Abstract
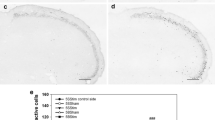
This study examined differences in nociceptive responses between lip and tongue. Formalin-induced pain-related behaviour and c-Fos expression in the trigeminal caudal nucleus (Vc) with/without systemic preadministration of a γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) type A receptor antagonist, bicuculline (2 mg/kg, i.p., 10 min before formalin injection) or a μ-opioid receptor agonist, morphine (3 mg/kg, i.p., 10 min before formalin injection) have been studied. Formalin injection into the upper lip induced an immediate pain-related behaviour, mostly face-rubbing behaviour, for 15 min (phase 1, mean ± SEM/5 min, 81.2 ± 30.1), followed by a more increased activity for 15 min (phase 2, 205.4 ± 43.6) and a decline to baseline for next 15 min (phase 3, 63.9 ± 28.0). Formalin injection into the tongue induced similar amount of pain-related behaviour at phase 1 (67.9 ± 16.7), followed by similar activity at phase 2 (48.6 ± 6.2), and lesser behaviour at phase 3 (20.4 ± 7.6). The behaviour at phase 2 decreased following preadministration of bicuculline or morphine when formalin was injected into the lip (b, 62.5 ± 14.5; m, 95.8 ± 10.0) but not into the tongue (b, 31.0 ± 9.2; m, 77.4 ± 27.0). A considerable numbers of c-Fos-immunoreactive (IR) cells were induced in the caudal and inter-medio-lateral center of superficial layers of the Vc (VcI/II; mean ± SEM/section = 225.8 ± 12.9) and magnocellular zone of the Vc (VcIII/IV; 67.1 ± 4.7) 2 h after formalin injection into the lip. Much smaller numbers of c-Fos-IR cells were induced in the rostral and dorso-medial one-fourth of the VcI/II (72.6 ± 3.7) and VcIII/IV (55.6 ± 6.6) after formalin injection into the tongue. Following preadministration with systemic bicuculline or morphine, the formalin-induced c-Fos-IR cells were decreased more in the VcI/II when formalin was injected into the lip (VcI/II, 102.4 ± 8.0; VcIII/IV, 32.8 ± 1.4) than into the tongue (VcI/II, 49.5 ± 8.1; VcIII/IV, 31.7 ± 5.3). These results show that the lip is more sensitive to formalin-induced noxious stimulation and regulated more through GABAA and μ-opioid receptors than the tongue.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GABA:
-
γ-Aminobutyric acid
- NK-1:
-
Neurokinin 1
- IR:
-
Immunoreactive
- PB:
-
Phosphate buffer
- Spdh:
-
Spinal dorsal horn
- TG:
-
Trigeminal ganglion
- TSN:
-
Trigeminal sensory nuclei
- Vc:
-
Trigeminal caudal nucleus
- VcI/II:
-
Superficial layers of Vc
- VcIII/IV:
-
Magnocellular zone of Vc
- Vi:
-
Trigeminal interpolar nucleus
- Vidm:
-
Dorsomedial nucleus of Vi
- Vo:
-
Trigeminal nucleus oralis
- Vodm:
-
Dorsomedial nucleus of Vo
- Vp:
-
Trigeminal principal nucleus
- VspTr:
-
Trigeminal spinal tract
- WGA-HRP:
-
Horseradish peroxidase conjugated with wheat germ agglutinin
References
Abe T, Ohshita N, Sugiyo S, Moritani M, Kobayashi M, Takemura M (2005) Elimination of NK-1 neurons in caudal nucleus reverses the effects of systemic bicuculline on c-fos expression in rat trigeminal sensory nucleus: I. High intensity electrical stimulation of the trigeminal ganglion. Neuroscience 133:739–747
Alhaider AA, Lei SZ, Wilcox GL (1991) Spinal 5-HT3 receptor-mediated antinociception: possible release of GABA. J Neurosci 11:1881–1888
Almond JR, Westrum LE, Henry MA (1996) Post-embedding immunogold labeling of gamma-aminobutyric acid in lamina II of the spinal trigeminal subnucleus pars caudalis: I. A qualitative study. Synapse 24:39–47
Bernardi PS, Valtschanoff JG, Weinberg RJ, Schmidt HHHW, Rustioni A (1995) Synaptic interactions between primary afferent terminals and GABA and nitric oxide-synthesizing neurons in the superficial laminae of the rat spinal cord. J Neurosci 15:1363–1371
Carstens E, Saxe I, Ralph R (1995) Brainstem neurons expressing c-Fos immunoreactivity following irritant chemical stimulation of the rat’s tongue. Neuroscience 69:939–953
Chapman V, Besson JM (1997) Pharmacological studies of nociceptive systems using the c-Fos immunohistochemical technique: an indicator of noxiously activated spinal neurones. In: Dickenson A, Besson JM (eds) The pharmacology of pain. Springer, Berlin, pp 235–279
Clavelou P, Pajot J, Dallel R, Raboisson P (1989) Application of the formalin test to the study of orofacial pain in the rat. Neurosci Lett 103:346–353
Clavelou P, Dallel R, Orliaguet T, Woda A, Raboisson P (1995) The orofacial formalin test in rats: effects of different formalin concentrations. Pain 62:295–301
Clavier N, Lombard MC, Besson JM (1992) Benzodiazepines and pain: effects of midazolam on the activities of nociceptive non-specific dorsal horn neurons in the rat spinal cord. Pain 48:61–71
DiFiglia M, Aronin N (1990) Synaptic interactions between GABAergic neurons and trigeminothalamic cells in the rat trigeminal nucleus caudalis. Synapse 6:358–363
Drower EJ, Hammond DL (1988) GABAergic modulation of nociceptive threshold: effects of THIP and bicuculline microinjected in the ventral medulla of the rat. Brain Res 450:316–324
Dubuisson D, Dennis SG (1977) The formalin test: a quantitative study of the analgesic effects of morphine, meperidine, and brain stem stimulation in rats and cats. Pain 4:161–174
Fay R, Kubin L (2000) Pontomedullary distribution of 5-HT2A receptor-like protein in the rat. J Comp Neurol 418:323–345
Ginestal E, Matute C (1993) Gamma-aminobutyric acid-immunoreactive neurons in the rat trigeminal nuclei. Histochemistry 99:49–55
Hammond DL (1997) Inhibitory neurotransmitters and nociception: role of GABA and glycine. In: Dickenson A, Besson JM (eds) Handbook of experimental pharmacology. Springer, Berlin, pp 361–383
Heinricher MM, Kaplan HJ (1991) GABA-mediated inhibition in rostral ventromedial medulla: role in nociceptive modulation in the lightly anesthetized rat. Pain 47:105–113
Herdegen T, Kovary K, Leah J, Bravo R (1991) Specific temporal and spatial distribution of JUN, FOS and KROX-24 proteins in spinal neurons following noxious transsynaptic stimulation. J Comp Neurol 313:178–191
Kaneko M, Hammond DL (1997) Role of spinal γ-aminobutyric acidA receptors in formalin-induced nociception in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 282
Koyama N, Hanai F, Yokota T (1998) Does intravenous administration of GABAA receptor antagonists induce both descending antinociception and touch-evoked allodynia. Pain 76:327–336
Luccarini P, Childeric A, Gaydier A-M, Voisin D, Dallel R (2006) The orofacial formalin test in the mouse: a behavioural model for studying physiology and modulation of trigeminal nociception. J Pain 7:908–914
Ma QP, Woolf CJ (1996) Basal and touch-evoked fos-like immunoreactivity during experimental inflammation in the rat. Pain 6:307–316
Mesulam MM, Brushart TM (1979) Transganglionic and anterograde transport of horseradish peroxidase across dorsal root ganglia: a tetramethylbenzidine method for tracing central sensory connections of muscles and peripheral nerves. Neuroscience 4:1107–1117
Multon S, Pardutz A, Mosen J, Hua MT, Defays C, Honda S, Harada N, Bohotin C, Franzen R, Schoenen J (2005) Lack of estrogen increases pain in the trigeminal formalin model: a behavioural and immunocytochemical study of transgenic ArKO mice. Pain 114:257–265
Pajot J, Pelissier T, Sierralta F, Raboisson P, Dallel R (2000) Differential effects of trigeminal tractotomy on Aδ- and C-fiber-mediated nociceptive responses. Brain Res 863:289–292
Peterson MA, Basbaum AI, Abbadie C, Rohde DS, McKay WR, Taylor BK (1997) The differential contribution of capsaicin-sensitive afferents to behavioural and cardiovascular measures of brief and persistent nociception and to Fos expression in the formalin test. Brain Res 755:9–16
Sawynok J (1987) GABAergic mechanisms of analgesia: an update. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 26:463–474
Strassman AM, Vos BP (1993) Somatotopic and laminar organization of fos-like immunoreactivity in the medullary and upper cervical dorsal horn induced by noxious facial stimulation in the rat. J Comp Neurol 331:495–516
Sugimoto T, Takemura M, Sakai A, Ishimaru M (1986) Cell size analysis of trigeminal primary afferent neurons comprising individual peripheral branches of the rat mandibular nerve. Exp Neurol 93:565–573
Sugimoto T, Takemura M, Wakisaka S (1988) Cell size analysis of primary neurons innervating the cornea and tooth pulp of the rat. Pain 32:375–381
Sugiyo S, Satoh F, Asakura D, Kim DW, Abe T, Moritani M, Ohshita N, Yoshida A, Nakatsuka M, Iwai Y, Takemura M (2004) Difference in pain related behaviour and c-Fos expression between intra-oral and facial region after formalin injection. Abstr Soc Neurosci 293:15
Takemura M, Sugimoto T, Sakai A (1985) The cell body size of trigeminal primary neurons comprising the auriculotemporal and lingual nerves in the rat. Jpn J Oral Biol 27:1231–1233
Takemura M, Sugimoto T, Sakai A (1987) Topographic organization of central terminal region of different sensory branches of the rat mandibular nerve. Exp Neurol 96:540–557
Takemura M, Sugimoto T, Shigenaga Y (1991) Difference in central projection of primary afferents innervating facial and intraoral structures in the rat. Exp Neurol 111:324–331
Takemura M, Shimada T, Shigenaga Y (2000) GABAA receptor-mediated effects on expression of c-Fos in rat trigeminal nucleus following high- and low-intensity afferent stimulation. Neuroscience 98:325–332
Viggiano A, Monda M, Viggiano A, Chiefari M, Aurilio C, De Luca B (2004) Evidence that GABAergic neurons in the spinal trigeminal nucleus are involved in the transmission of inflammatory pain in the rat: a microdialysis and pharmacological study. Eur J Pharmacol 496:87–92
Viggiano A, Monda M, Viggiano A, Viggiano D, Viggiano E, Chiefari M, Aurilio C, De Luca B (2005) Trigeminal pain transmission requires reactive oxygen species production. Brain Res 1050:72–78
Yokota T, Nishikawa N (1982) Effects of picrotoxin upon response characteristics of wide dynamic range neurons in the spinal cord of cat and monkey. Neurosci Lett 28:259–263
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) from the Ministry of Education, Science/Sports and Culture of Japan (19592108 and 20791562). We thank Drs. Dong Wook. Kim and Daisuke Asakura for strong collaborations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugiyo, S., Uehashi, D., Satoh, F. et al. Effects of systemic bicuculline or morphine on formalin-evoked pain-related behaviour and c-Fos expression in trigeminal nuclei after formalin injection into the lip or tongue in rats. Exp Brain Res 196, 229–237 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-009-1842-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-009-1842-1