Abstract
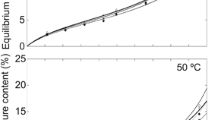
The sorption data for Corsican pine wood chemically modified with a homologous series of linear chain carboxylic acid anhydrides was analysed using various models, namely, BET, Dent, Le and Ly, Hailwood and Horrobin, Nelson, and Henderson. Hailwood and Horrobin resulted in the more appropriate model to represent the equilibrium data of chemically modified wood. In the present study, the parameter representing the molecular weight of the dry cell wall in the Hailwood and Horrobin isotherm was perfectly correlated with the weight percentage gain of anhydride. A linear relation was proposed between these two parameters in order to fit all experimental isotherms (the results showed an r2=0.993).








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson NT, McCarthy JL (1963) Two-parameter isotherm equation for fiber-water systems. Ind Eng Chem Proc DD 2:103–105
Avramidis S (1989) Evaluation of “three-variable” models for the prediction of equilibrium moisture content in wood. Wood Sci Technol 23:251–258
Bradley RS (1936) Polymolecular adsorbed films. Part II. The general theory of the condensation of vapors on finely divided solids. J Am Chem Soc 16:1799–1804
Brunauer S, Emmett PH, Teller E (1938) Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J Am Chem Soc 60:309–319
Chung DS, Pfost HB (1967) Adsorption and desorption of water vapor by cereal grains and their products. Part II: Development of a general isotherm equation. T ASAE 10:552–555
Day DL, Nelson GL (1965) Desorption isotherms for wheat. T ASAE 8:293–297
Dent RW (1977) A multilayer theory for gas sorption. I. Sorption of a single gas. Text Res J 47:145–52
Hailwood AJ, Horrobin S (1946) Absorption of water by polymers: analysis in terms of a simple model. T Faraday Soc B 42:84–102
Hartley ID, Avramidis S (1994) Water clustering phenomenon in two softwoods during adsorption and desorption processes. J Instit Wood Sci 13:98–102
Henderson SM (1952) A basic concept of equilibrium moisture. Agr Eng 33:29–33
Jerrold HZ (1999) Biostatistical analisis, 4th edn. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey
Langmuir I (1918) The absorption of gases on plain surfaces of glass, mica, and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1405
Le CV, Ly NG (1992) Multilayer adsorption of moisture in wool and its application in fabric steaming. Tex Res J 62(11):648–657
Nelson RM Jr (1983) A model for sorption of water vapor by cellulosic materials. Wood Fiber Sci 15(1):8–22
Papadopoulos AN, Hill CAS (2003) The sorption of water vapour by anhydride modified softwood. Wood Sci Technol 37(3–4):221–231
Popper R, Bariska M (1972) Acylation of wood. Part I: The sorption behaviour of water vapour. Holz Roh Werkst 30:289–294
Risi J, Arseneau DF (1957) Dimensional stabilisation of wood. Part I: Acetylation. Forest Prod J 7:210–213
Rowell RM (1983) Chemical modification of wood. For Prod Abstr 6:366–382
Simpson W (1980) Sorption theories applied to wood. Wood Fiber 12(3):183–195
Skaar C (1988) Wood water relations. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Spalt HA (1958) The fundamentals of water vapour sorption by wood. For Prod J 8:258–295
Stamm AJ (1964) Wood and cellulose science. Ronald Press, New York
Venkateswaran A (1970) Sorption of aqueous and non-aqueous media by wood and cellulose. Chem Rev 70:619–637
Yasuda R, Minato K, Norimoto M (1995) Moisture adsorption thermodynamics of chemically modified wood. Holzforshung 49:548–554
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papadopoulos, A.N., Avramidis, S. & Elustondo, D. The sorption of water vapour by chemically modified softwood: analysis using various sorption models. Wood Sci Technol 39, 99–111 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-004-0272-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-004-0272-2