Abstract
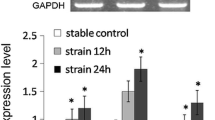
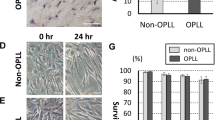
Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine (OPLL) is characterized by ectopic bone formation in the spinal ligaments. Mechanical stress, which acts on the posterior ligaments, is thought to be an important factor in the progression of OPLL. To clarify this mechanism, we investigated the effects of in vitro cyclic stretch (120% peak to peak, at 0.5 Hz) on cultured spinal ligament cells derived from OPLL (OPLL cells) and non-OPLL (non-OPLL cells) patients. The mRNA expressions of Cbfa1 (an osteoblast-specific transcription factor), type I collagen, alkaline phosphatase (ALP), osteocalcin and integrin β1 (a mechanotransducer) were increased by cyclic stretch in OPLL cells, whereas no change was observed in non-OPLL cells. The effects of cyclic stretch on the spinal ligament tissues derived from OPLL and non-OPLL patients were also analyzed by immunohistochemistry using an antibody against Cbfa1. The expression of Cbfa1 was increased by cyclic stretch at the center of the spinal ligament tissues of OPLL patients, whereas no change was observed in the tissues of non-OPLL patients. Furthermore, U0126, a specific inhibitor of MAPK kinase (MEK), suppressed the stretch-induced mRNA expressions of Cbfa1, ALP and type I collagen in OPLL cells. These results suggest that in OPLL cells, mechanical stress is converted by integrin β1 into intracellular signaling and that Cbfa1 is activated through the MAP kinase pathway. Therefore, we propose that mechanical stress plays a key role in the progression of OPLL through an increase in Cbfa1 expression.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
D Resnick SR Shaul JM Robins (1975) ArticleTitleDiffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH). Radiography 115 513–524 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSqC2Mbgs1M%3D
PN Wang SS Chen HC Liu JL Fuh BI Kuo SJ Wang (1999) ArticleTitleOssification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. A case-control risk factor study. Spine 24 142–144 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00007632-199901150-00010 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M7isFajtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9926384
H Baba N Furusawa M Fukuda Y Maezawa S Imura N Kawahara K Nakahashi K Tomita (1997) ArticleTitlePotential role of streptozotocin in enhancing ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the cervical spine in hereditary spinal hyperostotic mouse (twy/twy). Eur J Histochem 41 191–202 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXntlSmtbg%3D Occurrence Handle9359030
Y Ishida S Kawai (1993) ArticleTitleCharacteraixation of cultured cells derived from ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. Bone 14 85–91 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyA38nks1M%3D Occurrence Handle8392854
K Inaba S Matsunaga Y Ishidou T Imamura H Yoshida (1996) ArticleTitleEffect of transforming growth factor-beta on fibroblasts in ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. In Vivo 10 445–449 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XltF2qs78%3D Occurrence Handle8839792
T Kon M Yamazaki M Tagawa S Goto A Terakado H Moriya S Fujimura (1997) ArticleTitleBone morphogenetic protein-2 stimulates differentiation of cultured spnal ligament cells from patients with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Calcif Tissue Int 60 291–296 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002239900231 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXhsFKgs7k%3D Occurrence Handle9069168
K Goto M Yamazaki M Tagawa S Goto T Kon H Moriya S Fujimura (1998) ArticleTitleInvolvement of insuline-like growth factor I in development of ossification the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. Calcif Tissue Int 62 158–165
Y Ishida S Kawai (1993) ArticleTitleEffects of bone-seeking hormones on DNA synthesis, cyclic AMP level, and alkaline phosphatase activity in cultured cells from human posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. J Bone Miner Res 8 1291–1300
K Yonemori T Imamura Y Ishidou T Okano S Matsunaga H Yoshida M Kato TK Sampath K Miyazono P ten Dijke T Sakou (1997) ArticleTitleBone morphogenetic protein receptors and activin receptors are highly expressed in ossified ligament tissues of patients with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Am J Pathol 150 1335–1347 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiB2cbgvVE%3D Occurrence Handle9094990
H Koga T Sakou E Taketomi K Hayashi T Numasawa S Harata K Yone S Matsunaga B Otterud I Inoue M Leppert (1998) ArticleTitleGenetic mapping of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. Am J Hum Genet 62 1460–1467
T Numasawa H Koga K Ueyama S Maeda T Sakou S Harata M Leppert I Inoue (1999) ArticleTitleHuman retinoic X receptor beta: complete genomic sequence and mutation search for ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. J Bone Miner Res 14 500–508
K Furushima K Shimo-onoda S Maeda T Nobukuni K Ikari H Koga S Komiya T Nakajima S Harata I Inoue (2002) ArticleTitleLarge-scale screening for candidate genes of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. J Bone Miner Res 17 128–137
S Matsunaga T Sakou E Taketomi M Yamaguchi T Okano (1994) ArticleTitleThe natural course of myelopathy caused by ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament in the cervical spine. Clin. Orthop 305 168–177 Occurrence Handle8050226
H Nakamura (1994) ArticleTitleA radiographic study of the progression of ossification of the cervical posterior longitudinal ligament: the correlation between the ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament and that of the anterior longitudinal ligament. Nippon Seikeigeka Gakkai Zasshi 68 725–736 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqD2MzhtVw%3D Occurrence Handle7963927
T Takatsu Y Ishida K Suzuki H Inoue (1999) ArticleTitleRadiological study of cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J Spinal Disord 12 271–273 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1MzhtVWmtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10382784
S Matsunaga T Sakou E Taketomi K Nakanishi (1996) ArticleTitleEffects of strain distribution in the intervertebral discs on the progression of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligaments. Spine 21 184–189 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00007632-199601150-00005 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymA287lvFU%3D Occurrence Handle8720402
Y Yamamoto K Furukawa K Ueyama T Nakanishi M Takigawa S Harata (2002) ArticleTitlePossible roles of CTGF/Hcs24 in the initiation and development of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine 27 1852–1857 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00007632-200209010-00009 Occurrence Handle12221348
G Karsenty (1999) ArticleTitleThe genetic transformation of bone biology. Genes Dev 13 3037–3051 Occurrence Handle10.1101/gad.13.23.3037 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXhtFOitQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10601030
P Ducy G Karsenty (1995) ArticleTitleTwo distinct osteoblastic-specific cis-acting elements control expression of a mouse osteocalcin gene. Mol Cell Biol 15 1858–1869 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXksFWjsb4%3D Occurrence Handle7891679
H Harada S Tagashira M Fujiwara S Ogawa T Katsumata A Yamaguchi T Komori M Nakatsuka (1999) ArticleTitleCbfa1 isoforms exert functional differences in osteoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem 274 6972–69678 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXhvFWqtL4%3D Occurrence Handle10066751
B Kern J Shen M Starbuck G Karsenty (2001) ArticleTitleCbfa1 contributes to the osteoblast-specific expression of Type I collagen genes. J Biol Chem 276 7101–7107 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.M006215200 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXitVKlt7Y%3D Occurrence Handle11106645
P Ducy R Zhang V Geoffroy AL Ridall G Karsenty (1997) ArticleTitleOsf2/Cbfa1: a transcriptional activator of osteoblast differentiation. Cell 89 747–774 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXjs1ejsbg%3D Occurrence Handle9182762
P Ducy M Starbuck M Priemel J Shen G Pinero V Geoffrey M Amling G Karsenty (1999) ArticleTitleA Cbfa1-dependent genetic pathway controls bone formation beyond embryonic development. Genes Dev 13 1025–1036 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXivFGkurc%3D Occurrence Handle10215629
RA Hipskind G Bilbe (1998) ArticleTitleMAP kinase signaling cascades and gene expression in osteoblasts. Front Biosci 3 D804–D816 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXlvVWlsLs%3D Occurrence Handle9682034
J Lou Y Tu S Li PR Manske (2000) ArticleTitleInvolvement of ERK in BMP-2 induced osteoblastic differentiation of mesenchymal progenitor cell line C3H10T1/2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 268 757–762 Occurrence Handle10.1006/bbrc.2000.2210 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXhtFGis7g%3D Occurrence Handle10679278
S Gallea F Lallemand A Atfi G Rawadi V Ramez S Spinella-Jaegle S Kawai C Faucheu L Huet R Baron S Roman-Roman (2001) ArticleTitleActivation of mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades is involved in regulation of bone morphogenetic protein-2-induced osteoblast differentiation in pluripotent C2C12 cells. Bone 28 491–498 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S8756-3282(01)00415-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjtlChsL0%3D Occurrence Handle11344048
Z Huang SL Cheng E Slatopolsky (2001) ArticleTitleSustained activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway is required for extracellular calcium stimulation of human osteoblast proliferation. J Biol Chem 276 21351–21358 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.M010921200 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXksFGltbw%3D Occurrence Handle11292824
CF Lai L Chaudhary A Fausto LR Halstead DS Ory LV Avioli SL Cheng (2001) ArticleTitleErk is essential for growth, differentiation, integral expression, and cell function in human osteoblastic cells. J Biol Chem 276 14443–14450 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjt12rtLg%3D Occurrence Handle11278600
D Ingber (1991) ArticleTitleIntegrins as mechanochemical transducers. Curr Opin Cell Biol 3 841–848 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XhvFWnt7s%3D Occurrence Handle1931084
DA MacKenna F Dolfi K Vuori E Ruoslahti (1998) ArticleTitleExtracellular signal-regulated kinase and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activation by mechanical stretch is integrin-dependent and matrix-specific in rat cardiac fibroblasts. J Clin Invest 101 301–310 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXmtF2jtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9435301
FM Pavalko NX Chen CH Turner DB Burr S Atkinson YF Hsieh J Qiu RL Duncan (1998) ArticleTitleFluid shear-induced mechanical signaling in MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts requires cytoskeleton-integrin interactions. Am J Physiol 275 C1591–1601 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXhsFGltA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9843721
C Schmidt H Pommerenke F Durr B Nebe J Rychly (1998) ArticleTitleMechanical stressing of integrin receptors induces enhanced tyrosine phosphorylation of cytoskeletally anchored proteins. J Biol Chem 273 5081–5085 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXhs1Cgurg%3D Occurrence Handle9478959
H Pommerenke C Schmidt F Durr B Nebe F Luthen P Muller J Rychly (2002) ArticleTitleThe mode of mechanical integrin stressing controls intracellular signaling in osteoblasts. J Bone Miner 17 603–611
A Togari M Arai S Mizutani S Mizutani Y Koshihara T Nagatsu (1997) ArticleTitleExpression of mRNAs for neuropeptide receptors and beta-adrenergic receptors in human osteoblasts and human osteogenic sarcoma cells. Neurosci Lett 233 125–128 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3940(97)00649-6 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXmtlCntL0%3D Occurrence Handle9350848
L Tou N Quibria JM Alexander (2001) ArticleTitleRegulation of human cbfa1 gene transcription in osteoblasts by selective estrogen receptor modulators. Mol Cell Endocrinol 183 71–79 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0303-7207(01)00594-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXnsF2gsr4%3D Occurrence Handle11604227
MJ Buckley AJ Banes RD Jordan (1990) ArticleTitleThe effects of mechanical strain on osteoblasts in vitro. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 48 276–282 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BC2MrlvF0%3D Occurrence Handle2303937
LV Harter KA Hruska RL Duncan (1995) ArticleTitleHuman osteoblast-like cells respond to mechanical strain with increased bone matrix protein production independent of hormonal regulation. Endocrinology 136 528–535 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXjtleitLw%3D Occurrence Handle7530647
D Pavlin SB Dove R Zadro J Gluhak-Heinrich (2000) ArticleTitleMechanical loading stimulates differentiation of periodontal osteoblasts in a mouse osteoinduction model: effect on type I collagen and alkaline phosphatase genes. Calcif Tissue Int 67 163–172
Miyagawa J, Tanaka K, Ohkuma T (1983) The range of motion of cervical spine in ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Proceeding of the investigation committee on ossification of the spinal ligament. Tokyo: Investigation committee on ossification of the spinal ligament:168–176 (In Japanese)
Tominaga S (1981) The relationship between dynamic cervical motion and symptoms on myelopathy due to OPLL in the cervical spine. Proceeding of the investigation committee on ossification of the spinal ligament. Tokyo: Investigation committee on ossification of the spinal ligament:136–142 (In Japanese)
Nakamura H, Okajima Y, Hasegawa K (1993) Analysis of the dynamic cervical motion. Proceeding of the investigation committee on ossification of the spinal ligament. Tokyo: Investigation committee on ossification of the spinal ligament:173–176 (In Japanese)
P Ducy (2000) ArticleTitleCbfa1: a molecular switch in osteoblast biology. Dev Dyn 219 461–471 Occurrence Handle10.1002/1097-0177(2000)9999:9999<::AID-DVDY1074>3.0.CO;2-C Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXovVSgsbY%3D Occurrence Handle11084646
G Karsenty (2000) ArticleTitleRole of Cbfa1 in osteoblast differentiation and function. Semin Cell Dev Biol 11 343–346
M Inada T Yasui S Nomura S Miyake K Deguchi M Himeno M Sato H Yamagiwa T Kimura N Yasui T Ochi N Endo Y Kitamura T Kishimoto T Komori (1999) ArticleTitleMaturational disturbance of chondrocytes in Cbfa1-deficient mice. Dev Dyn 214 279–290 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-0177(199904)214:4<279::AID-AJA1>3.0.CO;2-W Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXitlOrs7w%3D Occurrence Handle10213384
EC Breen (2000) ArticleTitleMechanical strain increases type I collagen expression in pulmonary fibroblasts in vitro. J Appl Physiol 88 203–209 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXhtlGgtbw%3D Occurrence Handle10642382
PG Ziros AP Gil T Georgakopoulos I Habeos D Kletsas EK Basdra AG Papavassiliou (2002) ArticleTitleThe bone-specific transcriptional regulator Cbfa1 is a target of mechanical signals in osteoblastic cells. J Biol Chem 277 23934–23941 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.M109881200 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XltF2msrs%3D Occurrence Handle11960980
G Xiao R Gopalakrishnan D Jiang E Reith MD Benson RT Franceschi (2002) ArticleTitleBone morphogenetic proteins, extracellular matrix, and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways are required for osteoblast-specific gene expression and differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells. J Bone Miner Res 17 101–110
RS Carvalho JE Scott EH Yen (1995) ArticleTitleThe effects of mechanical stimulation on the distribution of beta 1 integrin and expression of beta 1-integrin mRNA in TE-85 human osteosarcoma cells. Arch Oral Biol 40 257–264 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0003-9969(95)98814-F Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXmt1eqs7k%3D Occurrence Handle7541624
RS Carvalho A Bumann C Schwarzer E Scott EH Yen (1996) ArticleTitleA molecular mechanism of integrin regulation from bone cells stimulated by orthodontic forces. Eur J Orthod 18 227–235 Occurrence Handle8791887
RH Kramer N Marks (1989) ArticleTitleIdentification of integrin collagen receptors on human melanoma cells. J Biol Chem 264 4684–4688 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXhslWjtrw%3D Occurrence Handle2538453
P Vihinen T Riikonen A Laine J Heino (1996) ArticleTitleIntegrin alpha 2 beta 1 in tumorigenic human osteosarcoma cell lines regulates cell adhesion, migration, and invasion by interaction with type I collagen. Cell Growth Differ 7 439–447 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XitFegt7o%3D Occurrence Handle9052985
Y Takeuchi K Nakayama T Matsumoto (1996) ArticleTitleDifferentiation and cell surface expression of transforming growth factor-beta receptors are regulated by interaction with matrix collagen in murine osteoblastic cells. J Biol Chem 271 3938–3944 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.271.7.3938 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XhtFOrsr8%3D Occurrence Handle8632016
A Jikko SE Harris D Chen DL Mendrick CH Damsky (1999) ArticleTitleCollagen integrin receptors regulate early osteoblast differentiation induced by BMP-2. J Bone Miner Res 14 1075–1083
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. Kazuhiko Seya and Miki Hashimoto of the Department of Pharmacology, Hirosaki University School of Medicine and Drs. Hirotaka Ohishi and Tomohiro Iwasawa of the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, for their technical assistance. We also acknowledge professors Hiroto Kimura, Keiichi Takagaki and Hideki Mizunuma, Hirosaki University School of Medicine, for their valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iwasaki, K., Furukawa, KI., Tanno, M. et al. Uni-axial Cyclic Stretch Induces Cbfa1 Expression in Spinal Ligament Cells Derived from Patients with Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament . Calcif Tissue Int 74, 448–457 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-002-0021-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-002-0021-1