Abstract
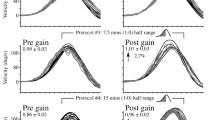
The vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) is responsible for stabilizing images on the fovea during head movements. However, in some situations, one needs to suppress the VOR to be able to follow a target moving along with the head. Evidence suggests that the visual mechanism underlying VOR suppression can be modulated by experience. Unfortunately, the non-visual mechanism underlying VOR suppression has never been examined in dancers and, consequently, it is still unsure whether dance training can enhance eye-head tracking accuracy. The goal of the present study was to look at the influence of dance training on the VOR suppression during passive head impulses. Twenty-four individuals participated, 12 controls and 12 dancers. VOR and VOR suppression were assessed using a head impulse paradigm as well as a suppression head impulse test paradigm (SHIMP) with video head impulse test, respectively. The results suggest that dancers display a significantly reduced VOR gain during the SHIMP at 60 ms in comparison to controls. Moreover, dancers with more than 10 years of dance training exhibited a significantly reduced VOR gain during the SHIMP at 60 ms. Overall, the results suggest that dance training improves VOR suppression, but also modulates VOR suppression abilities. Although studies are needed to shed light on the possible mechanisms involved in the modulation of the VOR gain, the observed changes in dancers’ vestibulo-cerebellum and its role in the modulation of the VOR gain makes the cerebellar–vestibular nuclei pathway a possible model to explain the present results.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelaki DE, Cullen KE (2008) Vestibular system: the many facets of a multimodal sense. Annu Rev Neurosci 31:125–150. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.060407.125555
Boyle R, Rabbitt RD, Highstein SM (2009) Efferent control of hair cell and afferent responses in the semicircular canals. J Neurophysiol 102:1513–1525. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.91367.2008
Bronstein AM, Hood JD (1986) The cervico-ocular reflex in normal subjects and patients with absent vestibular function. Brain Res 3673:399–408
Buizza A, Schmid R (1986) Velocity characteristics of smooth pursuit eye movements to different patterns of target motion. Exp Brain Res 63:395–401
Carl JR, Gellman RS (1987) Human smooth pursuit: stimulus-dependent responses. J Neurophysiol 57:1446–1463
Crane BT, Demers JL (1999) Latency of voluntary cancellation of the human vestibulo-ocular reflex during transient yaw rotation. Exp Brain Res 127:67–74
Cullen KE (2016) Physiology of central pathways. In: Furman JM, Lempert T (eds) Handbook of clinical neurology, vol 137. Elsevier, USA, pp 17–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63437-5.00002-9
Cullen KE, McCrea RA (1993) Firing behavior of brain stem neurons during voluntary cancellation of the horizontal vestibuloocular reflex. I. Secondary vestibular neurons. J Neurophysiol 70:828–843
Cullen KE, Minor LB (2002) Semicircular canal afferents similarly encode active and passive head-on-body rotations: implications for the role of vestibular efference. J Neurosci 22:RC226
Cullen KE, Belton T, McCrea RA (1991) A non-visual mechanism for voluntary cancellation of the vestibulo-ocular reflex. Exp Brain Res 83:237–252
Fitzpatrick RC, Watson SR (2015) Passive motion reduces vestibular balance and perceptual responses. J Physiol 593:2389–2398. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP270334
Ito M (1982) Cerebellar control of the vestibulo-ocular reflex—around the flocculus hypothesis. Annu Rev Neurosci 5:275–296
MacDougall HG, McGarvie LA, Halmagyi GM, Rogers SJ, Manzari L, Burgess AM, Curthoys IS, Weber KP (2016) A new saccadic indicator of peripheral vestibular function based on the video head impulse test. Neurology 87:410–418. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000002827
McGarvie LA, MacDougall HG, Halmagyi GM, Burgess AM, Weber KP, Curthoys IS (2015) The video head impulse test (vHIT) of semicircular canal function—age-dependent normative values of VOR gain in healthy subjects. Front Neurol 6:154. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2015.00154
Mitchell DE, Della Santina CC, Cullen KE (2016) Plasticity within non-cerebellar pathways rapidly shapes motor performance in vivo. Nat Commun 7:11238. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11238
Osterhammel P, Terkildsen K, Zilstorff K (1968) Vestibular habituation in ballet dancers. Acta Otolaryngol 66:221–228
Roy JE, Cullen KE (1998) A neural correlate for vestibulo-ocular reflex suppression during voluntary eye-head gaze shifts. Nat Neurosci 1:404–410. https://doi.org/10.1038/1619 Doi
Sadeghi SG, Minor LB, Cullen KE (2007) Response of vestibular-nerve afferents to active and passive rotations under normal conditions and after unilateral labyrinthectomy. J Neurophysiol 97:1503–1514
Smith PF, Zheng Y (2013) From ear to uncertainty: vestibular contribution to cognitive function. Front Intergr Neurosci 7:84. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnint.2013.00084
Tanguy S, Quarck G, Etard O, Gauthier A, Denise P (2008) Vestibulo-occular reflex and motion sickness in figure skaters. Eur J Appl Physiol 104:1031–1037. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0859-7
Teramoto K, Sakata E, Ohtsu K (1994) Use of the visual suppression test using post-rotatory nystagmus to determine skill in ballet dancers. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 251:218–223
Funding
This research was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) (Grant no. MFE194264) and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) (Grant no. RGPIN-2016-05211).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MM, LB and FC designed and performed the experiment. MM and FC wrote the paper and LB, AD, MN helped with the edition of the manuscript. All authors discussed the results and implications and commented on the manuscript at all stages.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maheu, M., Behtani, L., Nooristani, M. et al. Enhanced vestibulo-ocular reflex suppression in dancers during passive high-velocity head impulses. Exp Brain Res 237, 411–416 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-018-5431-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-018-5431-z