henriksson M, Henriksson G, Berglund LA, Lindström T (2007) An environmentally friendly method for enzyme-assisted preparation of microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) nanofibers. Eur Polym J 43:3434–3441
Iwamoto S, Nakagaito AN, Yano H, Nogi M (2005) Optically transparent composites reinforced with plant fibers- based nanofibers. Appl Phys 81:1109–1112
Iwamoto S, Abe K, Yano H (2008) The effect of hemicelluloses on wood pulp nanofibrillation and nanofiber network characteristics. Biomacromolecules 9:1022–1026
Iwatake A, Nogi M, Yano H (2008) Cellulose nanofiber-reinforced polylactic acid. Compos Sci Technol 68:2103–2106
Kim C-W, Kim D-S, Kang S-Y, Marquez M, Joo YL (2006) Structural studies of electrospun cellulose nanofibers. Polymer 47:5097–5107
Klemm D, Schumann D, Udhardt U, Marsch S (2001) Bacterial synthesized cellulose–artificial blood vessels for microsurgery. Prog Polym Sci 26:1561–1603
Klemm D, Heublein B, Fink H-P, Bohn A (2005) Cellulose: fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:3358–3393
Kulpinski P (2005) Cellulose nanofibers prepared by the N-Methylmorpholine-N-oxide method. J Appl Polym Sci 98:1855–1859
Lönnberg H, Fogelström L, Samir S, Berglund L, Malmström E, Hult A (2008) Surface grafting of microfibrillated cellulose with poly(ε-caprolactone). Synthesis and characterization. Eur Polym J 44:2991–2997
López-Rubio A, Lagaron JM, Ankerforsx T, Lindström T, Nordqvist D, Mattozzi A, Hedenqvist MS (2007) Enhanced film forming and film properties of amylopectin using micro-fibrillated cellulose. Carbohydr Polym 68:718–727
Nakagaito AN, Yano H (2004) Novel high-strength biocomposites based on microfibrillated cellulose having nano-order-unit web-like network structure. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 80:155–159
Pääkkö M, Ankerfors M, Kosonen H, Nykänen A, Ahola S, Österberg M, Ruokolainen J, Laine J, Larsson PT, Ikkala O, Lindström T (2007) Cellulose nanopaper structure of high toughness. Biomacromolecules 8:1934–1941
Rials TG, Wolcott MP (1997) Physical and mechanical properties of Agro-based fibers. In: Rowell MR, Young RA, Rowell JK (eds) Paper and composites from agro-based resources. CRC Lewis Publishers, New York, pp 63–79
Samir MA, Alloin F, Dufresne A (2005) Review of recent research into cellulosic whiskers, their properties and their application in nanocomposites field. Biomacromolecules 6:612–626
Shimazaki Y, Miyazaki Y, Takezawa Y, Nogi M, Abe K, Ifuku S, Yano H (2007) Excellent thermal conductivity of transparent cellulose nanofiber/epoxy resin nanocomposites. Biomacromolecules 8:2976–2978
Subramanian R, Knononov A, Kang T, Paltakari J, Paulapura H (2008) Structure and properties of some natural cellulosic fibrils. Bioresources 3:192–203
Svagan AJ, Samir MA, Berglund LA (2007) Biomimetic polysaccharide nanocomposites of high cellulose content and high toughness. Biomacromolecules 8:2556–2563
Taniguchi T, Okamura K (1998) New films produced from microfibrillated natural fibres. Polym Int 47:291–294
Turbak AF, Snyder FW, Sandberg KR (1983) Microfibrillated cellulose, a new cellulose product: properties, uses, and commercial potential. J Appl Polym Sci: Appl Polym Symp, 37 Proc. Cellul. Conf., 9th, 1982, Part 2, 815–827
Wise LE, Murphy M, D’Addieco AA (1946) Chlorite holocellulose, its fractionation and bearing on summative wood analysis and on studies on hemicellulose. Paper Trade J 122:35–43
Yano H, Sugiyama J, Nakagaito AN, Nogi M, Matsuura T, Hikita M, Handa K (2005) The effect of hemicelluloses on wood pulp nanofibrillation and nanofiber network characteristics. Adv Mater 17:153–155
Young RA (1997) Processing of agro-based resources into pulp and paper. In: Rowell MR, Young RA, Rowell JK (eds) Paper and composites from agro-based resources. CRC Lewis Publishers, New York, pp 137–245
Zhao H-P, Feng X-Q, Gao H (2007) Ultrasonic technique for extracting nanofibers from natural materials. Appl Phys Lett 90:073112
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank SIDA for the financial support of the collaboration between Luleå University of Technology, Sweden and National Research Center, Dokki, Cairo, Egypt.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, M.L., Mathew, A.P., Hassan, E.A. et al. Nanofibers from bagasse and rice straw: process optimization and properties. Wood Sci Technol 46, 193–205 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-010-0373-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-010-0373-z