Abstract
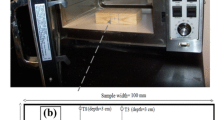
A standard X-ray source and an energy-sensitive detector were placed on both sides of a wood dryer which operates over a wide range of drying conditions. The spectrometric X-ray intensities transmitted through the wood sample were related to the mass concentration of wood and water using a rigorous calculation needed in the case of a polychromatic X-ray beam. The source and the detector are carried by a motion controller in order to scan the sample at different drying times and determine the moisture content (MC) profile along the board thickness. Treatment on spectrometric data and the evolution of the MC profiles in a Norway spruce board (Picea abies) are presented in this work.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bentz D, Hansen K (2000) Preliminary observations of water movement in cement pastes during curing using X-ray absorption. Cement Concrete Res 30(7):1157–1168
Davis J, Ilic J, Wells P (1993) Moisture content in drying wood using direct scanning gamma-ray densitometry. Wood Fiber Sci 25(2):153–162
Hu J, Stroeven P (2003) X-ray absorption study of drying cement paste and mortar. Cement Concrete Res 33:397–403
Jensen S, Damkilde L, Krabbenhoft K (2002) Non-destructive assessment and FEM simulations of moisture profiles in Sitka Spruce (Picea sitchensis) during drying. In: Proceeding of the 3rd European COST E15 Workshop on wood drying, 11–13 June. Helsinki, Finland
Lindgren L (1991) Medical CAT-scanning: X-ray absorption coefficients, CT-numbers and their relation to wood density. Wood Sci Technol 25:341–349
Pang S, Wiberg P (1998) Model predicted and CT scanned moisture distribution in a Pinus radiata board during drying. Holz Roh Werkst 56: 9–14
Perré P, Turner I (1996) Using a set of macroscopic equations to simulate heat and mass transfer in porous media: some possibilities illustrated by a wide range of configurations that emphasize the role of internal pressure. In: Turner I, Mujumdar A (eds) Numerical methods and mathematical modelling of the drying process. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 83–156
Perré P, Turner I (1999) TransPore: a generic heat and mass transfer computational model for understanding and visualizing the drying of porous media. Drying Technol 17 (7–8):1273–1290
Perré P, Thiercelin F, Aguiar O (2000) Prototype high temperature/high pressure kiln for the evaluation of wood drying schedules. Drying Technol 18(8):1849–1863
Rémond R (2004) Approche déterministe du séchage des avivés de résineux de fortes épaisseurs pour proposer des conduites industrielles adaptées. Doctoral Thesis. ENGREF. Nancy, France
Rémond R, Mougel E, Perré P (2005) The existence of a thin dry layer during convective drying as possible explanation of the evolution of thickness, temperature and moisture content of Norway Spruce boards. Drying Technol (in press)
Rosenkilde A, Glover P (2002) High resolution measurement of the surface layer moisture content during drying of wood using a novel magnetic resonance imaging technique. Holzforschung 56:312–317
Salin J (2002) Theoretical analysis of mass transfer from wooden surfaces. In: Proceeding of the 13th international drying symposium, 27–30 August. Beijing, pp 1826–1834
Wiberg P, Morén T (1999) Moisture flux determination in wood during drying above fibre saturation point using CT-scanning and digital image processing. Holz Roh Werkst 57:137–144
Wiberg P, Sehlstedt S, Morén T (2000) Heat and mass transfer during sapwood drying above the fibre saturation point. Drying Technol 18(8):1647–1664
Williams KL (1987) An introduction to X-ray spectrometry. Allen& Unwin, London
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the “French Ministry for Agriculture and Fisheries” for funding one part of this work in the framework of the research project no 61.45.39/01 entitled “Development of drying schedules adapted to large thickness of spruce lumber”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baettig, R., Rémond, R. & Perré, P. Measuring moisture content profiles in a board during drying: a polychromatic X-ray system interfaced with a vacuum/pressure laboratory kiln. Wood Sci Technol 40, 261–274 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-006-0068-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-006-0068-7