Abstract
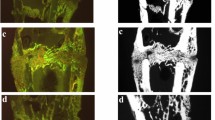
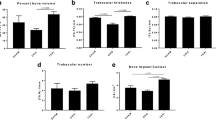
This study investigated the effects of combined teriparatide (an anabolic agent) and monthly risedronate (an anti-resorptive agent) therapy on cancellous bone mass in orchidectomized (ORX) rats. Fifty 14-week-old male Sprague–Dawley rats were randomized into five groups of ten animals each: sham-operation + vehicle; ORX + vehicle; ORX + risedronate (90 μg/kg subcutaneous, every 4 weeks); ORX + teriparatide (30 μg/kg subcutaneous, three times per week); and ORX + risedronate + teriparatide. After the 12-week experimental period, cancellous bone in the tibial proximal metaphysis was examined by static and dynamic histomorphometric analyses. ORX decreased bone volume per total volume (BV/TV) and trabecular number (Tb.N), and increased trabecular separation (Tb.Sp). Risedronate increased BV/TV and Tb.N above the sham control values, while teriparatide prevented the ORX-induced decrease in BV/TV and increased trabecular width (Tb.Wi) above sham control levels. Risedronate decreased Tb.Sp below control values, while teriparatide prevented the ORX-induced increase in Tb.Sp. The combination of teriparatide and risedronate further increased BV/TV and Tb.N and decreased Tb.Sp as a result of suppression of bone remodeling, compared with teriparatide alone. These results suggest that teriparatide and monthly risedronate exert different effects on cancellous bone structure and thus have additive effects on cancellous bone mass in ORX rats.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mosekilde L, Vestergaar P, Rejnmark L (2013) The pathogenesis, treatment and prevention of osteoporosis in men. Drugs 73:15–29
Murad MH, Drake MT, Mullan RJ, Mauck KF, Stuart LM, Lane MA, Abu Elnour NO, Erwin PJ, Hazem A, Puhan MA, Li T, Montori VM (2012) Comparative effectiveness of drug treatments to prevent fragility fractures: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:1871–1880
Nakamura T, Sugimoto T, Nakano T, Kishimoto H, Ito M, Fukunaga M, Hagino H, Sone T, Yoshikawa H, Nishizawa Y, Fujita T, Shiraki M (2012) Randomized Teriparatide [human parathyroid hormone (PTH) 1–34] Once-Weekly Efficacy Research (TOWER) trial for examining the reduction in new vertebral fractures in subjects with primary osteoporosis and high fracture risk. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:3097–3106
Cosman F, Eriksen EF, Recknor C, Miller PD, Guañabens N, Kasperk C, Papanastasiou P, Readie A, Rao H, Gasser JA, Bucci-Rechtweg C, Boonen S (2011) Effects of intravenous zoledronic acid plus subcutaneous teriparatide [rhPTH (1–34)] in postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res 26:503–511
Tsai JN, Uihlein AV, Lee H, Kumbhani R, Siwila-Sackman E, McKay EA, Burnett-Bowie SA, Neer RM, Leder BZ (2013) Teriparatide and denosumab, alone or combined, in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: the DATA study randomised trial. Lancet 382:50–56
Walker MD, Cusano NE, Sliney J Jr, Romano M, Zhang C, McMahon DJ, Bilezikian JP (2013) Combination therapy with risedronate and teriparatide in male osteoporosis. Endocrine 44:237–246
Harris ST, Watts NB, Genant HK, McKeever CD, Hangartner T, Keller M, Chesnut CH 3rd, Brown J, Eriksen EF, Hoseyni MS, Axelrod DW, Miller PD (1999) Effects of risedronate treatment on vertebral and nonvertebral fractures in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: a randomized controlled trial. Vertebral Efficacy With Risedronate Therapy (VERT) Study Group. JAMA 282:1344–1352
Reginster J, Minne HW, Sorensen OH, Hooper M, Roux C, Brandi ML, Lund B, Ethgen D, Pack S, Roumagnac I, Eastell R (2000) Randomized trial of the effects of risedronate on vertebral fractures in women with established postmenopausal osteoporosis. Vertebral Efficacy with Risedronate Therapy (VERT) Study Group. Osteoporos Int 11:83–91
McClung MR, Geusens P, Miller PD, Zippel H, Bensen WG, Roux C, Adami S, Fogelman I, Diamond T, Eastell R, Meunier PJ, Reginster JY, Hip Intervention Program Study Group (2001) Effect of risedronate on the risk of hip fracture in elderly women. Hip Intervention Program Study Group. N Engl J Med 344:333–340
Harris ST, Watts NB, Li Z, Chines AA, Hanley DA, Brown JP (2004) Two-year efficacy and tolerability of risedronate once a week for the treatment of women with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Curr Med Res Opin 20:757–764
McClung MR, Zanchetta JR, Racewicz A, Roux C, Benhamou CL, Man Z, Eusebio RA, Beary JF, Burgio DE, Matzkin E, Boonen S, Delmas P (2013) Efficacy and safety of risedronate 150-mg once a month in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis: 2-year data. Osteoporos Int 24:293–299
Ringe JD, Faber H, Farahmand P, Dorst A (2006) Efficacy of risedronate in men with primary and secondary osteoporosis: results of a 1-year study. Rheumatol Int 26:427–431
Confavreux CB, Canoui-Poitrine F, Schott AM, Ambrosi V, Tainturier V, Chapurlat RD (2012) Persistence at 1 year of oral antiosteoporotic drugs: a prospective study in a comprehensive health insurance database. Eur J Endocrinol 166:735–741
Iwamoto J, Takeda T, Katsumata T, Tanaka T, Ichimura S, Toyama Y (2002) Effect of etidronate on bone in orchidectomized and sciatic neurectomized adult rats. Bone 30:360–367
Iwamoto J, Yeh JK, Takeda T (2003) Effect of vitamin K2 on cortical and cancellous bones in orchidectomized and/or sciatic neurectomized rats. J Bone Miner Res 18:776–783
Iwamoto J, Takeda T, Yeh JK, Ichimura S, Toyama Y (2003) Effect of vitamin K2 on cortical and cancellous bones in orchidectomized young rats. Maturitas 44:19–27
Iwamoto J, Takeda T, Ichimura S, Sato Y, Yeh JK (2003) Comparative effects of orchidectomy and sciatic neurectomy on cortical and cancellous bone in young growing rats. J Bone Miner Metab 21:211–216
Iwamoto J, Takeda T, Ichimura S (2004) Differential effect of short-term etidronate treatment on three cancellous bone sites in orchidectomized adult rats. Keio J Med 53:12–17
Iwamoto J, Takeda T, Matsumoto H, Sato Y, Yeh JK (2008) Beneficial effects of combined administration of alendronate and alfacalcidol on cancellous bone mass of the tibia in orchidectomized rats: a bone histomorphometry study. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 54:11–17
Shahnazari M, Yao W, Dai W, Wang B, Ionova-Martin SS, Ritchie RO, Heeren D, Burghardt AJ, Nicolella DP, Kimiecik MG, Lane NE (2010) Higher doses of bisphosphonates further improve bone mass, architecture, and strength but not the tissue material properties in aged rats. Bone 46:1267–1274
Iwamoto J, Seki A, Sato Y (2014) Effect of Intermittent administration of hPTH (1–34) on cortical bone geometry in rats treated with high-dose glucocorticoids. Chin J Physiol 57:231–237
Dempster DW, Compston JE, Drezner MK, Glorieux FH, Kanis JA, Malluche H, Meunier PJ, Ott SM, Recker RR, Parfitt AM (2013) Standardized nomenclature, symbols, and units for bone histomorphometry: a 2012 update of the report of the ASBMR Histomorphometry Nomenclature Committee. J Bone Miner Res 28:2–17
Ohlsson C, Börjesson AE, Vandenput L (2012) Sex steroids and bone health in men. Bonekey Rep 1:2
Turner RT, Hannon KS, Demers LM, Buchanan J, Bell NH (1989) Differential effects of gonadal function on bone histomorphometry in male and female rats. J Bone Miner Res 4:557–563
Gunness M, Orwoll E (1995) Early induction of alterations in cancellous and cortical bone histology after orchiectomy in mature rats. J Bone Miner Res 10:1735–1744
Yamaura M, Nakamura T, Tsurukami H, Hijioka A, Narusawa K, Ohnishi H, Ohta T, Hosoda K (1996) Local bone turnover in the metaphysis of the proximal tibia and the lumbar vertebra during the early periods after ovariectomy in rats. Calcif Tissue Int 58:52–59
Díaz-Curiel M, de la Piedra C, Romero FI, Montero M, Gómez S, Lefort M, Carrascal MT, Phipps RJ (2008) Effect of risedronate on bone mass, remodelling and biomechanical strength in orchidectomized rats. Horm Res 70:93–99
Khedr NF, El-Ashmawy NE, El-Bahrawy HA, Haggag AA, El-Abd EE (2013) Modulation of bone turnover in orchidectomized rats treated with raloxifene and risedronate. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 27:526–534
Montero M, Serfati D, Luna S, Díaz-Curiel M, Carrascal MT, Gomez S, De la Piedra C (2010) The effectiveness of intermittent rat parathyroid hormone (1–34) treatment on low bone mass due to oestrogen or androgen depletion in skeletally mature rats. Aging Male 13:59–73
Gabet Y, Kohavi D, Müller R, Chorev M, Bab I (2005) Intermittently administered parathyroid hormone 1–34 reverses bone loss and structural impairment in orchidectomized adult rats. Osteoporos Int 16:1436–1443
Compston JE (2007) Skeletal actions of intermittent parathyroid hormone: effects on bone remodelling and structure. Bone 40:1447–1452
Iwamoto J, Seki A, Sato Y (2014) Effect of combined teriparatide and monthly minodronic acid therapy on cancellous bone mass in ovariectomized rats: a bone histomorphometry study. Bone 64:88–94
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Asahi Kasei Pharma, Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan.
Conflict of interest
J. Iwamoto and A. Seki declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This experiment was performed at the laboratory of Hamri Co., Ltd. (Ibaraki, Japan), which was approved by the Association for the Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care (AAALAC) International. All procedures performed in the experiment involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at Hamri Co., Ltd. (Ibaraki, Japan). The experimental protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Hamri Co., Ltd. (Ibaraki, Japan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iwamoto, J., Seki, A. Effect of Combined Teriparatide and Monthly Risedronate Therapy on Cancellous Bone Mass in Orchidectomized Rats: A Bone Histomorphometry Study. Calcif Tissue Int 97, 23–31 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-015-0006-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-015-0006-5