Abstract
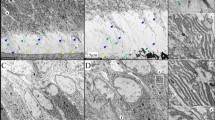
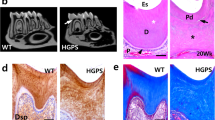
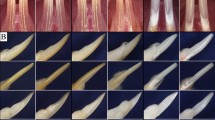
Small leucine-rich proteoglycans have been suggested to affect mineralization of dental hard tissues. To determine the functions of two of these small proteoglycans during the early stages of tooth formation, we characterized the dental phenotypes of biglycan (BGN KO) and decorin deficient (DCN KO) mice and compared them to that of wild type mice. Each targeted gene disruption resulted in specific effects on dentin and enamel formation. Dentin was hypomineralized in both knock out mice, although the effect was more prominent in the absence of decorin. Enamel formation was dramatically increased in newborn biglycan knockout mice but delayed in absence of decorin. Increased enamel formation in the former case resulted from an upregulation of amelogenin synthesis whereas delayed enamel formation in the later case was most probably an indirect consequence of the high porosity of the underlying dentin. Enamelin expression was unchanged in BGN KO, and reduced in DCN KO. Dentin sialoprotein (DSP), a member of the family of phosphorylated extracellular matrix proteins that play a role in dentinogenesis, was overexpressed in BGN-KO odontoblasts and in the sub-odontoblastic layer. In contrast, a decreased expression of DSP was detected in DCN KO. Dentin matrix protein-1 (DMP-1), bone sialoprotein (BSP) and osteopontin (OPN) were upregulated in BGN KO and downregulated in the DCN KO. Despite the strong effects induced by these deficiencies in newborn mice, no significant difference was detected between the three genotypes in adult mice, suggesting that the effects reported here in newborn mice are transient and subjected to self-repair.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruoslahti E (1988) Structure and biology of proteoglycans. Annu Rev Cell Biol 4:229–255
Iozzo RV, Murdoch AD (1996) Proteoglycans of the extracellular environment: clues from the gene and protein side offer novel perspectives in molecular diversity and function. FASEB J 10:598–614
Embery G, Hall R, Waddington R, Septier D, Goldberg M (2001) Proteoglycans in dentinogenesis. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 12:331–349
Fisher LW, Termine JD, Dejter SWJr, Whitson SW, Yanagishita M, Kimura JH, Hascall VC, Kleinman HK, Hassell JR, Nilsson B (1983) Proteoglycans of developing bone. J Biol Chem 258:6588–6594
Cheng H, Caterson B, Neame PJ, Lester GE, Yamauchi M (1996) Differential distribution of lumican and fibromodulin in tooth cementum. Connect Tissue Res 34:87–96
Baylink D, Wergedal J, Thompson E (1972) Loss of proteinpolysaccharides at sites where bone mineralization is initiated. J Histochem Cytochem 20:279–292
Chen CC, Boskey AL. (1985) Mechanisms of proteoglycan inhibition of hydroxyapatite growth. Calcif Tissue Int 37:395–400
Hunter GK (1991) Role of proteoglycan in the provisional calcification of cartilage. A review and reinterpretation. Clin Orthop 262:256–280
Linde A, Bhown M, Butler WT (1980) Noncollagenous proteins of dentin. A re-examination of proteins from rat incisor dentin utilizing techniques to avoid artifacts. J Biol Chem 255:5931–5942
Poole AR, Pidoux I, Rosenberg L (1982) Role of proteoglycans in endochondral ossification: immunofluorescent localization of link protein and proteoglycan monomer in bovine fetal epiphyseal growth plate. J Cell Biol 92:249–260
Ameye L, Young MF (2002) Mice deficient in small leucine-rich proteoglycans: novel in vivo models for osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, muscular dystrophy, and corneal diseases. Glycobiology 12:107R–116R
Iozzo RV (1997) The family of the small leucine-rich proteoglycans: key regulators of matrix assembly and cellular growth. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 32:141–174
Iozzo RV (1999) The biology of the small leucine-rich proteoglycans. Functional network of interactive proteins. J Biol Chem 274:18843–18846
Neame PJ, Kay CJ, McQuillan DJ, Beales MP, Hassell JR (2000) Independent modulation of collagen fibrillogenesis by decorin and lumican. Cell Mol Life Sci 57:859–863
Goldberg M, Takagi M (1993) Dentine proteoglycans: composition, ultrastructure and functions. Histochem J 25:781–806
Goldberg M, Septier D, Rapoport O, Young M, Ameye L (2002) Biglycan is a repressor of amelogenin expression and enamel formation: an emerging hypothesis. J Dent Res 81:520–524
Matsuura T, Duarte WR, Cheng H, Uzawa K, Yamauchi M (2001) Differential expression of decorin and biglycan genes during mouse tooth development. Matrix Biol 20:367–373
Septier D, Hall RC, Embery G, Goldberg M (2001) Immunoelectron microscopic visualization of pro- and secreted forms of decorin and biglycan in the predentin and during dentin formation in the rat incisor. Calcif Tissue Int 69:38–45
Takagi M, Hishikawa H, Hosokawa Y, Kagami A, Rahemtulla F (1990) Immunohistochemical localization of glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans in predentin and dentin of rat incisors. J Histochem Cytochem 38:319–324
Wilda M, Bachner D, Just W, Geerkens C, Kraus P, Vogel W, Hameister H (2000) A comparison of the expression pattern of five genes of the family of small leucine-rich proteoglycans during mouse development. J Bone Miner Res 15:2187–2196
Yoshiba N, Yoshiba K, Iwaku M, Ozawa H (1996) Immunolocalization of the small proteoglycan decorin in human teeth. Arch Oral Biol 41:351–357
Chen XD, Shi S, Xu T, Robey PG, Young MF (2002) Age-related osteoporosis in biglycan-deficient mice is related to defects in bone marrow stromal cells. J Bone Miner Res 17:331–340
Danielson KG, Baribault H, Holmes DF, Graham H, Kadler KE, Iozzo RV (1997) Targeted disruption of decorin leads to abnormal collagen fibril morphology and skin fragility. J Cell Biol 136:729–743
Xu T, Bianco P, Fisher LW, Longenecker G, Smith E, Goldstein S, Bonadio J, Boskey A, Heegaard AM, Sommer B, Satomura K, Dominguez P, Zhao C, Kulkarni AB, Robey PG, Young MF (1998) Targeted disruption of the biglycan gene leads to an osteoporosis-like phenotype in mice. Nat Genet 20:78–82
Fisher LW, Stubbs JTIII, Young MF (1995) Antisera and cDNA probes to human and certain animal model bone matrix noncollagenous proteins. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl 266:61–65
Gibson CW, Kucich U, Collier P, Shen G, Decker S, Bashir M, Rosenbloom J (1995) Analysis of amelogenin proteins using monospecific antibodies to defined sequences. Connect Tissue Res 32:109–114
Dohi N, Murakami C, Tanabe T, Yamakoshi Y, Fukae M, Yamamoto Y, Wakida K, Shimizu M, Simmer JP, Kurihara H, UchidaT (1998) Immunocytochemical and immunochemical study of enamelins, using antibodies against porcine 89-kDa enamelin and its N-terminal synthetic peptide, in porcine tooth germs. Cell Tissue Res 293:313–325
Satchell PG, Anderton X, Ryu OH, Luan X, Ortega AJ, Opamen R, Berman BJ, Witherspoon DE, Gutmann JL, Yamane A, Zeichner-David M, Simmer JP, Shuler CF, Diekwisch TG (2002) Conservation and variation in enamel protein distribution during vertebrate tooth development. J Exp Zool 294:91–106
Goldberg M, Septier D (1996) A comparative study of the transition between predentin and dentin, using various preparative procedures in the rat. Eur J Oral Sci 104:269–277
Ameye L, Aria D, Jepsen K, Oldberg A, Xu T, Young MF (2002) Abnormal collagen fibrils in tendons of biglycan/fibromodulin-deficient mice lead to gait impairment, ectopic ossification, and osteoarthritis. FASEB J 16:673–680
Corsi AT, Xu XD, Chen XD, Boyde A, Liang J, Mankani M, Sommer B, Iozzo RV, Eichstetter I, Robey PG, Bianco P, YoungMF (2002) Phenotypic effects of biglycan deficiency are linked to collagen fibril abnormalities, are synergized by decorin deficiency, and mimic Ehlers-Danlos-like changes in bone and other connective tissues. J Bone Miner Res 17:1180–1189
Fleischmajer R, Fisher LW, MacDonald ED, Jacobs, LJr, Perlish JS, Termine JD (1991) Decorin interacts with fibrillar collagen of embryonic and adult human skin. J Struct Biol 106:82–90
Gafni G, Septier D, Goldberg M (1999) Effect of chondroitin sulfate and biglycan on the crystallization of hydroxyapatite under physiological conditions. Journal of Crystal Growth 205:618–623
Hocking AM, Shinomura T, McQuillan DJ (1998) Leucine-rich repeat glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix. Matrix Biol 17:1–19
Papagerakis P, MacDougall M, Hotton D, Bailleul-Forestier I, Oboeuf M, Berdal A (2003) Expression of amelogenin in odontoblasts. Bone 32:228–240
Schonherr E, Witsch-Prehm P, Harrach B, Robenek H, Rauterberg J, Kresse H (1995) Interaction of biglycan with type I collagen. J Biol Chem 270:2776–2783
Scott JE, Dyne KM, Thomlinson AM, Ritchie M, Bateman J, Cetta G, M.Valli M (1998) Human cells unable to express decoron produced disorganized extracellular matrix lacking “shape modules” (interfibrillar proteoglycan bridges). Exp Cell Res 243:59–66
Veis A, Tompkins K, Alvares K, Wei K, Wang L, Wang XS, Brownell AG, Jengh SM, Healy KE (2000) Specific amelogenin gene splice products have signaling effects on cells in culture and in implants in vivo. J Biol Chem 275:41263–41272
Mitani Y, Honda A, Jasin HE (2001) Polymorphonuclear leukocyte adhesion to articular cartilage is inhibited by cartilage surface macromolecules. Rheumatol Int 20:180–185
Fincham AG, Moradian-Oldak J, Simmer JP (1999) The structural biology of the developing dental enamel matrix. J Struct Biol 126:270–299
Kagayama M, Akita H, SasanoY (1995) Immunohistochemical localization of connexin 43 in the developing tooth germ of rat. Anat Embryol (Berl) 191:561–568
Kasper M, Karsten U, Stosiek P, Moll R (1989) Distribution of intermediate-filament proteins in the human enamel organ: unusually complex pattern of coexpression of cytokeratin polypeptides and vimentin. Differentiation 40:207–214
Nishikawa S, Tsukita S, Tsukita S, Sasa S (1990) Localization of adherens junction proteins along the possible sliding interface between secretory ameloblasts of the rat incisor. Cell Struct Funct 15:245–249
Bianco P, Fisher LW, Young MF, Termine JD, Robey PG (1990) Expression and localization of the two small proteoglycans biglycan and decorin in developing human skeletal and non-skeletal tissues. J Histochem Cytochem 38:1549–1563
Kinsella MG, Tsoi CK, Jarvelainen HT, Wight TN (1997) Selective expression and processing of biglycan during migration of bovine aortic endothelial cells. The role of endogenous basic fibroblast growth factor. J Biol Chem 272:318–325
Weber CK, Sommer G, Michl P, Fensterer H, Weimer M, Gansauge F, Leder G, Adler G, Gress TM (2001) Biglycan is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and induces G1-arrest in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Gastroenterology 121:657–667
Moreno M, Munoz R, Aroca F, Labarca M, Brandan E, Larrain J (2005) Biglycan is a new extracellular component of the Chordin-BMP4 signaling pathway. EMBO J 24:1397–1405
Wiethoff CM, Smith JG, Koe GS, Middaugh CR (2001) The potential role of proteoglycans in cationic lipid-mediated gene delivery. Studies of the interaction of cationic lipid-DNA complexes with model glycosaminoglycans. J Biol Chem 276:32806–32813
Csordas G, Santra M, Reed CC, Eichstetter I, McQuillan DJ, Gross D, Nugent MA, Hajnoczky G, Iozzo RV (2000) Sustained down-regulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor by decorin. A mechanism for controlling tumor growth in vivo. J Biol Chem 275:32879–32887
Iozzo RV, Moscatello DK, McQuillan DJ, Eichstetter I (1999) Decorin is a biological ligand for the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem 274:4489–4492
Snead ML, Luo W, Lau EC, Slavkin HC (1988) Spatial- and temporal-restricted pattern for amelogenin gene expression during mouse molar tooth organogenesis. Development 104:77–85
Wurtz T, Lundmark C, Christersson C, Bawden JW, Slaby I, Hammarstrom L (1996) Expression of amelogenin mRNA sequences during development of rat molars. J Bone Miner Res 11:125–131
InaiT, Kukita T, Ohsaki Y, Nagata K, Kukita A, Kurisu K (1991) Immunohistochemical demonstration of amelogenin penetration toward the dental pulp in the early stages of ameloblast development in rat molar tooth germs. Anat Rec 229:259–270
Nakamura M, Bringas P Jr, Nanci A, Zeichner-David M, Ashdown B, Slavkin HC (1994) Translocation of enamel proteins from inner enamel epithelia to odontoblasts during mouse tooth development. Anat Rec 238:383–396
SawadaT, Nanci A (1995) Spatial distribution of enamel proteins and fibronectin at early stages of rat incisor tooth formation. Arch Oral Biol 40:1029–1038
Beniash E, Traub W, Veis A, Weiner S (2000) A transmission electron microscope study using vitrified ice sections of predentin: structural changes in the dentin collagenous matrix prior to mineralization. J Struct Biol 132:212–225
Goldberg M, Septier D, Escaig-Haye F (1987) Glycoconjugates in dentinogenesis and dentine. Prog Histochem Cytochem 17:1–112
Terasawa M, Shimokawa R, Terashima T, Ohya K, Takagi Y, Shimokawa H ((2004) Expression of dentin matrix protein 1 (DMP1) in nonmineralized tissues. J Bone Miner Metab 22:430–438
Ogbureke KU, Fisher LW (2004) Expression of SIBLINGs and their partener MMPs in salivary glands. J Dent Res 83:664–670
Fisher LW, Jain A, Tayback M, Fedarko NS (2004) Small integrin binding ligand N-linked glycoprotein gene family expression in different cancers. Clin Cancer Res 15:8501–8511
Ogbureke KU, Fisher LW (2005) Renal expression of SIBLING proteins and their partner matrix metalloporteinases (MMPs). Kidney Int 68:155–166
Tartaix PH, Doulaverakis M, George A, Fisher LW, Butler WT, Qin C, Salih E, Tan M, Fujimoto Y, Spevak L, Boskey AL (2004) In vitro effects of dnetin matrix protein-1 on hydroxyapatite formation provide insights into in vivo functions. J Biol Chem 279:18115–18120
Boskey AL (1995) osteopontin and related phosphorylated sialoproteins: effects on mineralization. Ann N Y Acad Sci 21:249–256
Boskey A, Spevak L, Tan M, Doty SB, Butler WT (2000) Dentin sialoprotein (DSP) has limited effects on in vitro apatite formation and growth. Calcif Tissue Int 67:472–478
MacDougall M, Nydegger J, Gu TT, Simmons D, Luan X, Cavender A, D’Souza RN (1998) Developmental regulation of dnetin sialophosphoprotein during ameloblast differentiation: a potential enamel matrix nucleator. Connect Tissue Res 39:25–37
Boskey AL, Muresca S, Doty S, Sabsay B, Veis A (1990) Concentration dependent effects od dentin phosphoryn in the regulation of in vitro hydroxyapatite formation and growth. Bone Mineral 11:55–65
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Karine Vidal for critical reading of the manuscript and Jennifer Clough for reviewing the English. We thanks also the Institute Benjamin Delessert for the grant kindly provided on “Proteoglycans and dental tissues”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goldberg, M., Septier, D., Rapoport, O. et al. Targeted Disruption of Two Small Leucine-rich Proteoglycans, Biglycan and Decorin, Excerpts Divergent Effects on Enamel and Dentin Formation. Calcif Tissue Int 77, 297–310 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-005-0026-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-005-0026-7