Abstract
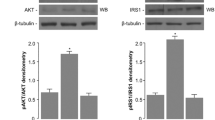
Visfatin (also known as pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor or PBEF) is a novel adipocytokine that is highly expressed in visceral fat and upregulated in obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Visfatin binds to and activates the insulin receptor (IR), thereby exerting insulin-mimetic effects in various cell lines. IR has been detected in osteoblasts, which is consistent with the role of insulin as an important osteotropic hormone. This study investigated the actions of visfatin on human primary osteoblasts. The expression and tyrosine phosphorylation of IR, IR substrate-1 (IRS-1), and IRS-2 were determined by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting. Cell proliferation was determined by measuring [3H]thymidine incorporation and cell number. Glucose uptake was determined by measuring 2-[3H]deoxyglucose incorporation. Real-time quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was used for determining alkaline phosphatase (ALP), osteocalcin, and type I collagen mRNA expression. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and radioimmunoassay were used for measuring ALP activity, osteocalcin secretion, and type I collagen production. We found that visfatin induced tyrosine phosphorylation of IR, IRS-1, and IRS-2. Moreover, the effects of visfatin – glucose uptake, proliferation, and type I collagen enhancement of cultured human osteoblast-like cells – bore a close resemblance to those of insulin and were inhibited by hydroxy-2-naphthalenylmethylphosphonic acid tris-acetoxymethyl ester, a specific inhibitor of IR tyrosine kinase activity. We also unexpectedly found that visfatin downregulated osteocalcin secretion from human osteoblast-like cells. These data indicate that the regulation of glucose uptake, proliferation, and type I collagen production by visfatin in human osteoblasts involves IR phosphorylation, the same signal-transduction pathway used by insulin.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stewart KJ, Deregis RJ, Turner KL, Bacher AC, Sung J, Hees PS, Tayback M, Ouyang P (2002) Fitness, fatness and activity as predictors of bone mineral density in older persons. J Intern Med 252:381–388
Lim S, Joung H, Shin CS, Lee HK, Kim KS, Shin EK, Kim HY, Lim MK, Cho SI (2004) Body composition changes with age have gender-specific impacts on bone mineral density. Bone 35:792–798
Lindsay R, Cosman F, Herrington BS, Himmelstein S (1992) Bone mass and body composition in normal women. J Bone Miner Res 7:55–62
Felson DT, Zhang Y, Hannan MT, Anderson JJ (1993) Effects of weight, and body mass index on bone mineral density in men and women. J Bone Miner Res 8:567–573
Glauber HS, Vollmer WM, Nevitt MC, Ensrud KE, Orwoll ES (1995) Body weight versus body fat distribution, adiposity, and frame size as predictors of bone density. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 80:1118–1123
Khosla S, Atkinson EJ, Riggs BL, Melton LJ (1996) Relationship between body composition and bone mass in women. J Bone Miner Res 11:857–863
Schwartz AV (2003) Diabetes mellitus: does it affect bone? Calcif Tissue Int 73:515–519
Dominguez LJ, Muratore M, Quarta E, Zagone G, Barbagallo M (2004) Osteoporosis and diabetes. Reumatismo 56:235–241
Kwon DJ, Kim JH, Chung KW, Kim JH, Lee JW, Kim SP, Lee HY (1996) Bone mineral density of the spine using dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 22:157–162
de Liefde II, van der Klift M, de Laet CE, van Daele PL, Hofman A, Pols HA (2005) Bone mineral density and fracture risk in type-2 diabetes mellitus: the Rotterdam Study. Osteoporos Int 16:1713–1720
Akin O, Gol K, Akturk M, Erkaya S (2003) Evaluation of bone turnover in postmenopausal patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus using biochemical markers and bone mineral density measurements. Gynecol Endocrinol 17:19–29
Fukuhara A, Matsuda M, Nishizawa M, Segawa K, Tanaka M, Kishimoto K, Matsuki Y, Murakami M, Ichisaka T, Murakami H, Watanabe E, Takagi T, Akiyoshi M, Ohtsubo T, Kihara S, Yamashita S, Makishima M, Funahashi T, Yamanaka S, Hiramatsu R, Matsuzawa Y, Shimomura I (2005) Visfatin: a protein secreted by visceral fat that mimics the effects of insulin. Science 307:426–430
Berndt J, Kloting N, Kralisch S, Kovacs P, Fasshauer M, Schon MR, Stumvoll M, Bluher M (2005) Plasma visfatin concentrations and fat depot-specific mRNA expression in humans. Diabetes 54:2911–2916
Haider DG, Schindler K, Schaller G, Prager G, Wolzt M, Ludvik B (2006) Increased plasma visfatin concentrations in morbidly obese subjects are reduced after gastric banding. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:1578–1581
Chen MP, Chung FM, Chang DM, Tsai JC, Huang HF, Shin SJ, Lee YJ (2006) Elevated plasma level of visfatin/pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:295–299
Thomas DM, Hards DK, Rogers SD, Ng KW, Best JD (1996) Insulin receptor expression in bone. J Bone Miner Res 11:1312–1320
Thrailkill KM, Lumpkin CK Jr, Bunn RC, Kemp SF, Fowlkes JL (2005) Is insulin an anabolic agent in bone? Dissecting the diabetic bone for clues. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 289:E735–E745
Thrailkill KM, Liu L, Wahl EC, Bunn RC, Perrien DS, Cockrell GE, Skinner RA, Hogue WR, Carver AA, Fowlkes JL, Aronson J, Lumpkin CK Jr (2005) Bone formation is impaired in a model of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 54:2875–2881
Stolk RP, Van Daele PL, Pols HA, Burger H, Hofman A, Birkenhager JC, Lamberts SW, Grobbee DE (1996) Hyperinsulinemia and bone mineral density in an elderly population: the Rotterdam Study. Bone 18:545–549
Cornish J, Callon KE, Reid IR (1996) Insulin increases histomorphometric indices of bone formation in vivo. Calcif Tissue Int 59:492–495
Kasuga M, Hedo JA, Yamada KM, Kahn CR (1982) The structure of insulin receptor and its subunits. Evidence for multiple nonreduced forms and a 210,000 possible proreceptor. J Biol Chem 257:10392–10399
Chang L, Chiang SH, Saltiel AR (2004) Insulin signaling and the regulation of glucose transport. Mol Med 10:65–71
Robey PG, Termine JD (1985) Human bone cells in vitro. Calcif Tissue Int 37:453–460
Xie H, Tang SY, Cui RR, Huang J, Ren XH, Yuan LQ, Lu Y, Yang M, Zhou HD, Wu XP, Luo XH, Liao EY (2006) Apelin and its receptor are expressed in human osteoblasts. Regul Pept 134:118–125
Luo XH, Guo LJ, Yuan LQ, Xie H, Zhou HD, Wu XP, Liao EY (2005) Adiponectin stimulates human osteoblasts proliferation and differentiation via the MAPK signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res 309:99–109
Bodine PV, Trailsmith M, Komm BS (1996) Development and characterization of a conditionally transformed adult human osteoblastic cell line. J Bone Miner Res 11:806–819
White MF (2003) Insulin signaling in health and disease. Science 302:1710–1711
Pawson T, Scott JD (1997) Signaling through scaffold, anchoring, and adaptor proteins. Science 278:2075–2080
Kotani K, Wilden P, Pillay TS (1998) SH2 Balpha is an insulin-receptor adapter protein and substrate that interacts with the activation loop of the insulin-receptor kinase. Biochem J 335:103–109
Dong X, Park S, Lin X, Copps K, Yi X, White MF (2006) Irs1 and Irs2 signaling is essential for hepatic glucose homeostasis and systemic growth. J Clin Invest 116:101–114
Kido Y, Burks DJ, Withers D, Bruning JC, Kahn CR, White MF, Accili D (2000) Tissue-specific insulin resistance in mice with mutations in the insulin receptor, IRS-1, and IRS-2. J Clin Invest 105:199–205
Withers DJ, Gutierrez JS, Towery H, Burks DJ, Ren JM, Previs S, Zhang Y, Bernal D, Pons S, Shulman GI, Bonner-Weir S, White MF (1998) Disruption of IRS-2 causes type 2 diabetes in mice. Nature 391:900–904
Ituarte EA, Halstead LR, Iida-Klein A, Ituarte HG, Hahn TJ (1989) Glucose transport system in UMR-106–01 osteoblastic osteosarcoma cells: regulation by insulin. Calcif Tissue Int 45:27–33
Hahn TJ, Westbrook SL, Sullivan TL, Goodman WG, Halstead LR (1988) Glucose transport in osteoblast-enriched bone explants: characterization and insulin regulation J Bone Miner Res 3:359–365
Qutob S, Dixon SJ, Wilson JX (1998) Insulin stimulates vitamin C recycling and ascorbate accumulation in osteoblastic cells. Endocrinology 139:51–56
Thomas DM, Rogers SD, Sleeman MW, Pasquini GM, Bringhurst FR, Ng KW, Zajac JD, Best JD (1995) Modulation of glucose transport by parathyroid hormone and insulin in UMR 106–01, a clonal rat osteogenic sarcoma cell line. J Mol Endocrinol 14:263–275
Hickman J, McElduff A (1989) Insulin promotes growth of the cultured rat osteosarcoma cell line UMR-106–01: an osteoblast-like cell. Endocrinology 124:701–706
Craig RG, Rowe DW, Petersen DN, Kream BE (1989) Insulin increases the steady state level of alpha-1(I) procollagen mRNA in the osteoblast-rich segment of fetal rat calvaria. Endocrinology 125:1430–1437
Kim SJ, Chun JY, Kim MS (2000) Insulin stimulates production of nitric oxide via ERK in osteoblast cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 278:712–718
Pun KK, Lau P, Ho PW (1989) The characterization, regulation, and function of insulin receptors on osteoblast-like clonal osteosarcoma cell line. J Bone Miner Res 4:853–862
Kream B, Harrison J, Bailey R, Petersen D, Rowe D, Lichtler A (1989) Hormonal regulation of collagen gene expression in osteoblastic cell – overview and new findings. Connect Tissue Res 20:187–192
Kream BE, Smith MD, Canalis E, Raisz LG (1985) Characterization of the effect of insulin on collagen synthesis in fetal rat bone. Endocrinology 116:296–302
Rosen DM, Luben RA (1983) Multiple hormonal mechanisms for the control of collagen synthesis in an osteoblast-like cell line, MMB-1. Endocrinology 112:992–999
Sasaki T, Haneda K (1991) Insulin deficiency impairs procollagen synthesis in osteoblasts and periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Showa Shigakkai Zasshi 11:28–37
Rubinacci A, Boniforti F, Tessari L (1991) Effect of insulin on the activity of bone alkaline phosphatase in culture. Minerva Endocrinol 16:187–191
Owen M (1988) Marrow stromal stem cells. J Cell Sci 10:63–76
Prockop DJ (1997) Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science 276:71–74
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by grants 30200322, 30572078, 30600661 and 30400218 from the China National Natural Scientific Foundation, a Foundation for the Author of National Excellent Doctoral Dissertation of P.R. China (200259), and the Hunan Provincial Outstanding Youth Foundation of P.R. China (03JJY1005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
H. Xie and S.-Y. Tang, X.-H. Luo1 contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, H., Tang, SY., Luo, XH. et al. Insulin-Like Effects of Visfatin on Human Osteoblasts. Calcif Tissue Int 80, 201–210 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-006-0155-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-006-0155-7