Abstract
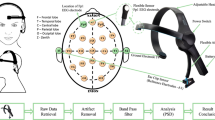
Topographical patterns of bipolar EEG coherence are frequency specific, indicating the presence of diverse neuroanatomical and neurophysiological factors in EEG production. Bipolar EEG coherence values were calculated at 50 frequency bins ranging from 3 to 28 Hz for 39 coherence pairs. Data were derived from 4.25 min of resting EEG obtained from 106 healthy adult male subjects and analyzed in 0.5 Hz bins by Fourier transform methods. Frequency bands were clearly separated at 8.5 and 13 Hz, with a less distinct separations at 6 and 20 Hz. Within pair (non-topographic) and across pair (topographic), measures gave similar patterns of separation. Significant pathways were primarily anterior–posterior interhemispheric or perpendicular to the anterior–posterior axis. There was little difference between left and right for comparable pairs. Theta band coherent activity involves distinct midline and temporal sources, with temporal sources showing anterior/posterior differentiation. In contrast, alpha activity has a distinct posterior focus, while beta activity shows no clear global structure. A spatially homogeneous model based on characteristics of thalamocortical connectivity accounts for much of the data, but departures from the model indicate the contribution of other neural factors to coherence.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astolfi L, Cincotti F, Mattia D, De Vico Fallani F, Tocci A, Colosimo A, Salinari S, Marciani MG, Hesse W, Witte H, Ursino M, Zavaglia M, Babiloni F (2008) Tracking the time-varying cortical connectivity patterns by adaptive multivariate estimators. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 55(3):902–913
Babiloni F, Babiloni C, Fattorini L, Carducci F, Onorati P, Urbano A (1995) Performances of surface Laplacian estimators: a study of simulated and real scalp potential distributions. Brain Topogr 8(1):35–45
Beckmann CF, DeLuca M, Devlin JT, Smith SM (2005) Investigations into resting-state connectivity using independent component analysis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 360(1457):1001–1013
Bendat J, Piersol A (1971) Random data: analysis and measurement procedures. Wiley, New York
Breakspear M, Terry JR (2002) Topographic organization of nonlinear interdependence in multichannel human EEG. Neuroimage 16(3 Pt 1):822–835
Breakspear M, Williams LM, Stam CJ (2004) A novel method for the topographic analysis of neural activity reveals formation and dissolution of ‘dynamic cell assemblies’. J Comput Neurosci 16(1):49–68
Bruce A, Gao H (1994) S+ wavelets user’s manual. Mathsoft Inc., Seattle
Buzsáki G, Draguhn A (2004) Neuronal oscillations in cortical networks. Science 304(5679):1926–1929
Cantero JL, Atienza M, Salas RM (2002) Human alpha oscillations in wakefulness, drowsiness period, and REM sleep: different electroencephalographic phenomena within the alpha band. Neurophysiol Clin 32(1):54–71
Chorlian DB, Tang Y, Rangaswamy M, O’Connor S, Rohrbaugh J, Taylor R, Porjesz B (2007) Heritability of EEG coherence in a large sib-pair population. Biol Psychol 75(3):260–266
Cover KS, Stam CJ, van Dijk BW (2004) Detection of very high correlation in the alpha band between temporal regions of the human brain using MEG. Neuroimage 22(4):1432–1437
David O, Friston KJ (2003) A neural mass model for MEG/EEG: coupling and neuronal dynamics. Neuroimage 20(3):1743–1755
De Luca M, Beckmann CF, De Stefano N, Matthews PM, Smith SM (2006) fMRI resting state networks define distinct modes of long-distance interactions in the human brain. Neuroimage 29(4):1359–1367
Durbin J, Watson GS (1950) Testing for serial correlation in least squares regression, I. Biometrika 37:409–428
Durbin J, Watson GS (1951) Testing for serial correlation in least squares regression, II. Biometrika 38 :159–179
Feige B, Scheffler K, Esposito F, Di Salle F, Hennig J, Seifritz E (2005) Cortical and subcortical correlates of electroencephalographic alpha rhythm modulation. J Neurophysiol 93(5):2864–2872
Feshchenko VA, Reinsel RA, Veselis RA (2001) Multiplicity of the alpha rhythm in normal humans. J Clin Neurophysiol 18(4):331–344
Fox MD, Raichle ME (2007) Spontaneous fluctuations in brain activity observed with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Nat Rev Neurosci 8(9):700–711
Fox MD, Snyder AZ, Vincent JL, Raichle ME (2007) Intrinsic fluctuations within cortical systems account for intertrial variability in human behavior. Neuron 56(1):171–184
Fries P, (2005) A mechanism for cognitive dynamics: neuronal communication through neuronal coherence. Trends Cogn Sci 9(10):474–480
Gasser T, Sroka L, Mocks J (1985) The transfer of EOG activity into the EEG for eyes open and closed. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 61: 181–193
Gasser T, Sroka L, Mocks J (1986) The correction of EOG artifacts by frequency dependent and frequency independent methods. Psychophysiology 23:704–712
Goldman RI, Stern JM, Engel J Jr, Cohen MS (2002) Simultaneous EEG and fMRI of the alpha rhythm. Neuroreport 13(18):2487–2492
Greicius MD, Krasnow B, Reiss AL, Menon V (2003) Functional connectivity in the resting brain: a network analysis of the default mode hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(1):253–258
Grieve PG, Emerson RG, Fifer WP, Isler JR, Stark RI (2003) Spatial correlation of the infant and adult electroencephalogram. Clin Neurophysiol 114(9):1594–1608
Hagmann P, Cammoun L, Gigandet X, Meuli R, Honey CJ, Wedeen VJ, Sporns O (2008) Mapping the structural core of human cerebral cortex. PLoS Biol 6(7):e159
Hamming R (1983) Digital filters. Prentice, Englewood Cliffs
Hanslmayr S, Aslan A, Staudigl T, Klimesch W, Herrmann CS, Bäuml KH Prestimulus oscillations predict visual perception performance between and within subjects. Neuroimage 37(4):1465–1473
Honey CJ, Kötter R, Breakspear M, Sporns O (2007) Network structure of cerebral cortex shapes functional connectivity on multiple time scales. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(24):10240–10245
Hughes SW, Crunelli V (2005) Thalamic mechanisms of EEG alpha rhythms and their pathological implications. Neuroscientist 11(4):357–372
Hughes JR, John ER (1999) Conventional and quantitative electroencephalography in psychiatry. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 11(2):190–208
Kaminski M, Ding M, Truccolo WA, Bressler SL (2001) Evaluating causal relations in neural systems: granger causality, directed transfer function and statistical assessment of significance. Biol Cybern 85(2):145–157
Karameh FN, Dahleh MA, Brown EN, Massaquoi SG (2006) Modeling the contribution of lamina 5 neuronal and network dynamics to low frequency EEG phenomena. Biol Cybern 95(4):289–310
Koenig T, Studer D, Hubl D, Melie L, Strik WK (2005) Brain connectivity at different time-scales measured with EEG. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 360(1457):1015–1023
Laufs H, Kleinschmidt A, Beyerle A, Eger E, Salek-Haddadi A, Preibisch C, Krakow K (2003) EEG-correlated fMRI of human alpha activity. Neuroimage 19(4):1463–1476
Laufs H, Krakow K, Sterzer P, Eger E, Beyerle A, Salek-Haddadi A, Kleinschmidt A (2003) Electroencephalographic signatures of attentional and cognitive default modes in spontaneous brain activity fluctuations at rest. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(19):11053–11058
Laufs H, Holt JL, Elfont R, Krams M, Paul JS, Krakow K, Kleinschmidt A (2006) Where the BOLD signal goes when alpha EEG leaves. Neuroimage 31(4):1408–1418
Möller E, Schack B, Arnold M, Witte H (2001) Instantaneous multivariate EEG coherence analysis by means of adaptive high-dimensional autoregressive models. J Neurosci Methods 105(2):143–158
Mantini D, Perrucci MG, Del Gratta C, Romani GL, Corbetta M (2007) Electrophysiological signatures of resting state networks in the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(32):13170–13175
Marple SL (1987) Digital spectral analysis. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Moosmann M, Ritter P, Krastel I, Brink A, Thees S, Blankenburg F, Taskin B, Obrig H, Villringer A (2003) Correlates of alpha rhythm in functional magnetic resonance imaging and near infrared spectroscopy. Neuroimage 20(1):145–158
Murias M, Swanson JM, Srinivasan R (2007) Functional connectivity of frontal cortex in healthy and ADHD children reflected in EEG coherence. Cereb Cortex 17(8):1788–1799
Murias M, Webb SJ, Greenson J, Dawson G (2007) Resting state cortical connectivity reflected in EEG coherence in individuals with autism. Biol Psychiatry 62(3):270–273
Nunez PL, Srinivasan R, Westdorp AF, Wijesinghe RS, Tucker DM, Silberstein RB, Cadusch PJ (1997) EEG coherency. I: statistics, reference electrode, volume conduction, Laplacians, cortical imaging, and interpretation at multiple scales. Clin Neurophysiol 103:499–515
Nunez PL, Silberstein RB, Shi Z, Carpenter MR, Srinivasan R, Tucker DM, Doran SM, Cadusch PJ, Wijesinghe RS (1999) EEG coherency II: experimental comparisons of multiple measures. Clin Neurophysiol 110(3):469–486
Nunez PL, Silberstein RB (2000) On the relationship of synaptic activity to macroscopic measurements: does co-registration of EEG with fMRI make sense? Brain Topogr 13(2):79–96
Nunez PL, Srinivasan R (2006) A theoretical basis for standing and traveling brain waves measured with human EEG with implications for an integrated consciousness. Clin Neurophysiol 117(11):2424–2435
Nunez PL, Wingeier BM, Silberstein RB (2001) Spatial–temporal structures of human alpha rhythms: theory, microcurrent sources, multiscale measurements, and global binding of local networks. Hum Brain Mapp 13(3):125–164
O’Connor SC, Robinson PA (2004) Spatially uniform and nonuniform analyses of electroencephalographic dynamics, with application to the topography of the alpha rhythm. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys70(1 Pt 1):011911
Porjesz B, Almasy L, Edenberg HJ, Wang K, Chorlian DB, Foroud T, Goate A, Rice JP, O’Connor SJ, Rohrbaugh J, Kuperman S, Bauer LO, Crowe RR, Schuckit MA, Hesselbrock V, Conneally PM, Tischfield JA, Li TK, Reich T, Begleiter H (2002) Linkage disequilibrium between the beta frequency of the human EEG and a GABAA receptor gene locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(6):3729–3733
Raichle ME, Gusnard DA (2005) Intrinsic brain activity sets the stage for expression of motivated behavior. J Comp Neurol 493(1):167–176
Raichle ME, Snyder AZ (2007) A default mode of brain function: a brief history of an evolving idea. Neuroimage 37(4):1083–1090
Rangaswamy M, Porjesz B, Chorlian DB, Wang K, Jones KA, Bauer LO, Rohrbaugh J, O’Connor SJ, Kuperman S, Reich T, Begleiter H (2002) Beta power in the EEG of alcoholics. Biol Psychiatry 52(8):831–842
Rangaswamy M, Porjesz B, Chorlian DB, Choi K, Jones KA, Wang K, Rohrbaugh J, O’Connor S, Kuperman S, Reich T, Begleiter H (2003) Theta power in the EEG of alcoholics. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 27(4):607–615
Rangaswamy M, Porjesz B, Chorlian DB, Wang K, Jones KA, Kuperman S, Rohrbaugh J, O’Connor SJ, Bauer LO, Reich T, Begleiter H (2004) Resting EEG in offspring of male alcoholics: beta frequencies. Int J Psychophysiol 51(3):239–251
Robinson PA (2003) Neurophysical theory of coherence and correlations of electroencephalographic and electrocorticographic signals. J Theor Biol 222(2):163–175
Robinson PA, Rennie CJ, Rowe DL, O’Connor SC, Wright JJ, Gordon E, Whitehouse RW (2003) Neurophysical modeling of brain dynamics. Neuropsychopharmacology 28(Suppl 1):S74–S79
Robinson PA (2005) Propagator theory of brain dynamics. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys 72(1 Pt 1):011904
Salvador R, Suckling J, Coleman MR, Pickard JD, Menon D, Bullmore E (2005) Neurophysiological architecture of functional magnetic resonance images of human brain. Cereb Cortex 15(9):1332–1342
Sarnthein J, Morel A, von Stein A, Jeanmonod D (2005) Thalamocortical theta coherence in neurological patients at rest and during a working memory task. Int J Psychophysiol 57(2):87–96
Sarnthein J, Jeanmonod D (2007) High thalamocortical theta coherence in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 27(1):124–131
Schreckenberger M, Lange-Asschenfeldt C, Lochmann M, Mann K, Siessmeier T, Buchholz HG, Bartenstein P, Grunder G (2004) The thalamus as the generator and modulator of EEG alpha rhythm: a combined PET/EEG study with lorazepam challenge in humans. Neuroimage 22(2):637–644
Srinivasan R, Nunez PL, Silberstein RB (1998) Spatial filtering and neocortical dynamics: estimates of EEG coherence. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 45(7):814–826
Srinivasan R (1999) Spatial structure of the human alpha rhythm: global correlation in adults and local correlation in children. Clin Neurophysiol 110(8):1351–1362
Srinivasan R, Winter WR, Nunez PL (2006) Source analysis of EEG oscillations using high-resolution EEG and MEG. Prog Brain Res 159:29–42
Srinivasan R, Winter WR, Ding J, Nunez PL (2007) EEG and MEG coherence: measures of functional connectivity at distinct spatial scales of neocortical dynamics. J Neurosci Methods 166(1):41–52
Steyn-Ross ML, Steyn-Ross DA, Wilson MT, Sleigh JW (2007) Gap junctions mediate large-scale Turing structures in a mean-field cortex driven by subcortical noise. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys 76(1 Pt 1):011916
Strang G, Nguyen T (1996) Wavelets and filter banks. Wellesley-Cambridge Press, Wellesley
Tang Y, Chorlian DB, Rangaswamy M, O’Connor S, Taylor R, Rohrbaugh J, Porjesz B, Begleiter H (2007) Heritability of bipolar EEG spectra in a large sib-pair population. Behav Genet 37(2):302–313
Tang Y, Chorlian DB, Rangaswamy M, Porjesz B, Bauer L, Kuperman S, O’Connor S, Rohrbaugh J, Schuckit M, Stimus A, Begleiter H (2007) Genetic influences on bipolar EEG power spectra. Int J Psychophysiol 65(1):2–9
Tenenbaum JB, de Silva V, Langford JC (2000) A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction. Science 290 (5500):2319–2323
Thatcher RW, Krause PJ, Hrybyk M (1986) Cortico-cortical associations and EEG coherence: a two-compartmental model. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 64(2):123–143
van de Ven VG, Formisano E, Prvulovic D, Roeder CH, Linden DE (2004) Functional connectivity as revealed by spatial independent component analysis of fMRI measurements during rest. Hum Brain Mapp 22(3):165–178
Ursino M, Zavaglia M (2007) Modeling analysis of the relationship between EEG rhythms and connectivity among different neural populations. J Integr Neurosci 6(4):597–623
von Stein A, Sarnthein J (2000) Different frequencies for different scales of cortical integration: from local gamma to long range alpha/theta synchronization. Intl J Psychophysiol 38:301–313
Wang K, Begleiter H (1999) Local polynomial estimate of surface Laplacian. Brain Topogr 12(1):19–29
Wang SY, Tang MX (2004) Exact confidence interval for magnitude-squared coherence estimates. IEEE Signal Process Lett 11(3):326–329
Zavaglia M, Astolfi L, Babiloni F, Ursino M (2008) The effect of connectivity on EEG rhythms, power spectral density and coherence among coupled neural populations: analysis with a neural mass model. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 55(1):69–77
Acknowledgments
We thank our present and former colleagues at the Henri Begleiter Neurodynamics Laboratory for their help in preparing this paper. We thank Jay Weedon for enlightening discussions of data analysis, as well as two anonymous reviewers whose comments and questions led to signficant improvements in this paper. We dedicate this paper to the memory of Henri Begleiter, who encouraged the first steps in its creation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by NIAAA Grants AA002686, AA005524, and AA008401 at SUNY Downstate Medical Center.
Appendix: location of coherence pairs
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chorlian, D.B., Rangaswamy, M. & Porjesz, B. EEG coherence: topography and frequency structure. Exp Brain Res 198, 59–83 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-009-1936-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-009-1936-9