Abstract
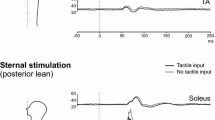
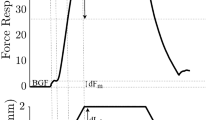
Fifteen patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1A (CMT1A) disease and 46 normal controls were studied. In the patients, leg muscle strength, touch-pressure, vibration and joint position sense were reduced; lower limb ten-don reflexes were absent in 12 or markedly decreased. Motor and sensory conduction velocity (CV) of leg nerves was either reduced or not measurable. The Neurological Disability Score and the Neuropathy Score were obtained from clinical and electrophysiological examination, respectively. Tilt of a supporting platform elicited short- (SLR) and medium-latency (MLR) responses to stretch in the foot muscle flexor digitorum brevis (FDB) in controls. In the patients, the former response was absent and the latter delayed. These findings are in keeping with the known loss of large-diameter myelinated fibres, with relative sparing of the smaller fibres. The MLR delay was fully accounted for by the slowed CV of the motor fibres. The MLR afferent time was similar to that in normal subjects. Body sway area (SA) during quiet stance was recorded with eyes open or closed, and with feet apart or together. Under all postural and visual conditions, SA was within normal range in the less severely affected patients, but was moderately increased in the patients with a more severe neuropathy score. Across all patients, no correlation was found between SA and muscle force, motor CV, touch pressure, vibration and joint position sense, considered either separately or as an aggregate. We suggest that: (1) functional integrity of the largest afferent fibres is not necessary for appropriate equilibrium control during quiet stance and (2) any unsteadiness is related to additional functional alterations in smaller fibres, most likely group II spindle afferent fibres.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asbury AK, Consensus Panel (1988) Report and Recommendations of the San Antonio Conference on Diabetic Neuropathy. Neurology 38:1161–1165
Behse F, Buchthal F, Carlsen F (1977) Nerve biopsy and conduction studies in diabetic neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 40:1072–1082
Bergin PS, Bronstein AM, Murray NMF, Sancovic S, Zeppenfeld normal aging and in patients with polyneuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 58:335–340
Coma S, Tarantola J, Nardone A, Giordano A, Schieppati M (1999) Standing on a continuously moving platform: is body inertia counteracted or exploited? Exp Brain Res 124:331–341
Diener HC, Dichgans J, Bacher M, Gompf B (1984a) Quantification of postural sway in normals and patients with cerebellar disease. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 57:134–142
Diener HC, Dichgans J, Guschlbauer B, Mau H (1984b) The significance of proprioception on postural stabilization as assessed by ischemia. Brain Res 296:103–109
Dietz V, Mauritz K-H, Dichgans J (1980) Body oscillations in balancing due to segmental stretch reflex activity. Exp Brain Res 40:89–95
Dyck PJ, Sherman WR, Hallcher LM, Service FJ, O’Brien PC, Grina LA, Palumbo PJ, Swanson CJ (1980) Human diabetic endoneurial sorbitol, fructose, and myo-inositol related to sural nerve morphometry. Ann Neurol 8:590–596
Dyck PJ, Chance P, Lebo R, Carney JA (1993a) Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathies. In: Dyck PJ, Thomas PK, Griffin JW, Low PA, Poduslo JF (eds) Peripheral neuropathy. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 1094–1136
Dyck PJ, O’Brien PC, Kosanke JL, Gillen DA, Karnes JL (1993b) A 4, 2, and 1 stepping algorithm for quick and accurate estimation of cutaneous sensation threshold. Neurology 43:1508–1512
Fitzpatrick R, McCloskey DI (1994) Proprioceptive, visual and vestibular thresholds for the perception of sway during standing in humans. J Physiol (Lond) 478:173–186
Gatev P, Thomas S, Kepple T, Hallett M (1999) Feedforward ankle strategy of balance during quiet stance in adults. J Physiol (Lond) 514:915–928
Griffin JW, Cornblath DR, Alexander E, Campbell J, Low PA, Bird S, Feldman EL (1990) Ataxic sensory neuropathy and dorsal root ganglionitis associated with Sjogren’s syndrome. Ann Neurol 27:304–315
Gurfinkel EV (1973) Physical foundations of stabilography. Agressologie 14:9–13
Horak FB, Macpherson JM (1996) Postural orientation and equilibrium. In: Rowell LB, Shepherd JT (eds) Handbook of physiology, sect 12. Exercise: regulation and integration of multiple systems. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 255–292
Katz R, Meunier S, Pierrot-Deseilligny E (1988) Changes in pre-synaptic inhibition of la fibres in man while standing. Brain 111:417–437
Koceja DM, Trimble MH, Earles DR (1993) Inhibition of the soleus H reflex in standing man. Brain Res 629:155–158
Le Quesne PM, Fowler CJ, Parkhouse N (1990) Peripheral neuropathy profile in various groups of diabetics. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 53:558–563
Magnusson M, Enbom H, Johansson R, Pyykko I (1990) Significance of pressor input from the human feet in anterior-posterior postural control. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 110:182–188
Mauritz K-H, Dichgans J, Hufschmidt A (1979) Quantification of postural sway in late cortical cerebellar atrophy of the anterior lobe and other forms of cerebellar ataxia. Brain 102:461–482
Morasso P, Schieppati M (1999) Can muscle stiffness alone stabilize upright standing? J Neurophysiol 83:1622–1626
Nardone A, Schieppati M (1998) Mediumlatency response to muscle stretch in human lower limb: estimation of conduction velocity of group II fibres and central delay. Neurosci Lett 249:29–32
Nardone A, Di Francesco G, Schieppati M (1986) Reflex excitability of the soleus mucle in standing man, at rest or prior to a voluntary triceps contraction. Neurosci Lett 26:S165
Nardone A, Giordano A, Corra T, Schieppati M (1990) Responses of leg muscles in humans displaced while standing. Effects of types of perturbation and of postural set. Brain 113:65–84
Nardone A, Siliotto R, Grasso M, Schieppati M (1995) Influence of aging on leg muscle reflex responses to stance perturbation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 76:158–165
Nardone A, Grasso M, Giordano A, Schieppati M (1996) Different effect of height on latency of leg and foot short- and medium-latency EMG responses to perturbation of stance in humans. Neurosci Lett 206:89–92
Nardone A, Pisano F, Miscio G, Azan G (1997a) Demyelinating neuropathy affects to a different extent the short- and medium-latency responses of lower limb muscles to stance perturbation. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2:99
Nardone A, Tarantola J, Giordano A, Schieppati M (1997b) Fatigue effects on body balance. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 105:309–320
Nardone A, Miscio G, Pisano F, Schieppati M (1998) Sensory ataxia in polyneuropathy is connected to dysfunction of group II afferent fibers. J Peripher Nerv Syst 3:151
Nardone A, Corna S, Grasso M, Tarantola J, Schieppati M (1999) Role of group II spindle afferent fibres in balance control. International symposium on gait disorders. Galen, Prague, pp 191–192
Nardone A, Grasso M, Tarantola J, Corna S, Schieppati M (2000) Postural coordination in elderly subjects standing on a periodically moving platform. Arch Phys Med Rehabil (in press)
Pareyson D (1999) Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and related neuropathies: molecular basis for distinction and diagnosis. Muscle Nerve 22:1498–1509
Peterka RJ, Benolken MS (1995) Role of somatosensory and vestibular cues in attenuating visually induced human postural sway. Exp Brain Res 105:101–110
Schieppati M, Nardone A (1997) Medium-latency stretch reflexes of foot and leg muscles analysed by cooling the lower limb in standing humans. J Physiol (Lond) 503:691–698
Schieppati M, Nardone A (1999) Group II spindle afferent fibers in humans: their possible role in the reflex control of stance. In: Binder MD (ed) Progress in brain research, vol 123. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp 461–472
Schieppati M, Hugon M, Grasso M, Nardone A, Galante M (1994) The limits of equilibrium in young and elderly normal subjects and in parkinsonians. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 93:286–298
Schieppati M, Nardone A, Siliotto R, Grasso M (1995) Early and late stretch responses of human foot muscles induced by perturbation of stance. Exp Brain Res 105:411–422
Schieppati M, Tacchini E, Nardone A, Tarantola J, Corna S (1999) Subjective perception of body sway. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 66:313–322
Simoneau GG, Ulbrecht JS, Derr JA, Becker CKMB, Cavanagh PR (1994) Postural instability in patients with diabetic sensory neuropathy. Diabetes Care 17:1411–1421
Weiss JA, White JC (1986) Correlation of 1A afferent conduction with the ataxia of Fisher syndrome. Muscle Nerve 9:327–332
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published online: 11 August 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nardone, A., Tarantola, J., Miscio, G. et al. Loss of large-diameter spindle afferent fibres is not detrimental to the control of body sway during upright stance: evidence from neuropathy. Exp Brain Res 135, 155–162 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210000513
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210000513