Abstract
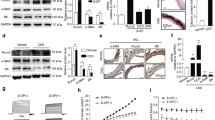
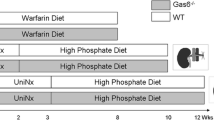
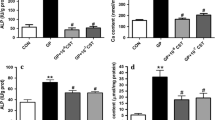
Vascular calcification (VC) is frequently observed in patients with chronic renal failure and appears to be an active process involving transdifferentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) to osteoblast-like cells. Reports of VC prevention in uremic rodents by calcimimetics coupled with identification of the calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) in VSMCs led us to hypothesize that CaSR activation in arterial cells and VSMCs may elicit expression of an endogenous inhibitor of VC. Toward this end, we determined the effects of calcium and the calcimimetic AMG 641 on arterial wall and isolated VSMC expression of matrix-Gla protein (MGP). Bovine VSMCs were incubated with increasing calcium chloride or AMG 641 concentrations, while in vivo experiments were carried out on healthy and uremic rats. Both AMG 641 and hypercalcemia induced MGP expression in the arterial wall in healthy and uremic rats. The results obtained in vitro supported those from in vivo experiments. In conclusion, selective CaSR activation, either by extracellular calcium or AMG 641, increased MGP expression in vivo in the arterial wall and in vitro in bovine VSMCs. This local upregulation of MGP expression provides one potential mechanism by which calcimimetics prevent VC.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedin M, Tintut Y, Demer LL (2004) Vascular calcification: mechanisms and clinical ramifications. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24:1161–1170
Block GA, Klassen PS, Lazarus JM et al (2004) Mineral metabolism, mortality, and morbidity in maintenance hemodialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:2208–2218
Cozzolino M, Brancaccio D, Gallieni M, Slatopolsky E (2005) Pathogenesis of vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 68:429–436
Goodman WG, Goldin J, Kuizon BD et al (2000) Coronary-artery calcification in young adults with end-stage renal disease who are undergoing dialysis. N Engl J Med 342:1478–1483
Chen NX, Moe SM (2004) Vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. Semin Nephrol 24:61–68
Chen NX, Moe SM (2006) Uremic vascular calcification. J Investig Med 54:380–384
Steitz SA, Speer MY, Curing G, Yang HY, Haynes P, Aebersold R, Schinke T, Karsenty G, Giachelli GM (2001) Smooth muscle cell phenotypic transition associated with calcification: upregulation of Cbfa1 and downregulation of smooth muscle lineage markers. Circ Res 89:1147–1154
Ganesh SK, Stack AG, Levin NW et al (2001) Association of elevated serum PO4, Ca × PO4 product, and parathyroid hormone with cardiac mortality risk in chronic hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:2131–2138
London GM, Drueke TB (1997) Atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis in chronic renal failure. Kidney Int 51:1678–1695
Shalhoub V, Shatzen E, Henley C, Boedigheimer M, McNinch J, Manoukian R, Damore M, Fitzpatrick D, Haas K, Twomey B, Kiaei P, Ward S, Lacey DL, Martin D (2006) Calcification inhibitors and Wnt signaling proteins are implicated in bovine artery smooth muscle cell calcification in the presence of phosphate and vitamin D sterols. Calcif Tissue Int 79:431–442
Moe SM, Reslerova M, Ketteler M, O’Neill K, Duan D, Koczman J, Westenfeld R, Jahnen-Dechent W, Chen NX (2005) Role of calcification inhibitors in the pathogenesis of vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease (CKD). Kidney Int 67:2295–2304
Luo G, Ducy P, McKee MD, Pinero GJ, Loyer E, Behringer RR, Karsenty G (1997) Spontaneous calcification of arteries and cartilage in mice lacking matrix Gla protein. Nature 386:78–81
Price P, Otsuka A, Poser J, Kristaponis J, Raman N (1976) Characterization of a gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing protein from bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73:1447–1451
Proudfoot D, Skepper JN, Shanahan CM, Weissberg PL (1998) Calcification of human vascular cells in vitro is correlated with high levels of matrix gla protein and low levels of osteopontin expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 18:379–388
Shanahan CM, Proudfoot D, Tyson KL, Cary NR, Edmons M, Weissberg PL (2000) Expression of mineralisation-regulating proteins in association with human vascular calcification. Z Kardiol 89(Suppl 2):63–68
Spronk HMH, Soute BAM, Schurgers LJ, Cleutjens JPM, Thijssen HHW, De Mey JGR, Vermeer C (2001) Matrix Gla protein accumulates at the border of regions of calcification and normal tissue in the media of the arterial vessel wall. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 289:485–490
Munroe PB, Olgunturk RO, Fryns JP, Van Maldergem L, Ziereisen F, Yuksel B, Gardiner RM, Chung E (1999) Mutations in the gene encoding the human matrix Gla protein cause Keutel syndrome. Nat Genet 21:142–144
Price PA, Faus SA, Williamson MK (1998) Warfarin causes rapid calcification of the elastic lamellae in rat arteries and heart valves. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 18:1400–1407
Ivanovski O, Nikolov IG, Joki N, Caudrillier A, Phan O, Mentaverri R, Maizel J, Hamada Y, Nguyen-Khoa T, Fukagawa M, Kamel S, Lacour B, Drüeke TB, Massy ZA (2009) The calcimimetic R-568 retards uremia-enhanced vascular calcification and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E deficient (apoE−/−) mice. Atherosclerosis 205:55–62
Lopez I, Aguilera-Tejero E, Mendoza FJ, Almaden Y, Perez J, Martin D, Rodriguez M (2006) Calcimimetic R-568 decreases extraosseous calcifications in uremic rats treated with calcitriol. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:795–804
De Francisco AL, Izquierdo M, Cunningham J, Piñera C, Palomar R, Fresnedo GF, Amado JA, Unzueta MG, Arias M (2008) Calcium-mediated parathyroid hormone release changes in patients treated with the calcimimetic agent cinacalcet. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:2895–2901
Lopez I, Mendoza FJ, Aguilera-Tejero E, Perez J, Guerrero F, Martin D, Rodriguez M (2008) The effect of calcitriol, paricalcitol and calcimimetic AMG 641 on extraosseous calcifications in uremic rats. Kidney Int 73:300–307
Garfia B, Cañadillas S, Canalejo A, Luque F, Siendones E, Quesada M, Almaden Y, Aguilera-Tejero E, Rodriguez M (2003) Regulation of parathyroid vitamin D receptor expression by extracellular calcium. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:2945–2952
Price PA, Faus SA, Williamson MK (2000) Warfarin-induced artery calcification is accelerated by growth and vitamin D. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:317–327
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (2006) The single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction: twenty-something years on. Nat Protoc 1:581–585
Bas A, Lopez I, Perez J, Rodriguez M, Aguilera-Tejero E (2006) Reversibility of calcitriol-induced medial artery calcification in rats with intact renal function. J Bone Miner Res 21:484–490
Jono S, Nishizawa Y, Shioi A, Morii H (1998) 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 increases in vitro vascular calcification by modulating secretion of endogenous parathyroid hormone-related peptide. Circulation 98:1302–1306
Shanahan CM, Cary NR, Metcalfe JC, Weissberg PL (1994) High expression of genes for calcification-regulating proteins in human atherosclerotic plaques. J Clin Invest 93:2393–2402
Mori K, Shioi A, Jono S, Nishizawa Y, Morii H (1998) Expression of matrix Gla protein (MGP) in an in vitro model of vascular calcification. FEBS Lett 433:19–22
Farzaneh-Far A, Proudfoot D, Weissberg PL, Shanahan CM (2000) Matrix gla protein is regulated by a mechanism functionally related to the calcium-sensing receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 277:736–740
Nakatani S, Mano H, Ryanghyok IM, Shimizu J, Wada M (2006) Excess magnesium inhibits excess calcium-induced matrix-mineralization and production of matrix gla protein (MGP) by ATDC5 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 348:1157–1162
Farzaneh-Far A, Weissberg PL, Proudfoot D, Shanahan CM (2001) Transcriptional regulation of matrix gla protein. Z Kardiol 3:38–42
Molostvov G, James S, Fletcher S, Bennett J, Lehnert H, Bland R, Zehnder D (2007) Extracellular calcium-sensing receptor is functionally expressed in human artery. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293:F946–F955
Alam MU, Kirton JP, Wilkinson FL, Towers E, Sinha S, Rouhi M, Vizard TN, Sage AP, Martin D, Ward DT, Alexander MY, Riccardi D, Canfield AE (2009) Calcification is associated with loss of functional calcium-sensing receptor in vascular smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Res 81:260–268
Molostvov G, Fletcher S, Bland R, Zehnder D (2008) Extracellular calcium-sensing receptor mediated signalling is involved in human vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and apoptosis. Cell Physiol Biochem 22:413–422
Smajilovic S, Hansen JL, Christoffersen TE, Lewin E, Sheikh SP, Terwilliger EF, Brown EM, Haunso S, Tfelt-Hansen J (2006) Extracellular calcium sensing in rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 348:1215–1223
Suttamanatwong S, Jensen ED, Schilling J, Franceschi RT, Carlson AE, Mansky KC, Gopalakrishnan R (2009) Sp proteins and Runx2 mediate regulation of matrix Gla protein (MGP) expression by parathyroid hormone. J Cell Biochem 107:284–292
Zebboudj AF, Shin V, Boström K (2003) Matrix GLA protein and BMP-2 regulate osteoinduction in calcifying vascular cells. J Cell Biochem 90:756–765
Koos R, Krueger T, Westenfeld R, Kühl HP, Brandenburg V, Mahnken AH, Stanzel S, Vermeer C, Cranenburg EC, Floege J, Kelm M, Schurgers LJ (2009) Relation of circulating matrix Gla-protein and anticoagulation status in patients with aortic valve calcification. Thromb Haemost 101:706–713
Schurgers LJ, Cranenburg ECM, Vermeer C (2008) Matrix-Gla protein: the calcification inhibitor in need of vitamin K. Thromb Haemost 100:593–603
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Holly Tomlin (employee and stockholder of Amgen, Inc.) for her editing assistance and manuscript formatting support. The work reported here was supported by government grants PI080852, SAF2005-01444, PI070315, and PI070287 from Institution Carlos III; European Union funds (FEDER); 195/04, 202/05, and 025/07 from Consejeria de Salud de la Junta de Andalucia; Red de Investigacion Renal (REDinREN) RD 06/00116/0007; and Amgen. Y. A. is supported by Fundacion Progreso y Salud from Consejeria de Salud de la Junta de Andalucia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The first two authors contributed equally to this work.
Henley is an employee and shareholder at Amgen, Inc. Rodriguez receives research funding from Amgen, Inc. All other authors have stated that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mendoza, F.J., Martinez-Moreno, J., Almaden, Y. et al. Effect of Calcium and the Calcimimetic AMG 641 on Matrix-Gla Protein in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Calcif Tissue Int 88, 169–178 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-010-9442-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-010-9442-4