Abstract
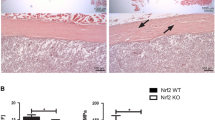
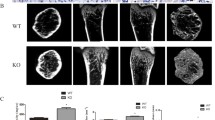
The P2X7 nucleotide receptor (P2X7R) is an ATP-gated ion channel expressed in bone cells. Homozygous null P2X7R (P2X7R–/–) mice have reduced bone formation, so we hypothesized that P2X7R–/– mice have impaired fracture healing compared to P2X7R+/+ control mice. To test the hypothesis, adult P2X7R–/– mice and P2X7R+/+ mice were studied. Osteotomy of the right femur was performed and a stainless-steel pin was inserted into the medullary cavity to stabilize the fracture site. No differences in callus development were seen in the radiograph, micro computed tomography, or dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry measurements. Mechanical testing showed that the recovery of ultimate force, stiffness, and energy to failure were slightly decreased in P2X7R–/– mice compared with the control. Histomorphometric measurements of the callus revealed that mineralizing surface and bone formation were significantly decreased, by 22% (p < 0.001) and 29% (p < 0.05), respectively, in P2X7R–/– mice in comparison with the wild-type control. These data show that a null mutation of the P2X7R does not affect the amount of callus formed in our osteotomy fracture model. However, callus remodeling was significantly delayed. Our data suggest the different role of the P2X7R in woven bone and lamellar bone formation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Genetos DC, Geist DJ, Liu D, Donahue HJ, Duncan RL (2005) Fluid shear-induced ATP secretion mediates prostaglandin release in MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts. J Bone Miner Res 20:41–49
Li J, Liu D, Ke HZ, Duncan RL, Turner CH (2005) The P2X7 nucleotide receptor mediates skeletal mechanotransduction. J Biol Chem 280:42952–42959
Bowler WB, Dixon CJ, Halleux C, Maier R, Bilbe G, Fraser WD, Gallagher JA, Hipskind RA (1999) Signaling in human osteoblasts by extracellular nucleotides. Their weak induction of the c-fos proto-oncogene via Ca2+ mobilization is strongly potentiated by a parathyroid hormone/cAMP-dependent protein kinase pathway independently of mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem 274:14315–14324
North RA (2002) Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol Rev 82:1013–1067
Surprenant A, Rassendren F, Kawashima E, North RA, Buell G (1996) The cytolytic P2Z receptor for extracellular ATP identified as a P2X receptor (P2X7). Science 272:735–738
Ferrari D, Chiozzi P, Falzoni S, Dal Susino M, Melchiorri L, Baricordi OR, Di Virgilio F (1997) Extracellular ATP triggers IL-1 beta release by activating the purinergic P2Z receptor of human macrophages. J Immunol 159:1451–1458
Ferrari D, Los M, Bauer MK, Vandenabeele P, Wesselborg S, Schulze-Osthoff K (1999) P2Z purinoreceptor ligation induces activation of caspases with distinct roles in apoptotic and necrotic alterations of cell death. FEBS Lett 447:71–75
Kim M, Jiang LH, Wilson HL, North RA, Surprenant A (2001) Proteomic and functional evidence for a P2X7 receptor signalling complex. EMBO J 20:6347–6358
Ke HZ, Qi H, Weidema AF, Zhang Q, Panupinthu N, Crawford DT, Grasser WA, Paralkar VM, Li M, Audoly LP, Gabel CA, Jee WS, Dixon SJ, Sims SM, Thompson DD (2003) Deletion of the P2X7 nucleotide receptor reveals its regulatory roles in bone formation and resorption. Mol Endocrinol 17:1356–1367
Cui L, Ma YF, Yao W, Zhou H, Setterberg RB, Liang TC, Jee WS (2001) Cancellous bone of aged rats maintains its capacity to respond vigorously to the anabolic effects of prostaglandin E2 by modeling-dependent bone gain. J Bone Miner Metab 19:29–37
Mo A, Yao W, Li C, Tian X, Su M, Ling Y, Zhang Q, Setterberg RB, Jee WS (2002) Bipedal stance exercise and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and its synergistic effect in increasing bone mass and in lowering the PGE2 dose required to prevent ovariectomized-induced cancellous bone loss in aged rats. Bone 31:402–406
Yao W, Jee WS, Zhou H, Lu J, Cui L, Setterberg R, Liang T, Ma Y (1999) Anabolic effect of prostaglandin E2 on cortical bone of aged male rats comes mainly from modeling-dependent bone gain. Bone 25:697–702
Solle M, Labasi J, Perregaux DG, Stam E, Petrushova N, Koller BH, Griffiths RJ, Gabel CA (2001) Altered cytokine production in mice lacking P2X(7) receptors. J Biol Chem 276:125–132
Bonnarens F, Einhorn TA (1984) Production of a standard closed fracture in laboratory animal bone. J Orthop Res 2:97–101
Li C, Mori S, Li J, Kaji Y, Akiyama T, Kawanishi J, Norimatsu H (2001) Long-term effect of incadronate disodium (YM-175) on fracture healing of femoral shaft in growing rats. J Bone Miner Res 16:429–436
Li J, Mori S, Kaji Y, Kawanishi J, Akiyama T, Norimatsu H (2000) Concentration of bisphosphonate (incadronate) in callus area and its effects on fracture healing in rats. J Bone Miner Res 15:2042–2051
Li J, Mori S, Kaji Y, Mashiba T, Kawanishi J, Norimatsu H (1999) Effect of bisphosphonate (incadronate) on fracture healing of long bones in rats. J Bone Miner Res 14:969–979
Dimitriou R, Tsiridis E, Giannoudis PV (2005) Current concepts of molecular aspects of bone healing. Injury 36:1392–1404
Gerstenfeld LC, Alkhiary YM, Krall EA, Nicholls FH, Stapleton SN, Fitch JL, Bauer M, Kayal R, Graves DT, Jepsen KJ, Einhorn TA (2006) Three-dimensional reconstruction of fracture callus morphogenesis. J Histochem Cytochem 54:1215–1228
Ai-Aql ZS, Alagl AS, Graves DT, Gerstenfeld LC, Einhorn TA (2008) Molecular mechanisms controlling bone formation during fracture healing and distraction osteogenesis. J Dent Res 87:107–118
Pelegrin P, Barroso-Gutierrez C, Surprenant A (2008) P2X7 receptor differentially couples to distinct release pathways for IL-1beta in mouse macrophage. J Immunol 180:7147–7157
Shigemoto-Mogami Y, Koizumi S, Tsuda M, Ohsawa K, Kohsaka S, Inoue K (2001) Mechanisms underlying extracellular ATP-evoked interleukin-6 release in mouse microglial cell line, MG-5. J Neurochem 78:1339–1349
Wang CM, Chang YY, Sun SH (2003) Activation of P2X7 purinoceptor-stimulated TGF-beta 1 mRNA expression involves PKC/MAPK signalling pathway in a rat brain-derived type-2 astrocyte cell line, RBA-2. Cell Signal 15:1129–1137
Korcok J, Raimundo LN, Ke HZ, Sims SM, Dixon SJ (2004) Extracellular nucleotides act through P2X7 receptors to activate NF-kappaB in osteoclasts. J Bone Miner Res 19:642–651
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Institutes of Health Grant R01AR046530 (C.H.T.) and AR051901 (R.L.D.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Meyer, R., Duncan, R.L. et al. P2X7 Nucleotide Receptor Plays an Important Role in Callus Remodeling During Fracture Repair. Calcif Tissue Int 84, 405–412 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-009-9237-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-009-9237-7