Abstract
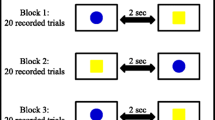
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) of 1 mA for 13 min was reported to create a linear inter-dependency between the intensity and duration of the current and the effects of the stimulation. tDCS on the primary motor cortex (M1) has been shown to have an effect on both motor-evoked potential (MEP) and motor learning. However, recent findings have shown that the known linear effect is invalid in a 2 mA stimulation for 20 min, where cathodal stimulation led to excitability, rather than inhibition, as measured by MEP changes. Here we aim to replicate the non-linear effect of cathodal stimulation over the M1, using a cognitive task. Twenty-two healthy subjects participated in three sessions, where they were administered with a 2 mA anodal and cathodal stimulation for 20 min over the left M1, and a sham stimulation, while performing the serial reaction time task (SRTT). The overall analysis failed to show any effects of either polarity of tDCS on SRTT performance and hence did not replicate previous findings. However, given our goal to replicate the previously reported reversed polarity effects on MEP, we conducted an exploratory analysis to see whether there were any more subtle signs of a change in sign of the cathodal effect compared with anodal. Anodal stimulation led to faster performance than cathodal stimulation before 13 min of stimulation have passed, however, after 13 min, the pattern had switched, and performance under cathodal stimulation was faster. We conclude that cathodal tDCS has a non-linear effect, and the known polarity-dependent effects of tDCS shift after 13 min of stimulation, leading to an increased, rather than decreased, excitability.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrus GG, Chaieb L, Stilling R, Rothkegel H, Antal A, Paulus W (2016) Monitoring transcranial direct current stimulation induced changes in cortical excitability during the serial reaction time task. Neurosci Lett 616:98–104
Batsikadze G, Moliadze V, Paulus W, Kuo MF, Nitsche MA (2013) Partially non-linear stimulation intensity-dependent effects of direct current stimulation on motor cortex excitability in humans. J Physiol 591(7):1987–2000. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2012.249730
Buch ER, Santarnecchi E, Antal A, Born J, Celnik PA, Classen J et al (2017) Effects of tDCS on motor learning and memory formation: a consensus and critical position paper. Clin Neurophysiol 128(4):589–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2017.01.004
Chew T, Ho KA, Loo CK (2015) Inter-and intra-individual variability in response to transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) at varying current intensities. Brain Stimul 8(6):1130–1137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2015.07.031
Fitz NS, Reiner PB (2013) The challenge of crafting policy for do-it-yourself brain stimulation. J Med Ethics Medethics 2013. https://doi.org/10.1136/medethics-2013-101458
Foerster Á, Rocha S, Wiesiolek C, Chagas AP, Machado G, Silva E et al (2013) Site-specific effects of mental practice combined with transcranial direct current stimulation on motor learning. Eur J Neurosci 37(5):786–794. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.12079
Fox PT, Narayana S, Tandon N, Fox SP, Sandoval H, Kochunov P, Capaday C, Lancaster JL (2006) Intensity modulation of TMS-induced cortical excitation: primary motor cortex. Hum Brain Mapp 27:478–487. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20192
Jacobson L, Koslowsky M, Lavidor M (2012) tDCS polarity effects in motor and cognitive domains: a meta-analytical review. Exp Brain Res 216(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-011-2891-9
Kang EK, Paik NJ (2011) Effect of a tDCS electrode montage on implicit motor sequence learning in healthy subjects. Exp Transl Stroke Med 3(1):4. https://doi.org/10.1186/2040-7378-3-4
Karni A, Meyer G, Rey-Hipolito C, Jezzard P, Adams MM, Turner R, Ungerleider LG (1998) The acquisition of skilled motor performance: fast and slow experience-driven changes in primary motor cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95(3):861–868. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.3.861
Kuo MF, Unger M, Liebetanz D, Lang N, Tergau F, Paulus W, Nitsche MA (2008) Limited impact of homeostatic plasticity on motor learning in humans. Neuropsychologia 46(8):2122–2128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2008.02.023
Lindenberg R, Nachtigall L, Meinzer M, Sieg MM, Flöel A (2013) Differential effects of dual and unihemispheric motor cortex stimulation in older adults. J Neurosci 33(21):9176–9183
López-Alonso V, Cheeran B, Río-Rodríguez D, Fernández-del-Olmo M (2014) Inter-individual variability in response to non-invasive brain stimulation paradigms. Brain Stimul 7(3):372–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2014.02.004
López-Alonso V, Cheeran B, Fernández-del-Olmo M (2015a) Relationship between non-invasive brain stimulation-induced plasticity and capacity for motor learning. Brain Stimul 8(6):1209–1219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2015.07.042
López-Alonso V, Fernández-del-Olmo M, Costantini A, Gonzalez-Henriquez JJ, Cheeran B (2015b) Intra-individual variability in the response to anodal transcranial direct current stimulation. Clin Neurophysiol 126(12):2342–2347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2015.03.022
Nissen MJ, Bullemer P (1987) Attentional requirements of learning: evidence from performance measures. Cogn Psychol 19(1):1–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-0285(87)90002-8
Nitsche MA, Paulus W (2000) Excitability changes induced in the human motor cortex by weak transcranial direct current stimulation. J Physiol 527(3):633–639. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.t01-1-00633.x
Nitsche MA, Paulus W (2001) Sustained excitability elevations induced by transcranial DC motor cortex stimulation in humans. Neurology 57(10):1899–1901. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.57.10.1899
Nitsche MA, Nitsche MS, Klein CC, Tergau F, Rothwell JC, Paulus W (2003a) Level of action of cathodal DC polarisation induced inhibition of the human motor cortex. Clin Neurophysiol 114(4):600–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1388-2457(02)00412-1
Nitsche MA, Schauenburg A, Lang N, Liebetanz D, Exner C, Paulus W, Tergau F (2003b) Facilitation of implicit motor learning by weak transcranial direct current stimulation of the primary motor cortex in the human. J Cogn Neurosci 15(4):619–626. https://doi.org/10.1162/089892903321662994
Oldfield RC (1971) The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9(1):97–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/0028-3932(71)90067-4
Poreisz C. Boros K. Antal A. Paulus W (2007) Safety aspects of transcranial direct current stimulation concerning healthy subjects and patients. Brain Res Bull 72(4–6):208–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2007.01.004
Priori A, Berardelli A, Rona S, Accornero N, Manfredi M (1998) Polarization of the human motor cortex through the scalp. NeuroReport 9:2257–2260
Reis J, Fritsch B (2011) Modulation of motor performance and motor learning by transcranial direct current stimulation. Curr Opin Neurol 24(6):590–596. https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0b013e32834c3db0
Reis J, Schambra HM, Cohen LG, Buch ER, Fritsch B, Zarahn E, Celnik PA, Krakauer JW (2009) Noninvasive cortical stimulation enhances motor skill acquisition over multiple days through an effect on consolidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(5):1590–1595. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0805413106
Stagg CJ, Nitsche MA (2011) Physiological basis of transcranial direct current stimulation. Neuroscientist 17(1):37–53. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858410386614
Stagg CJ, Jayaram G, Pastor D, Kincses ZT, Matthews PM, Johansen-Berg H (2011) Polarity and timing-dependent effects of transcranial direct current stimulation in explicit motor learning. Neuropsychologia 49(5):800–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2011.02.009
Tremblay S, Larochelle-Brunet F, Lafleur LP, El Mouderrib S, Lepage JF, Théoret H (2016) Systematic assessment of duration and intensity of anodal transcranial direct current stimulation on primary motor cortex excitability. Eur J Neurosci 44(5):2184–2190. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.13321
Vines BW, Cerruti C, Schlaug G (2008) Dual-hemisphere tDCS facilitates greater improvements for healthy subjects’ non-dominant hand compared to uni-hemisphere stimulation. BMC Neurosci 9(1):103. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-9-103
Wiethoff S. Hamada M. Rothwell JC (2014) Variability in response to transcranial direct current stimulation of the motor cortex. Brain Stimul 7(3):468–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2014.02.003
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Israel Science Foundation, Grant no. 367/14.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shilo, G., Lavidor, M. Non-linear effects of cathodal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) of the primary motor cortex on implicit motor learning. Exp Brain Res 237, 919–925 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-019-05477-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-019-05477-3