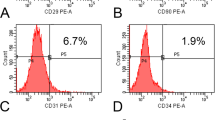
Abstract
It has been well established that core binding factor a-1/osteoblast-specific factor-2 (cbfa1/osf2) is a key regulator of osteoblast differentiation and function, however, it is not known whether it can induce bone formation in vitro and in vivo. To investigate the effect of cbfa1/osf2 on bone formation, we used a recombinant adenoviral vector carrying the mouse cbfa1/osf2 gene to transduce primary cultured bone marrow stromal cells (MSCs) of BALB/c mice. We found that Ad-cbfa1/osf2-transduced MSCs produced cbfa1/osf2 protein and differentiated into osteoblast-like cells. The transduced MSCs had increased alkaline phosphatase activity, increased expression of osteocalcin, osteopontin and bone sialoprotein, and increased matrix mineralization in vitro. To observe the induction of bone formation in vivo, MSCs transduced with Ad-cbfa1/osf2 were transplanted into a 5 mm diameter critical-sized skull defect in BALB/c mice, with type I collagen as scaffolding material. Healing of the defect in treatment and control groups was examined grossly and histologically at four weeks. Skull defects transplanted with Ad-cbfa1/osf2-transduced MSCs had an average of 85% osseous closure at four weeks. Control groups in which the defects were not treated (group 1), treated with collagen only (group 2), or treated with collagen and nontransduced MSCs (group 3) showed little or no osseous healing. These studies indicate that cbfa1/osf2 can induce osteoblast differentiation and bone formation both in vitro and in vivo, suggesting that MSCs transduced with the cbfa1/osf2 gene may be useful in treating bone defects.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
WF Anderson (2001) ArticleTitleExcitement in gene therapy. Hum Gene Ther 12 IssueID12 1483–1484 Occurrence Handle10.1089/10430340152480212 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXmt1Skur0%3D Occurrence Handle11506691
DS Musgrave R Pruchnic P Bosch BH Ziran J Whalen J Huard (2002) ArticleTitleHuman skeletal muscle cells in ex vivo gene therapy to deliver bone morphogenetic protein-2. J Bone Joint Surg Br 84 IssueID1 120–127
KN Kishimoto Y Watanabe H Nakamura S Kokubun (2002) ArticleTitleEctopic bone formation by electroporatic transfer of bone morphogenetic protein-4 gene. Bone 31 IssueID2 340–347 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S8756-3282(02)00825-6 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XlvVWgtbc%3D Occurrence Handle12151088
RT Franceschi D Wang PH Krebsbach RB Rutherford (2000) ArticleTitleGene therapy for bone formation: In vitro and in vivo osteogenic activity of an adenovirus expressing BMP7. J Cell Biochem 78 IssueID3 476–486 Occurrence Handle10.1002/1097-4644(20000901)78:3<476::AID-JCB12>3.0.CO;2-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXltlShtLg%3D Occurrence Handle10861845
MR Urist (1997) ArticleTitleBone morphogenetic protein: the motecularization of skeletal system development. J Bone Miner Res 12 IssueID3 343–346
A Yamaguchi K Toshihisa S Tatsuo (2000) ArticleTitleRegulation of osteoblast differentiation mediated by bone morphogenetic proteins, hedgehogs, and cbfa1. Endocr Re 21 IssueID4 393–411 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXmtlSktLY%3D
G Karsenty (2000) ArticleTitleBone formation and factors affecting this process. Matrix Biol 19 IssueID2 85–89 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXkt1aqurY%3D Occurrence Handle10842091
E Ogawa M Maruyama H Kagoshima M Inuzuka J Lu M Satake K Shigesada Y Ito (1993) ArticleTitlePEBP2/PEA2 represents a family of transcription factors homologous to the products of the Drosophila runt gene and the human AML1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sd USA 90 IssueID14 6859–6863 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXlvFKqtrY%3D
ZS Xiao R Thomas TK Hinson LD Quaries (1998) ArticleTitleGenomic structure and isoform expression of the mouse, rat and human Cbfa1/osf2 transcription factor. Gene 214 IssueID1-2 187–197 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-1119(98)00227-3 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXltlKksLw%3D Occurrence Handle9651525
G Karsenty (2000) ArticleTitleRole of Cbfa1 in osteoblast differentiation and function. Semin Cell Dev Biol 11 IssueID5 343–346 Occurrence Handle10.1006/scdb.2000.0188 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXovVaqsrs%3D Occurrence Handle11105898
P Ducy G Karsenty (1999) ArticleTitleA Cbfa1-dependent genetic pathway controls bone formation beyond embryonic development. Genes Dev 13 IssueID8 1025–1036 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXivFGkurc%3D Occurrence Handle10215629
P Ducy R Zhang V Geoffroy AL Ridall G Karsenty (1997) ArticleTitleOsf2/Cbfa1: a transcriptional activator of osteoblast differentiation. Cell 89 IssueID5 747–754 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXjs1ejsbg%3D Occurrence Handle9182762
C Banerjee LR McCabe JY Choi SW Hiebert JL Stein GS Stein JB Lian (1997) ArticleTitleRunt homology domain proteins in osteoblast differentiation: AML3/CBFA1 is a major component of a bone-specific complex. . 66 IssueID1 1–8 Occurrence Handle10.1006/adnd.1997.0740
B Lee K Thirunavukkarasu L Zhou L Pastore A Baldini J Hecht V Geoffroy P Ducy G Karsenty (1997) ArticleTitleMissense mutations abolishing DNA binding of the osteoblast-specific transcription factor OSF2/CBFA1 in cleidocranial dysplasia. Nat Genet 16 IssueID3 307–410 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXktFKjsL0%3D Occurrence Handle9207800
S Mundlos F Otto C Mundlos JB Mulliken AS Aylsworth S Albright D Lindhout WG Cole W Henn JH Knoll MJ Owen R Mertelsmann BU Zabei BR Olsen (1997) ArticleTitleMutations involving the transcription factor CBFA1 cause cleidocranial dysplasia. Cell 89 IssueID5 773–779 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXjs1ejt74%3D Occurrence Handle9182765
T Komori H Yagi S Nomura A Yamaguchi K Sasaki K Deguchi Y Shimizu RT Bronson YH Gao M Inada M Sato R Okamoto Y Kitamura S Yoshiki T Kishimoto (1997) ArticleTitleTargeted disruption of Cbfa1 results in a complete lack of bone formation owing to maturational arrest of osteoblasts. Cell 89 IssueID5 755–764 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXjs1ejtr4%3D Occurrence Handle9182763
P Ducy M Starbuck M Priemel J Shen G Pinero V Geoffroy M Amling G Karsenty (1999) ArticleTitleA Cbfa1-dependent genetic pathway controls bone formation beyond embryonic development. Genes Dev 13 IssueID8 1025–1036 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXivFGkurc%3D Occurrence Handle10215629
G Karsenty P Ducy M Starbuck M Priemel J Shen V Geoffroy M Amling (1999) ArticleTitleCbfa1 as a regulator of osteoblast differentiation and function. Bone 25 IssueID1 107–108 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S8756-3282(99)00111-8 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1MzkvFyqtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10423032
TC He S Zhou LT da Costa J Yu KW Kinzler B Vogelstein (1998) ArticleTitleA simplified system for generating recombinant adenoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95 IssueID5 2509–2514 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXhslehsLw%3D Occurrence Handle9482916
SL Cheng J Lou NM Wright CF Lai LV Avioli KD Riew (2001) ArticleTitle In vitro and in vivo induction of bone formation using a recombinant adenoviral vector carrying the human BMP-2 gene. Calcif Tissue Int 68 IssueID2 87–94 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXkvFersr4%3D Occurrence Handle11310352
JY Lee D Musgrave D Pelinkovic K Fukushima J Cummins A Usas P Robbins FH Fu J Huard (2001) ArticleTitleEffect of bone morphogenetic protein-2-expressing muscle-derived cells on healing of critical-sized bone defects in mice. J Bone Joint Surg Am 83-A IssueID7 1032–1039 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MvgtVGrtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11451972
JO Taboas RJ Ceremsak (1967) ArticleTitleA rapid hematoxylin and eosin stain. Tech Bull Regist Med Technol 37 IssueID4 119–120 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CCiB2MnptFE%3D Occurrence Handle4167192
I Reiter M Tzukerman G Maor (2002) ArticleTitleSpontaneous differentiating primary chondrocytic tissue culture: a model for endochondral oassification. Bone 31 IssueID2 333–339 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S8756-3282(02)00823-2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XlvVWgtbg%3D Occurrence Handle12151087
S Spinella-Jaegle S Roman-Roman C Faucheu FW Dunan S Kawai S Gallea V Stiot AM Blanchet B Courtois R Baron G Rawadi (2001) ArticleTitleOpposite effects of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and transforming growth factor-beta1 on osteoblast differentiation. Bone 29 IssueID4 323–330 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S8756-3282(01)00580-4 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXnsVSlsLg%3D Occurrence Handle11595614
G Karsenty (1999) ArticleTitleThe genetic transformation of bone biology. Genes Dev 13 IssueID23 3037–3051 Occurrence Handle10.1101/gad.13.23.3037 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXhtFOitQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10601030
A Vortkamp S Pathi GM Peretti EM Caruso DJ Zaleske CJ Tabin (1998) ArticleTitleRecapitulation of signals regulating embryonic bone formation during postnatal growth and in fracture repair. Mech Dev 71 IssueID1–2 65–76 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0925-4773(97)00203-7 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXhs1Ggtro%3D Occurrence Handle9507067
C Ferguson E Alpem T Miclau JA Helms (1999) ArticleTitleDoes adult fracture repair recapitulate embryonic skeletal formation?. Mech Dev 87 IssueID1–2 57–66 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0925-4773(99)00142-2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXmtVyjtrc%3D Occurrence Handle10495271
DA Oakes JR Lieberman (2000) ArticleTitleOsteoinductive applications of regional gene therapy: ex vivo gene transfer. Clin Orthop 379 IssueIDsupp S101–112 Occurrence Handle11039758
SP Bruder N Jaiswal NS Ricalton JD Mosca KM Kraus S Kadiyala (1998) ArticleTitleMesenchymai stem cells in osteobiology and applied bone regeneration. Clin Orthop 355 IssueIDsupp S247–256 Occurrence Handle9917644
MJ Jimenez M Balbin JM Lopez J Alvarez T Komori C Lopez-Otin (1999) ArticleTitleCollagenase 3 is a target of Cbfa1, a transcription factor of the runt gene family involved in bone formation. Mol Cell Biol 19 IssueID6 4431–4442 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjt1yis7w%3D Occurrence Handle10330183
H Harada S Tagashira M Fujiwara S Ogawa T Katsumata A Yamaguchi T Komori M Nakatsuka (1999) ArticleTitleCbfa1 isoforms exert functional differences in osteoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem 274 IssueID11 6972–6978 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXhvFWqtL4%3D Occurrence Handle10066751
C Banerjee LR McCabe JY Choi SW Hiebert JL Stein GS Stein JB Lian (1997) ArticleTitleRunt homology domain proteins in osteoblast differentiation: AML3/CBFA1 is a major component of a bone-specific complex. J Cell Biochem 66 IssueID1 1–8 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-4644(19970701)66:1<1::AID-JCB1>3.0.CO;2-V Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXktl2isL0%3D Occurrence Handle9215522
A Banfi A Muraglia B Dozin M Mastrogiacomo R Cancedda R Quarto (2000) ArticleTitleProliferation kinetics and differentiation potential of ex vivo expanded human bone marrow stromal cells: implications for their use in cell therapy. Exp Hernatol 28 IssueID6 707–715 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0301-472X(00)00160-0 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3czpsFeisQ%3D%3D
S Tamura H Kataoka Y Matsui Y Shionoya K Ohno KI Michi K Takahashi A Yamaguchi (2001) ArticleTitleThe effects of transplantation of osteoblastic cells with bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)/carrier complex on bone repair. Bone 29 IssueID2 169–175 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S8756-3282(01)00498-7 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXlvFWkurs%3D Occurrence Handle11502479
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Karsenty G (Department of Molecular and Human Genetics, Baylor College of Medicine, Huston, TX) for providing cDNA of mouse cbfa1/osf2 and Dr. He TC (Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Baltimore, MD) for providing the AdEasy System.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, H., Guo, Z., Ma, Q. et al. Cbfa1/osf2 Transduced Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Facilitate Bone Formation In Vitro and In Vivo . Calcif Tissue Int 74, 194–203 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-003-0004-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-003-0004-x