Abstract
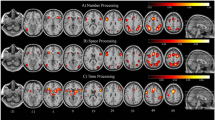
We used multidimensional scaling (MDS) to characterize the integrative neural mechanisms during viewing and subsequently copying nine geometrical shapes. Human subjects initially looked at a central fixation point (“rest” period), then looked at a geometrical shape (“visual” period) which they copied without visual feedback (“copying” period). BOLD signal was recorded from voxels in 28 cortical areas (14 from each hemisphere) using a 4 Tesla magnet. For each voxel, signal ratios of “Visual versus Rest” (VR), and “Copy versus Visual” (CV) were calculated and used to construct two sets of Euclidean distance dissimilarity matrices for the nine shapes, with separate matrices defined for each region of interest (ROI) across subjects. The relations of perceptual and motor aspects of the shapes to MDS dimensions and specific ROIs were assessed using stepwise multiple regressions. The optimal individually scaled (INDSCAL) solutions were 2-dimensional. For the VR condition, MDS dimensions were significantly associated with the presence of crossing in a shape (Dimension 1), and with perimeter, height, cycles, peak segment speed, and horizontal symmetry (Dimension 2). ROIs most prominently associated with these dimensions essentially comprised the medial frontal lobe bilaterally, the inferior frontal gyrus bilaterally, and the left intraparietal sulcus (Dimension 1), and visual areas, including the calcarine sulcus and cuneus bilaterally (Dimension 2). These results document the expected involvement of visual areas and support the hypothesis advanced on the basis of previous findings (Lewis et al. 2003a) that a motor rehearsal of the upcoming shape copying is occurring during this visual presentation period. For the CV condition, practically one motor feature (number of segments drawn) dominated both dimensions, with a secondary engagement of horizontal symmetry in Dimension 1. The right postcentral gyrus, right intraparietal sulcus, right superior parietal lobule and right inferior parietal lobule contributed mostly to Dimension 1; the superior frontal gyrus bilaterally, right middle frontal gyrus, left postcentral gyrus, left inferior parietal lobule contributed mostly to Dimension 2; and the left superior parietal lobule and left intraparietal sulcus contributed to both dimensions approximately equally. CV BOLD activation of ROIs contributing to Dimension 1 (or to both dimensions) was significantly associated with the number of shape segments drawn. Since the direction of movement differs in successively drawn shape segments, the number of segments (minus one) equals the number of changes in the direction of movement. We conclude that this fundamental spatial motor aspect of drawing geometrical shapes is the critical variable, independent of the particular shape drawn, that dominates cortical activation during copying.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelini R, Frasca R, Grossi D (1992) Are patients with constructional disorders different in visuo-spatial abilities? Acta Neurol 14:595–604
Arabie P, Carroll JD, DeSarbo WS (1987) Three-way scaling and clustering. Sage, Newbury Park
Averbeck BB, Chafee MV, Crowe DA, Georgopoulos AP (2002) Parallel processing of serial movements in prefrontal cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:13172–13177
Averbeck BB, Chafee MV, Crowe DA, Georgopoulos AP (2003a) Neural activity in prefrontal cortex during copying geometrical shapes. I. Single cells encode shape, sequence, and metric parameters. Exp Brain Res 150:127–141
Averbeck BB, Crowe DA, Chafee MV, Crowe DA, Georgopoulos AP (2003b) Neural activity in prefrontal cortex during copying geometrical shapes II. Decoding shape segments from neural ensembles. Exp Brain Res 150:142–153
Averbeck BB, Chafee MV, Crowe DA, Georgopoulos AP (2005) Parietal representation of hand velocity in a copy task. J Neurophysiol 93:508–518
Averbeck BB, Crowe DA, Chafee MV, Crowe DA, Georgopoulos AP (2008) Differential contribution of superior parietal and dorsal-lateral prefrontal cortices in copying. Cortex [Epub ahead of print]
Behrmann M, Winocur G, Moscovitch M (1992) Dissociation between mental imagery and object recognition in a brain-damaged patient. Nature 359:636–637
Benson DF, Barton MI (1970) Disturbances in constructional ability. Cortex 6:19–46
Benton AL (1962) The visual retention test as a constructional praxis task. Confin Neurol 22:141–155
Benton AL (1967) Constructional apraxia and the minor hemisphere. Confin Neurol 29:1–16
Benton AL (1968) Differential behavioral effects in frontal lobe disease. Neuropsychologia 6:53–60
Carroll D, Chang J (1970) Analysis of individual differences in multidimensional scaling via an n-way generalization of “Eckart-Young” decomposition. Psychometrika 35:283–319
Cox RW, Jesmanowicz A (1999) Real-time 3d image registration for functional MRI. Magn Reson Med 42:1014–1018
De Renzi E (1982) Disorders of space exploration and cognition. Wiley, Baffins Lane
Deiber MP, Ibañez V, Sadato N, Hallett M (1996) Cerebral structures participating in motor preparation in humans: a positron emission tomography study. J Neurophysiol 75:233–247
Gainotti G (1985) Constructional apraxia. In: Frederiks JAM (ed) Handbook of clinical neurology. Amsterdam, Elsevier, pp 491–506
Georgopoulos AP (1999) Neural mechanisms of motor cognitive processes: functional MRI and neurophysiological studies. In: Gazzaniga MS (ed) The new cognitive neurosciences 2nd edn. MIT, Cambridge, pp 525–538
Grossi D, Orsini A, Modafferi A, Liotti M (1986) Visuoimaginal constructional apraxia: on a case of selective deficit of imagery. Brain Cogn 5:255–267
Kherif F, Poline JB, Mériaux S, Benali H, Flandin G, Brett M (2003) Group analysis in functional neuroimaging: selecting subjects using similarity measures. Neuroimage 20:2197–2208
Kim SG, Hendrich K, Hu X, Merkle H, Uğurbil K (1994) Potential pitfalls of functional MRI using conventional gradient-recalled echo techniques. NMR biomed 7:69–74
Kleist K (1934) Gehirnpathologie. Barth, Leipzig
Koski L, Iacoboni M, Mazziotta JC (2002) Deconstructing apraxia: understanding disorders of intentional movement after stroke. Curr Opin Neurobiol 15:71–77
Krams M, Rushworth MFS, Deiber M-P, Frackowiak RSJ, Passingham RE (1998) The preparation, execution and suppression of copied movements in the human brain. Exp Brain Res 120:386–398
Kruskal JB, Wish M (1978) Multidimensional scaling. SAGE, Newbury Park
Laeng B (2006) Constructional apraxia after left or right unilateral stroke. Neuropsychologia 44:1595–1606
Lewis SM, Jerde TA, Tzagarakis C, Georgopoulos MA, Tsekos N, Amirikian B, Kim SG, Uğurbil K, Georgopoulos AP (2003a) Cerebellar activation during copying geometrical shapes. J Neurophysiol 90:3874–3887
Lewis SM, Jerde TA, Tzagarakis C, Tsekos N, Amirikian B, Georgopoulos MA, Kim SG, Ugurbil K, Georgopoulos AP (2003b) Activation in the frontal and parietal lobes during performance of a copy task: an fMRI study. Soc Neurosci Abstr 620:1
Lewis SM, Jerde TA, Tzagarakis C, Gourtzelidis P, Georgopoulos MA, Tsekos N, Amirikian B, Kim SG, Uğurbil K, Georgopoulos AP (2005) Logarithmic transformation for high-field BOLD fMRI data. Exp Brain Res 165:447–453
Lukashin AV, Georgopoulos AP (1994) A neural network for coding of trajectories by time series of neuronal population vectors. Neural Comput 6:19–28
Lukashin AV, Wilcox GL, Georgopoulos AP (1994) Overlapping neural networks for multiple motor engrams. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:8651–8654
Luria AR, Tsvetkova LS (1964) The programming of constructive activity in local brain injuries. Neuropsychologia 2:95–107
MacCallum R (1977) Effects of conditionality on indscal and alscal weights. Psychometrika 42:297–305
Mack JL, Levine RN (1981) The basis of visual constructional disability in patients with unilateral cerebral lesions. Cortex 17:515–532
Makuuchi M, Kaminaga T, Sugishita M (2003) Both parietal lobes are involved in drawing: a functional MRI study and implications for constructional apraxia. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 16:338–347
Marchini JL, Ripley BD (2000) A new statistical approach to detecting significant activation in functional MRI. Neuroimage 12:366–380
Oldfield RC (1971) The assessment and analysis of handedness: the edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9:97–113
Osterrieth PA (1944) Le test de copie d’une figure complexe: contribution à l’étude de la perception et de la mémoire. Archives de Psychologie 30:206–356
Paus T, Petrides M, Evans AC, Meyer E (1993) Role of the human anterior cingulate cortex in the control of oculomotor, manual, and speech responses: a positron emission tomography study. J Neurophysiol 70:453–469
Piercy M, Hécaen H, Ajuriaguerra J (1960) Constructional apraxia associated with unilateral cerebral lesions. Left and right sided cases compared. Brain 83:225–242
Pillon B (1981) Troubles visuoconstructifs et methods de compensation: Resultats de 85 patients atteints de lesions cerebrales. Neuropsychologia 19:375–383
Poppelreuter W (1917) Die psychische Schadigungen durch Kopfschuss im Kriege, vol 1. Leipzig, Voss
Porro CA, Francescato MP, Cettolo V, Diamond ME, Baraldi P, Zuiani C, Bazzocchi M, di Prampero PE (1996) Primary motor and sensory cortex activation during motor performance and motor imagery: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. J Neurosci 16:7688–7698
Porteus SD (1965) The Porteus maze test; 50 years’ application. Pacific books, Palo Alto
Rey A (1941) Psychological examination of traumatic encephalopathy. Archives de Psychologie 28:286–340
Salvador R, Suckling J, Coleman MR, Pickard JD, Menon D, Bullmore E (2005) Neurophysiological architecture of functional magnetic resonance images of human brain. Cereb Cortex 15:1332–1342
Schwartz AB (1994) Direct cortical representation of drawing. Science 265:540–542
Strupp JP (1996) Stimulate: a gui based fMRI analysis software package. Neuroimage 3:S607
Suchan B, Yaguez L, Wunderlich G, Canavan AG, Herzog H, Tellmann L, Homberg V, Seitz RJ (2002) Neural correlates of visuospatial imagery. Behav Brain Res 131:163–168
Tagaris GA, Richter W, Kim SG, Pellizzer G, Andersen P, Ugurbil K, Georgopoulos AP (1998) Functional magnetic resonance imaging of mental rotation and memory scanning: a multidimensional scaling analysis of brain activation patterns. Brain Res Rev 26:106–112
Turner RS, Grafton ST, Votaw JR, Delong MR, Hoffman JM (1998) Motor subcircuits mediating the control of movement velocity: a pet study. J Neurophysiol 80:2162–2176
Viviani P, Terzuolo C (1982) Trajectory determines movement dynamics. Neuroscience 7:431–437
Welchew DE, Honey GD, Sharma T, Robbins TW, Bullmore ET (2002) Multidimensional scaling of integrated neurocognitive function and schizophrenia as a disconnexion disorder. Neuroimage 17:1227–1239
Welchew DE, Ashwin C, Berkouk K, Salvador R, Suckling J, Baron-Cohen S, Bullmore E (2005) Functional disconnectivity of the medial temporal lobe in Asperger’s syndrome. Biol Psychiatry 57:991–998
Young FW, Harris DF (1990) Multidimensional scaling: procedure ALSCAL. In SPSS base system user’s guide. SPSS, Chicago, pp 397–461
Acknowledgments
We thank Joshua Lynch for data preprocessing and Marc Coutanche for comments on the manuscript. This work was supported by US NIH grant NS32919, the US Department of Veterans Affairs, and the American Legion Chair in Brain Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tzagarakis, C., Jerde, T.A., Lewis, S.M. et al. Cerebral cortical mechanisms of copying geometrical shapes: a multidimensional scaling analysis of fMRI patterns of activation. Exp Brain Res 194, 369–380 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-009-1709-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-009-1709-5