Abstract
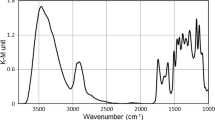
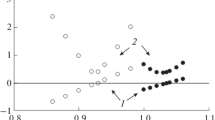
The validity of the Kubelka–Munk (K-M) theory was investigated to determine the IR absorption spectra of wood based on diffuse reflection infrared Fourier transform (DRIFT) measurements taken on photodegraded samples. After analysing plenty of DRIFT spectra of wood and examining the shape of the K-M equation, it can be concluded that the measured K-M function can be used as an absorption spectrum if the values of the function are below 14 K-M units. Above this limit, the K-M theory, which was created for poorly absorbing materials, does not give the absorption of wood properly. If a matt aluminium plate is used as a background material and the values are between 14 and 40, absorption changes can be calculated after normalisation of the spectra. This normalising manipulation is only successful if there is an absorption peak close to the examined one which does not change its absorption during the photodegradation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldock JA, Smernik RJ (2002) Chemical composition and bioavailability of thermally altered Pinus resinosa (Red pine) wood. Org Geochem 33:1093–1109
Barta E, Papp G, Preklet E, Tolvaj L, Berkesi O, Nagy T, Szatmári S (2005) Changes of absorption in infrared spectra of softwood materials irradiated by UV-laser as a function of energy. Acta Silvatica et Lignaria Hungarica 1(1):83–91 (http://www.aslh.nyme.hu/)
Berben SA, Rademacher JP, Sell LO, Easy DB (1987) Estimation of lignin in wood pulp by diffuse reflectance fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Tappi J 70:129–131
Bouchard J, Douek M (1993) Structural and concentration effects on the diffuse reflectance FTIR spectra of cellulose, lignin and pulp. J Wood Chem Technol 13:481–499
Chang ST, Wu CL, Wang SY, Chang HT (1998) Influence of concentration and particle size on the DRIFT spectroscopy of wood. Taiwan J For Sci 13:1–18
Craciun R, Kamdem PD (1997) XPS and FTIR applied to the study of waterborne copper naphthenate wood preservatives. Holzforschung 51:207–213
Cui W, Kamdem D, Rypstra T (2004) Diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFT) and color changes of artificial weathered wood. Wood Fiber Sci 36:291–301
Faix O, Böttcher JH (1992) The influence of particle size and concentration in transmission and diffuse reflectance spectroscopy of wood. Holz Roh Werkst 50:221–226
Faix O, Németh K (1988) Monitoring of wood photodegradation by DRIFT-spectroscopy. Holz Roh Werkst 46:112
Ferraz A, Baeza J, Rodriguez J, Freer J (2000) Estimating the chemical composition of biodegraded pine and eucalyptus wood by DRIFT spectroscopy and multivariate analysis. Bioresource Technol 74:201–212
Forsskåhl I, Janson J (1995) Sequential treatment of mechanical and chemimechanical pulps with light and heat. Part 2. FTIR and UV-VIS absorption-scattering spectra. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 7:48–54
Freer J, Ruiz J, Peredo MA, Rodriguez J, Baeza J (2003) Estimating the density and pulping yield of E-globulus wood by DRIFT-MIR spectroscopy and principal components regression (PCR). J Chilean Chem Soc 48:19–22
Hembree DM, Smyrl HR (1989) Anomalous dispersion effects in diffuse reflectance infrared fourier transform spectroscopy: a study of optical geometries. Appl Spectrosc 43:267–274
Holmgren A, Bergström B, Gref R, Ericsson A (1999) Detection of pinosylvins in solid wood of scots pine using fourier transform raman and infrared spectroscopy. J Wood Chem Technol 19:139–150
Hon DNS, Feist WC (1986) Weathering characteristics of hardwood surfaces. Wood Sci Technol 20:169–183
Hon DNS, Ifju G (1978) Measuring penetration of light into wood by detection of photo-induced free radicals. Wood Sci 11:118–127
Horn BA, Qiu J, Owen NL, Feist WC (1994) FT-IR studies of weathering effects in western redcedar and southern pine. Appl Spectrosc 48:662–668
Jones HG, Heitner C (1973) Optical measurement of absorption and scattering properties of wood using the Kubelka-Munk equations. Pulp Pap Mag Can 74:T182–T186
Kataoka Y, Kiguchi M (2001) Depth profiling of photo-induced degradation in wood by FT-IR microspectroscopy. J Wood Sci 47:325–327
Kataoka Y, Kiguchi M, Evans PD (2004) Photodegradation depth profile and penetration of light in Japanese cedar earlywood (Criptomeria japonica D. Don) exposed to artificial solar radiation. Surf Coatings Int Part B-coatings Trans 87(3):187–193
Kataoka Y, Kiguchi M, Fujiwara T, Evans PD (2005) The effects of within-species and between-species variation in wood density on the photodegradation depth profiles of sugi (Cryptomeria japonica) and hinoki (Chamaecyparis obtusa). J Wood Sci 51(5):531–536
Kataoka Y, Kiguchi M, Williams RS, Evans PD (2007) Violet light causes photodegradation of wood beyond the zone affected by ultraviolet radiation. Holzforschung 61(1):23–27
Kishino M, Nakano T (2004) Artificial weathering of tropical woods. Part 1: Changes in wettability. Holzforschung 58:552–557
Kosikova B, Tolvaj L (1998) Structural changes of lignin- polysaccharide complex during photodegradation of Populus grandis. Drev Vysk 43:37–46
Kubelka PJ (1948) New contributions to the optics of intensely light-scattering materials. Part I. J Opt Soc Am 38:448–457
Kubelka PJ, Munk F (1931) Ein Beitrag zur Optik der Farbanstriche. Zeitschrift für Technische Physik 11a:593–601
Michell AJ (1991) An anomalous effect in the DRIFT spectra of woods and papers. J Wood Chem Technol 11:33–40
Michell AJ, Nelson PJ, Chin CWJ (1989) Diffuse reflectance spectroscopic studies of the bleaching and yellowing of eucalyptus regnans cold soda pulp. Appita J 42:443–448
Mitsui K, Tsuchikawa S (2005) Low atmospheric temperature dependence on photodegradation of wood. J Photochem Photobiol B: Biol 81:84–88
Mitsui K, Murata A, Tolvaj L (2003) Investigation of the change in the DRIFT spectra of light-irradiated wood with heat treatment. Holz Roh Werkst 61:82
Moore AK, Owen NL (2001) Infrared spectroscopic studies of solid wood. Appl Spectrosc Rev 36:65–86
Müller U, Rätzsch M, Schwanninger M, Steiner M, Zöbl H (2003) Yellowing and IR-changes of spruce wood as result of UV-irradiation. J Photochem Photobiol B: Biol 69:97–105
Nuopponen MH, Birch GM, Sykes RJ, Lee SJ, Stewart D (2006) Estimation of wood density and chemical composition by means of diffuse reflectance mid-infrared Fourier transform (DRIFT-MIR) spectroscopy. J Agric Food Chem 54:34–40
Ohkoshi MJ (2002) FTIR-PAS study of light-induced changes in the surface of acetylated or polyethylene glycol-impregnated wood. J Wood Sci 48:394–401
Owen NL, Pawlak Z (1989) An infrared study of the effect of liquid ammonia on wood surfaces. J Mol Struct 198:435–449
Owen NL, Thomas DW (1989) Infrared studies of “Hard” and “Soft” woods. Appl Spectrosc 43:451–455
Pandey KK (1999) A study of chemical structure of soft and hardwood and wood polymers by FTIR spectroscopy. J Appl Polym Sci 71:1969–1975
Pandey KK (2005) Study of the effect of photo-irradiation on the surface chemistry of wood. Polym Degr Stab 90:9–20
Pandey KK, Khali DP (1998) Accelerated weathering of wood surfaces modified by chromium trioxide. Holzforschung 52(5):467–471
Pandey KK, Theagarajan KS (1997) Analysis of wood surfaces and ground wood by diffuse reflectance (DRIFT) and photoacustic (PAS) Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic techniques. Holz Roh Werkst 55:383–390
Papp G, Barta E, Tolvaj L, Berkesi O, Nagy T, Szatmári S (2005) Changes in DRIFT spectra of wood irradiated by UV laser as a function of energy. J Photochem Photobiol A: Chem 173(2):137–142
Ristolainen M, Alén R, Malkavaara P, Pere J (2002) Reflectance FTIR microspectroscopy for studying effect of xylan removal on unbleached and bleached birch kraft pulp. Holzforschung 56(5):513–521
Shen J, Zhou JQ, Vazquez O (2000) Experimental study of optical scattering and fiber orientation determination of softwood and hardwood with different surface finishes. Appl Spectrosc 54:1793–1804
Stewart D, Wilson HM, Hendra PJ, Morrison IM (1995) Fourier-transform infrared and raman-spectroscopic study of biochemical and chemical treatments of oak wood (Quercus-Rubra) and barley (Hordeum-Vulgare) straw. J Agric Food Chem 43:2219–2225
Sudiyani Y, Imamura Y, Doi S, Yamauchi S (2003) Infrared spectroscopic investigations of weathering effects on the surface of tropical wood. J Wood Sci 49:86–92
Takei T, Hamajima M, Kamba N (1997) Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic analysis of the degradation of structural lumber in Horyi-ji temple. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 43:285–294
Toivanen TJ, Alen R (2007) A.FTIR/PLS method for determining variations in the chemical composition of birch (Betula pendula/B-publescens) stem wood. Appita J 60:155–160
Tolvaj L, Faix O (1995) Artifical ageing of wood monitored by DRIFT spectroscopy and CIE L*a*b* color measurements. I. Effect of UV light. Holzforschung 49:397–404
Tolvaj L, Mitsui K (2004) Surface preparation and direction dependence of DRIFT spectra of wood. Appl Spectrosc 58:1137–1140
Tolvaj L, Mitsui K (2005) Light source dependence of the photodegradation of wood. J Wood Sci 51:468–473
Umemura K, Yamauchi H, Ito T, Shibata M, Kawai S (2008) Durability of isocyanate resin adhesives for wood V: changes of color and chemical structure in photodegradation. J Wood Sci 54:289–293
Vane CH (2003) Monitoring decay of black gum wood (Nyssa sylvatica) during growth of the shiitake mushroom (Lentinula edodes) using diffuse reflectance infrared spectroscopy. Appl Spectrosc 57:514–517
Weiland JJ, Guyonnet R (2003) Study of chemical modifications and fungi degradation of thermally modified wood using DRIFT spectroscopy. Holz Roh Werkst 61:216–220
Zanuttini M, Citroni M, Martinez MJ (1998) Application of diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy to the quantitative determination of acetyl groups in wood. Holzforschung 52:263–267
Zavarin E, Jones SJ, Cool LG (1990) Analysis of solid wood surfaces by diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform (DRIFT) spectroscopy. J Wood Chem Technol 10:495–513
Zhang J, Kamdem DP (2000) FTIR characterization of cooper ethanilamine–wood interaction for wood preservation. Holzforschung 54(2):119–122
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tolvaj, L., Mitsui, K. & Varga, D. Validity limits of Kubelka–Munk theory for DRIFT spectra of photodegraded solid wood. Wood Sci Technol 45, 135–146 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-010-0314-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-010-0314-x