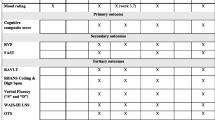
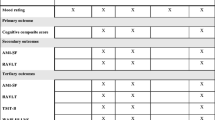
Abstract
Erythropoietin (Epo) has neuroprotective and neurotrophic effects and improves cognitive function in animal models of neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric illness. In humans, weekly Epo administration over 3 months improves cognitive function in schizophrenia. The neural underpinnings and time-course of this effect of Epo are currently unknown. It is also unclear whether the cognitive improvement reflects direct neurobiological actions or is secondary to hematological effects. We therefore assessed the actions of single administration of Epo (40,000 IU) vs. saline to healthy volunteers on cognitive and neural measures of executive function using a verbal fluency task and N-back working memory (WM) paradigm during functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) on day 3 and 7 after administration in two separate cohorts of subjects. Epo modulated neuronal response in a fronto-parietal network during WM performance at both time points; on day 3 after administration, activation was increased in left-hemisphere frontal and cingulate cortex and reduced in the right parietal cortex; in contrast, neural response was enhanced in a right-lateralized fronto-parietal network and reduced in left-side regions 1 week post-administration. In addition, Epo-treated volunteers displayed improved verbal fluency performance 1 week post-administration. These effects occurred in the absence of changes in hematological measures suggesting that they reflect direct neurobiological actions of Epo. The findings are co
nsistent with enduring effects of Epo on neurotrophic signaling and induction of neurochemical changes over time in neural networks typically affected in neuropsychiatric illness. The present study supports the notion that Epo may have clinical applications in the treatment of psychiatric disorder characterized by cognitive dysfunction.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aimone JB, Wiles J, Gage FH (2006) Potential role for adult neurogenesis in the encoding of time in new memories. Nat Neurosci 9:723–727
Bimonte HA, Nelson ME, Granholm AC (2003) Age-related deficits as working memory load increases: relationships with growth factors. Neurobiol Aging 24(1):37–48
Birn RM, Cox RW, Bandettini PA (2002) Detection versus estimation in event-related fMRI: choosing the optimal stimulus timing. Neuroimage 15:252–264
Brines ML, Ghezzi P, Keenan S, Agnello D, de Lanerolle NC, Cerami C et al (2000) Erythropoietin crosses the blood-brain barrier to protect against experimental brain injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:10526–10531
Brines M, Cerami A (2005) Emerging biological roles for erythropoietin in the nervous system. Nat Neurosci 6:484–494
Bonne O, Krausz Y, Aharon Y, Gelfin Y, Chisin R, Lerer B (1999). Clinical doses of fluoxetine and cerebral blood flow in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 143:24–28
Dupin N, Mailliet F, Rocher C, Kessal K, Spedding M, Jay TM (2006) Common efficacy of psychotropic drugs in restoring stress-induced impairment of prefrontal plasticity. Neurotox Res 10:193–198
Ehrenreich H, Hasselblatt M, Dembowski C, Cepek L, Lewczuk P, Stiefel M et al (2002) Erythropoietin therapy for acute stroke is both safe and beneficial. Mol Med 8:495–505
Ehrenreich H, Degner D, Meller J, Brines M, Behe M, Hasselblatt M, Woldt H, Falkai P, Knerlich F, Jacob S, von Ahsen N, Maier W, Bruck W, Ruther E, Cerami A, Becker W, Siren AL (2004) Erythropoietin: a candidate compound for neuroprotection in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 9:42–54
Ehrenreich H, Hinze-Selch D, Stawicki S, Aust C, Knolle-Veentjer S, Wilms S et al (2007) Improvement of cognitive function in chronic schizophrenic patients by recombinant human erythropoietin. Mol Psychiatry 12(2):206–220
Fletcher PC, Henson RN (2001) Frontal lobes and human memory: insights from functional neuroimaging. Brain 124:849–881
Grier JB (1971) Nonparametric indices for sensitivity and bias: computing formulas. Psychol Bull 75:9424–9429
Hariri AR, Goldberg TE, Mattay VS, Kolachana BS, Callicott JH, Egan MF, Weinberger DR (2003) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor val66met polymorphism affects human memory-related hippocampal activity and predicts memory performance. J Neurosci 23:6690–6694
Harvey PO, Fossati P, Pochon JB, Levy R, Lebastard G, Lehericy S, Allilaire JF, Dubois B (2005) Cognitive control and brain resources in major depression: an fMRI study using the n-back task. Neuroimage 26:860–869
Henry J, Crawford JR (2005) A meta-analytic review of verbal fluency deficits in depression. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 27:78–101
Jenkinson M, Smith S (2001) A global optimisation method for robust affine registration of brain images. Med Image Anal 5:143–156
Jenkinson M, Bannister P, Brady M, Smith S (2002) Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. Neuroimage 17:825–841
Lancaster JL, Woldorff MG, Parsons LM, Liotti M, Freitas CS, Rainey L et al (2000) Automated Talairach atlas labels for functional brain mapping. Hum Brain Mapp 10:120–131
Maldjian JA, Laurienti PJ, Kraft RA, Burdette JH (2003) An automated method for neuroanatomic and cytoarchitectonic atlas-based interrogation of fMRI data sets. Neuroimage 19:1233–1239
Manoach DS (2003) Prefrontal cortex dysfunction during working memory performance in schizophrenia: reconciling discrepant findings. Schizophr Res 60:285–298
Meyer-Lindenberg A, Poline JB, Kohn PD, Holt JL, Egan MF, Weinberger DR, Berman KF (2001) Evidence for abnormal cortical functional connectivity during working memory in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 158:1809–1817
Miskowiak K, O’Sullivan U, Harmer C (2007a) Erythropoietin enhances hippocampal response during memory retrieval in humans. J Neurosci 27:2788–2792
Miskowiak K, Inkster B, Selvaraj S, Goodwin G, Harmer C (2007b) Erythropoietin has no effect on hippocampal response during memory retrieval 3 days post-administration. Psychopharmacology (in press)
Prabhakaran V, Narayanan K, Zhao Z, Gabrieli JD (2000) Integration of diverse information in working memory within the frontal lobe. Nat Neurosci 3:85–90
Ransome MI, Turnley AM (2007) Systemically delivered Erythropoietin transiently enhances adult hippocampal neurogenesis. J Neurochem (in press)
Rybakowski JK, Borkowska A, Skibinska M, Szczepankiewicz A, Kapelski P, Leszczynska-Rodziewicz A, Czerski PM, Hauser J (2006) Prefrontal cognition in schizophrenia and bipolar illness in relation to Val66Met polymorphism of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 60:70–76
Talairach J, Tournoux P (1988) Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the human brain. Thieme, New York
van Asselen M, Kessels RP, Neggers SF, Kappelle LJ, Frijns CJ, Postma A (2006) Brain areas involved in spatial working memory. Neuropsychologia 44(7):1185–1194
van Veen V, Carter CS (2002) The anterior cingulate as a conflict monitor: fMRI and ERP studies. Physiol Behav 77:477–482
Viviani B, Bartesaghi S, Corsini E, Villa P, Ghezzi P, Garau A et al (2005). Erythropoietin protects primary hippocampal neurons increasing the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J Neurochem 93:412–421
Wang L, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Zhang R, Chopp M (2004) Treatment of stroke with erythropoietin enhances neurogenesis and angiogenesis and improves neurological function in rats. Stroke 35:1732–1737
Wager TD, Smith EE (2003) Neuroimaging studies of working memory: a meta-analysis. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 3:255–274
Walter H, Bretschneider V, Gron G, Zurowski B, Wunderlich AP, Tomczak R, Spitzer M (2003) Evidence for quantitative domain dominance for verbal and spatial working memory in frontal and parietal cortex. Cortex 39:897–911
Walter H, Wolf RC, Spitzer M, Vasic N (2006) Increased left prefrontal activation in patients with unipolar depression: an event-related, parametric, performance-controlled fMRI study. J Affect Disord (in press)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Lundbeckfonden, Denmark, the ESRC, UK, and the Goodger Scholarship, UK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miskowiak, K., Inkster, B., O’Sullivan, U. et al. Differential effects of erythropoietin on neural and cognitive measures of executive function 3 and 7 days post-administration. Exp Brain Res 184, 313–321 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-007-1102-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-007-1102-1