Abstract
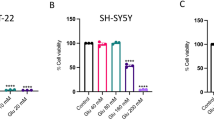
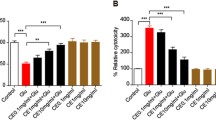
Excitotoxicity contributes to neuronal death and is involved in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD). In the present study, cryptotanshinone, an active ingredient from a Chinese plant, Salvia miltiorrhiza, was investigated to assess its neuroprotective effects against glutamate-induced toxicity in primary culture of rat cortical neurons. Cryptotanshinone reversed glutamate-induced neuronal toxicity, which was characterized by decreased cell viability, increased lactate dehydrogenase release, neuronal DNA condensation, and the alteration of the expression of Bcl-2 family proteins. The neuroprotective effects of cryptotanshinone could be blocked by LY294002 and wortmannin, two inhibitors of PI3K. The importance of the PI3K pathway was further confirmed by the activation of Akt and anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 by cryptotanshinone in a PI3K-dependent manner. These results suggest that cryptotanshinone protects primary cortical neurons from glutamate-induced neurotoxicity through the activation of PI3K/Akt pathway. Such neuroprotective effects may be of interest in AD and other neurodegenerative diseases.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JD, Wang R, Yang J, Lien EJ (2006) Preclinical and clinical examinations of Salvia miltiorrhiza and its tanshinones in ischemic conditions. Chin Med 1:1–15
Almeida RD, Manadas BJ, Melo CV (2005) Neuroprotection by BDNF against glutamate-induced apoptotic cell death is mediated by ERK and PI3-kinase pathways. Cell Death Differ 12:1329–1343
Bastianetto S, Ramassamy C, Poirier J, Quirion R (1999) Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) protects hippocampal cells from oxidative stress-induced damage. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 66:35–41
Burlacu A (2003) Regulation of apoptosis by Bcl-2 family proteins. J Cell Mol Med 7:249–257
Bussink J, van der Kogel AJ, Kaanders JH (2008) Activation of the PI3-K/AKT pathway and implications for radioresistance mechanisms in head and neck cancer. Lancet Oncol 9:288–296
Chalecka FE, Chuang DM (1999) Lithium activates the serine/threonine kinase Akt-1 and suppresses glutamate-induced inhibition of Akt-1 activity in neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:8745–8750
Choi DW (1988) Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of the nervous system. Neuron 1:623–634
Coyle JT, Puttfarcken P (1993) Oxidative stress, glutamate, and neurodegenerative disorders. Science 262:689–695
Deng YB, Liu XG, Liu ZG (2006) Implantation of BM mesenchymal stem cells into injured spinal cord elicits denovo neurogenesis and functional recovery: evidence from a study in rhesus monkeys. Cytotherapy 8:210–214
Dhandapani KM, Wade FM, Wakade C (2005) Neuroprotection by stem cell factor in rat cortical neurons involves AKT and NFkappaB. J Neurochem 95:9–19
Dijkhuizen PA, Ghosh A (2005) BDNF regulates primary dendrite formation in cortical neurons via the PI3-kinase and MAP kinase signaling pathways. J Neurobiol 62:278–288
Dong L, Lee S, Hart S (1999) Antibacterial activity of cryptotanshinone and dihydrotanshinone 1 from a medicinal herb, Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. J Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 63:2236–2239
Dwyer DS, Liu Y, Bradley RJ (1999) An ethanol-sensitive variant of the PC12 neuronal cell line: sensitivity to ethanol is associated with increased cell adhesion and decreased glucose accumulation. J Cell Physiol 178:93–101
Goossens V, Grooten J, Fiers W (1996) The oxidative metabolism of glutamine. J Biol Chem 271:192–196
Hajduch E, Litherland GJ, Hundal HS (2001) Protein kinase B (PKB/Akt)—a key regulator of glucose transport? FEBS Lett 492:199–203
Harris EW, Ganong AH, Cotman CW (1984) Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus involves activation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. Brain Res 323:132–137
Hishikawa K, Oemar BS, Tanner FC, Nakaki T, Fujii T, Luscher TF (1999) Overexpression of connective tissue growth factor gene induces apoptosis in human aortic smooth muscle cells. Circulation 100:2108–2112
Hur JM, Shim JS, Jung HJ, Kwon HJ (2005) Cryptotanshinone but not tanshinone IIA inhibits angiogenesis in vitro. Exp Mol Med 37:133–137
Ikeda H, Nagashima K, Yanase M, Tomiya T, Arai M, Inoue Y, Tejima K (2006) The herbal medicine inchin-ko-to (TJ-135) induces apoptosis in cultured rat hepatic stellate cells. Life Sci 78:2226–2233
Kan O, Baldwin S, Whetton A (1994) Apoptosis is regulated by the rate of glucose transport in an interleukin 3-dependent cell line. J Exp Med 180:917–923
Kanekura K, Hashimoto Y, Kita Y, Sasabe J (2005) A Rac1/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt3 anti-apoptotic pathway, triggered by AlsinLF, the product of the ALS2 gene, antagonizes Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase (SOD1) mutant-induced motoneuronal cell death. J Biol Chem 280:4532–4543
Kang BY, Chung SW, Kim SH (2000) Inhibition of interleukin-12 and interferon-gamma production in immune cells by tanshinones from Salvia miltiorrhiza. Immunopharmacology 49:355–361
Kihara T, Shimohama S, Sawada H, Honda K, Nakamizo T, Kanki R, Yamashita H, Akaike A (2002) Protective effect of dopamine D2 agonists in cortical neurons via the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase cascade. J Neurosci Res 70:274–282
Kim DH, Jeon SJ, Jung JW (2007a) Tanshinone congeners improve memory impairments induced by scopolamine on passive avoidance tasks in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 574:140–147
Kim EJ, Jung SN, Son KH (2007b) Antidiabetes and antiobesity effects of cryptotanshinone via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Mol Pharmacol 72:62–72
Kuang P, Xiang J (1994) Effect of radix Salviae miltiorhizae on EAA and IAA during cerebral ischemia in gerbils: a microdialysis study. J Trad Chin Med 14:45–50
Lamarca HL, Dash PR, Vishnuthevan K, Harvey E (2008) Epidermal growth factor-stimulated extravillous cytotrophoblast motility is mediated by the activation of PI3-K, Akt and both p38 and p42/44 mitogen-activated protein kinases. Hum Reprod Advance Access published May 16, 2008. doi:10.1093/humrep/den178
Lawlor MA, Alessi DR (2001) PKB/Akt: a key mediator of cell proliferation, survival and insulin responses? J Cell Sci 114:2903–2910
Li L, Dai J, Ru L, Yin G (2004) Effects of tanshinone on neuropathological changes induced by amyloid beta-peptide(1–40) injection in rat hippocampus. Acta Pharm Sin 25:861–868
Lieberthal W, Menza SA, Levine JS (1998) Graded ATP depletion can cause necrosis or apoptosis of cultured mouse proximal tubular cells. Am J Physiol 274:315–327
Lipton SA, Rosenberg PA (1994) Excitatory amino acids as a final common pathway for neurologic disorders. N Engl J Med 330:613–622
Madisch A, Holtmann G, Plein K, Hotz J (2004) Treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with herbal preparations: results of a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, multi-centre trial. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 19:271–279
Matsuzawa A, Ichijo H (2001) Molecular mechanisms of the decision between life and death: regulation of apoptosis by apoptosis signal regulating kinase. J Biochem 130:1–8
Ohtake N, Yamamoto M, Takeda S, Aburada M, Ishige A, Watanabe K, Inoue M (2005) The herbal medicine Sho-saiko-to selectively inhibits CD8+ T-cell proliferation. Eur J Pharmacol 507:301–310
Park EJ, Zhao YZ, Kim YC, Sohn DH (2007) PF2401-SF, standardized fraction of Salvia miltiorrhiza and its constituents, tanshinone I, tanshinone IIA, and cryptotanshinone, protect primary cultured rat hepatocytes from bile acid-induced apoptosis by inhibiting JNK phosphorylation. Food Chem Toxicol 45:1891–1898
Peso DL, Gonzalez GM, Page C, Herrera R, Nunez G (1997) Interleukin-3-induced phosphorylation of BAD through the protein kinase Akt. Science 278:687–689
Reed JC (1997) Double identity for proteins of the Bcl-2 family. Nature 387:773–776
Ren Y, Houghton PJ, Hider RC (2004) Novel diterpenoid acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from Salvia miltiorhiza. Planta Med 70:201–204
Ryu SY, Oak MH, Kim KM (1999) Inhibition of mast cell degranulation by tanshinones from the roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza. Planta Med 65:654–655
Sun J, Huang SH, Tan BK, Whiteman M, Zhu YC, Wu YJ, Ng Y (2005) Effects of purified herbal extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza on ischemic rat myocardium after acute myocardial infarction. Life Sci 76:2849–2860
Tolosa L, Mir M, Asensio VJ, Olmos G, Llado J (2008) Vascular endothelial growth factor protects spinal cord motoneurons against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Neurochem 105:1080–1090
Wang AM, Sha SH, Lesniak W, Schacht J (2003) Tanshinone (Salviae miltiorrhizae extract) preparations attenuate aminoglycoside-induced free radical formation in vitro and ototoxicity in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:1836–1841
Wang P, Tang F, Li R, Zhang H, Chen S, Liu P (2007) Contribution of different Nox homologues to cardiac remodeling in two-kidney two-clip renovascular hypertensive rats: effect of valsartan. Pharmacol Res 55:408–417
Wu B, Liu M, Zhang S (2004) Dan Shen agents for acute ischaemic stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4:CD004295
Ye K (2005) PIKE/nuclear PI 3-kinase signaling in preventing programmed cell death. J Cell Biochem 96:463–472
Zhu YP (1998) Chinese material medica: chemistry, pharmacology and applications. Harwood Academic Publishers, Amsterdam
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30672459, No. 30772576) and the Key Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, People’s Republic of China (No. 7117380).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, F., Zheng, W., Pi, R. et al. Cryptotanshinone protects primary rat cortical neurons from glutamate-induced neurotoxicity via the activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Exp Brain Res 193, 109–118 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-008-1600-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-008-1600-9