Abstract
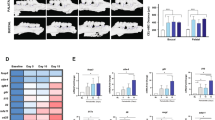
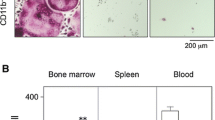
The host immune system, especially activated T cells, plays a crucial role in inflammatory bone resorption and osteoclastogenesis. Previously, we showed that T cells are involved in inflammatory bone resorption in vivo. However, little is known about whether B cells are involved in inflammatory bone resorption and how B cells take part in osteoclastogenesis. Therefore, the aim of this study was to examine whether B c ells truly influence inflammatory bone resorption in vivo. Alveolar bone resorption in normal mice, in SCID mice that lack both B and T cells, and in B cell-reconstituted SCID mice was compared histopathologically after repeated injections of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) into the gingiva. Furthermore, we examined whether the B cells that are stimulated by LPS are involved in osteoclastogenesis in vitro. As a result, the B cell-reconstituted SCID mice showed stronger inflammatory bone resorption than the SCID mice. Also, in vitro, LPS-stimulated B cells enhanced osteoclastogenesis and anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α antibody completely blocked osteoclastogenesis induced by LPS-stimulated B cells. These results suggest that B cells promote inflammatory bone resorption through TNF-α.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aubin JE, Bonnelye E (2000) Osteoprotegerin and its ligand: a new paradigm for regulation of osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption. Osteoporos Int 11:905–913
Fuller K, Wong B, Fox S, Choi Y, Chambers TJ (1998) TRANCE is necessary and sufficient for osteoblast-mediated activation of bone resorption in osteoclasts. J Exp Med 188:997–1001
Lacey DL, Timms E, Tan HL, Kelley MJ, Dunstan CR, Burgess T, Elliot R, Colombero A, Elliott G, Scully S, Hsu H, Sullivan J, Hawkins N, Davy E, Capparelli C, Eli A, Qian YX, Kaufman S, Sarosi I, Shalhoub V, Senaldi G, Guo J, Delaney J, Boyle WJ (1998) Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell 93:165–176
Yasuda H, Shima N, Nakagawa N, Yamaguchi K, Kinosaki M, Mochizuki S, Tomoyasu A, Yano K, Goto M, Murakami A, Tsuda E, Morinaga T, Higashio K, Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Suda T (1998) Osteoclast differentiation factor is a ligand for osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis-inhibitory factor and is identical to TRANCE/RANKL. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:3597–3602
Simonet WS, Lacy DL, Dunstan CR, Kelley M, Chang MS, Luthy R, Nguyen HQ, Wooden S, Bennett L, Boone T, Shimamoto G, DeRose M, Elliott R, Colombero A, Tan HL, Trail G, Sullivan J, Davy E, Bucay N, Renshaw-Gegg L, Hughes TM, Hill D, Pattison W, Campbell P, Boyle WJ (1997) Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the regulation of bone density. Cell 89:309–319
Tsuda E, Goto M, Mochizuki S, Yano K, Kobayashi F, Morinaga T, Higashio K (1997) Isolation of a novel cytokine from human fibroblasts that specifically inhibits osteoclastogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 234:137–142
Yasuda H, Shima N, Nakagawa N, Mochizuki SI, Yano K, Fujise N, Sato Y, Goto M, Yamaguchi K, Kuriyama M, Kanno T, Murakami A, Tsuda E, Morinaga T, Higashio K (1998) Identity of osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor (OCIF) and osteoprotegerin (OPG): a mechanism by which OPG/OCIF inhibits osteoclastogenesis in vitro. Endocrinology 139:1329–1337
Hofbauer LC, Khosla S, Dunstan CR, Lacey DL, Boyle WJ, Riggs BL (2000) The roles of osteoprotegerin and osteoprotegerin ligand in the paracrine regulation of bone resorption. J Bone Miner Res 15:2–12
Jiang Y, Mehta CK, Hsu TY, Alsulaimani FF (2002) Bacteria induce osteoclastogenesis via an osteoblast-independent pathway. Infect Immun 70:3143–3148
Takayanagi H, Ogasawara K, Hida S, Chiba T, Murata S, Sato K, Takaoka A, Yokochi T, Oda H, Tanaka K, Nakamura K, Taniguchi T (2000) T-cell-mediated regulation of osteoclastogenesis by signaling cross-talk between RANKL and IFN-gamma. Nature 408:600–605
Abu-Amer Y, Ross FP, Edwards J, Teitelbaum SL (1997) Lipopolysaccharide-stimulated osteoclastogenesis is mediated by tumor necrosis factor via its P55 receptor. J Clin Invest 100:1557–1565
Hara Y, Ukai T, Yoshimura A, Shiku H, Kato I (1998) Histopathological study of the role of CD4- and CD8-positive T cells on bone resorption induced by Escherichia coli endotoxin. Calcif Tissue Int 63:63–66
Ukai T, Hara Y, Kato I (1996) Effects of T cell adoptive transfer into nude mice on alveolar bone resorption induced by endotoxin. J Periodontal Res 31:414–422
Moriyama H, Ukai T, Hara Y (2002) Interferon-gamma production changes in parallel with bacterial lipoplysaccharide induced bone resorption in mice: an immunohistometrical study. Calcif Tissue Int 71:53–58
Medzhitov R (2001) Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Nature Rev Immunol 1:135–145
Donahue AC, Fruman DA (2003) Proliferation and survival of activated B cells requires sustained antigen receptor engagement and phosphoinositide 3-kinase activation. J Immunol 170:5851–5860
Kanematsu M, Sato T, Takai H, Watanabe K, Ikeda K, Yamada Y (2000) Prostaglandin E2 induces expression of receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand/osteoprotegrin ligand on pre-B cells: implications for accelerated osteoclastogenesis in estrogen deficiency. J Bone Miner Res 15:1321–1329
Manabe N, Kawaguchi H, Chikuda H, Miyaura C, Inada M, Nagai R, Nabeshima Y, Nakamura K, Sinclair AM, Scheuermann RH, Kuro-o M (2001) Connection between B lymphocyte and osteoclast differentiation pathways. J Immunol 167:2625–2631
Nutt SL, Heavey B, Rolink AG, Busslinger M (1999) Commitment to the B-lymphoid lineage depends on the transcription factor Pax5. Nature 401:556–562
Sato T, Shibata T, Ikeda K, Watanabe K (2001) Generation of bone-resorbing osteoclasts from B220+ cells: its role in accelerated osteoclastogenesis due to estrogen deficiency. J Bone Miner Res 16:2215–2221
Weitzmann MN, Cenci S, Haug J, Brown C, DiPersio J, Pacifici R (2000) B lymphocytes inhibit human osteoclastogenesis by secretion of TGFβ. J Cell Biochem 78:318–324
Choi Y, Kim JJ (2003) B cells activated in the presence of Th1 cytokines inhibit osteoclastogenesis. Exp Mol Med 35:385–392
Rossi JF, Chappard D, Marcelli C, Laplante J, Commes T, Baldet P, Janbon C, Jourdan J, Alexandre C, Bataille (1990) R Micro-osteoclast resorption as a characteristic feature of B-cell malignancies other than multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 76:469–475
Masuzawa T, Miyaura C, Onoe Y, Kusano K, Ohta H, Nozawa S, Suda T (1994) Estrogen deficiency stimulates B lymphopoiesis in mouse bone marrow. J Clin Invest 94:1090–1097
Sato Y, Mukai K, Watanabe S, Goto M, Shimosato Y (1986) The AMeX method. A simplified technique of tissue processing and paraffin embedding with improved preservation of antigens for immunostaining. Am J Pathol 125:431–435
Katayama I, Li CY, Yam LT (1972) Histochemical study of acid phosphatase isoenzyme in leukemic reticuloendotheliosis. Cancer 29:157–164
Lam J, Takeshita S, Barker JE, Kanagawa O, Ross FP, Teitelbaum SL (2000) TNF-α induces osteoclastogenesis by direct stimulation of macrophages exposed to permissive levels of RANK ligand. J Clin Invest 106:1481–1488
Kobayashi K, Takahashi N, Jimi E, Udagawa N, Takami M, Kotake S, Nakagawa N, Kinosaki M, Yamaguchi K, Shima N, Yasuda H, Morinaga T, Higashio K, Martin TJ, Suda T (2000) Tumor necrosis factor alpha stimulates osteoclast differentiation by a mechanism independent of the ODF/RANKL-RANK interaction. J Exp Med 191:275–286
Azuma Y, Kaji K, Katogi R, Takeshita S, Kudo A (2000) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces differentiation of and bone resorption by osteoclasts. J Biol Chem 275:4858–4864
Kitaura H, Sands MS, Aya K, Zhou P, Hirayama T, Uthgenannt B, Wei S, Takeshita S, Novack DV, Silva MJ, Abu-Amer Y, Ross FP, Teitelbaum SL (2004) Marrow stromal cells and osteoclast precursors differentially contribute to TNF-alpha-induced osteoclastogenesis in vivo. J Immunol 173:4838–4846
Teng YT, Nguyen H, Gao X, Kong YY, Gorczynski RM, Singh B, Ellen RP, Penninger JM (2000) Functional human T-cell immunity and osteoprotegerin ligand control alveolar bone destruction in periodontal infection J Clin Invest 106:R59–R67
Choi Y, Woo KM, Ko S-H, Lee YJ, Park S-J, Kim H-M, Kwon BS (2001) Osteoclastogenesis is enhanced by activated B cells but suppressed by activated CD8+ T cells. Eur J Immunol 31:2179–2188
Abu-Amer Y, Erdmann J, Alexopoulou L, Kollias G, Ross FP, Teitelbaum SL (2000) Tumor necrosis factor receptors types 1 and 2 differentially regulate osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem 275:27307–27310
Merkel KD, Erdmann JM, McHugh KP, Abu-Amer Y, Ross FP, Teitelbaum SL (1999) Tumor necrosis factor-α mediates orthopedic implant osteolysis. Am J Pathol 154:203–210
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kozuka, Y., Ozaki, Y., Ukai, T. et al. B Cells Play an Important Role in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Bone Resorption. Calcif Tissue Int 78, 125–132 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-005-0149-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-005-0149-x