Abstract
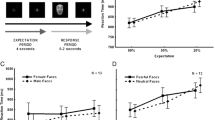
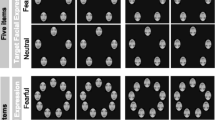
It has been argued that the amygdala represents an integral component of a vigilance system that is primarily involved in the perception of ambiguous stimuli of biological relevance. The present investigation was conducted to examine the relationship between automatic amygdala responsivity to fearful faces which may be interpreted as an index of trait-like threat sensitivity and spatial processing characteristics of facial emotions. During 3T fMRI scanning, pictures of human faces bearing fearful, angry, and happy expressions were presented to 20 healthy volunteers using a backward masking procedure based on neutral facial expressions. Subsequently, a computer-based face-in-the-crowd task using schematic face stimuli was administered. The neural response of the (right) amygdala to masked fearful faces correlated consistently with response speed to negative and neutral faces. Neither amygdala activation during the masked presentation of angry faces nor amygdala activation during the presentation of happy faces was correlated with any of the response latencies in the face-in-the-crowd task. Our results suggest that amygdala responsivity to masked facial expression is differentially related to the general visual search speed for facial expression. Neurobiologically defined threat sensitivity seems to represent an important determinant of visual scanning behaviour.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre G, Zarahn E, D’Esposito M (1998) The inferential impact of global signal covariates in functional neuroimaging analyses. Neuroimage 8:302–306
Beringer J (1999) Experimental run time system. Version 3.28. User’s manual. BeriSoft, Frankfurt
Bishop S, Duncan J, Lawrence AD (2004) State anxiety modulation of the amygdala response to unattended threat-related stimuli. J Neurosci 24:10364–10368
Bradley BP, Mogg K, Falla SJ, Hamilton JR (1998) Attentional bias for threatening facial expressions in anxiety: manipulation of stimulus duration. Cogn Emot 12:737–753
Bradley BP, Mogg K, White J, Groom C, deBono J (1999) Attentional bias for emotional faces in generalized anxiety disorder. Br J Clin Psychol 38:267–278
Brett M, Anton JL, Valabregue R, Poline JB (2002) Region of interest analysis using an SPM toolbox. Neuroimage 16:497 (abstract)
Critchley H, Daly E, Phillips M, Brammer M, Bullmore E, Williams S, van Amelsvoort T, Robertson D, David A, Murphy D (2000) Explicit and implicit neural mechanisms for processing of social information from facial expressions: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Hum Brain Mapp 9:93–105
Das P, Kemp AH, Liddell BJ, Brown KJ, Olivieri G, Peduto A, Gordon E, Williams LM (2005) Pathways for fear perception: modulation of amygdala activity by thalamo-cortical systems. Neuroimage 26:141–148
Davis M, Whalen PJ (2001) The amygdala: vigilance and emotion. Mol Psychiatry 6:13–34
Ekman P, Friesen WV (1976) Pictures of facial affect. Consulting Psychologists, Palo Alto
Esteves F, Öhman A (1993) Masking the face: recognition of emotional facial expressions as a function of the parameters of backward masking. Scand J Psychol 34:1–18
Etkin A, Klemenhagen KC, Dudman JT, Rogan MT, Hen R, Kandel ER, Hirsch J (2004) Individual differences in trait anxiety predict the response of the basolateral amygdala to unconsciously processed fearful faces. Neuron 44:1043–1055
Eysenck MW (1992) Anxiety. The cognitive perspective. Lawrence Erlbaum, Hillsdale
Fox E (2002) Processing emotional facial expressions: the role of anxiety and awareness. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 2:53–62
Fox E, Lester V, Russo R, Bowles RJ, Pichler A, Dutton K (2000) Facial expressions of emotion: are angry faces detected more efficiently? Cogn Emot 14:61–92
Gläscher J, Adolphs R (2003) Processing of the arousal of subliminal and supraliminal emotional stimuli by the human amygdala. J Neurosci 23:10274–10282
Hanley JA, McNeil BJ (1983) A method of comparing the areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve derived from the same cases. Radiology 148:839–843
Hutchinson M, Schiffer W, Joseffer S, Liu U, Schlosser RD, Dikshit S, Goldberg E, Brodie JD (1999) Task-specific deactivation patterns in functional magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 17:1427–1436
Izard CE, Dougherty FE, Bloxom BM, Kotsch WE (1974) The Differential Emotions Scale: a method of measuring the subjective experience of discrete emotions. Vanderbilt University, Nashville
Karparova SP, Kersting A, Suslow T (2005) Disengagement of attention from facial emotion in unipolar depression. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 59:723–729
Killgore WD, Yurgelun-Todd DA (2004) Activation of the amygdala and anterior cingulate during nonconscious processing of sad versus happy faces. Neuroimage 21:1215–1223
Lange K, Williams LM, Young AW, Bullmore ET, Brammer MJ, Williams SCR, Gray JA, Phillips ML (2003) Task instructions modulate neural responses to fearful facial expressions. Biol Psychiatry 53:226–232
Laux L, Glanzmann P, Schaffner P, Spielberger CD (1981) Das State-Trait Angstinventar. Beltz, Weinheim
LeDoux JE (1996) The emotional brain. Simon and Schuster, New York
Macmillan NA, Creelman CD (1991) Detection theory: a user’s guide. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Mathews A (1990) Why worry? The cognitive function of anxiety. Behav Res Ther 28:455–468
McKelvie S (1973) The meaningfulness and meaning of schematic faces. Percept Psychophys 14:343–348
Merten J, Krause R (1993) DAS (Differentielle Affektskala). Saarbrücken: Arbeiten der Fachrichtung Psychologie der Universität des Saarlandes, Nr. 173. Fachbereich Psychologie, Universität Saarbrücken, Saarbrücken
Morris JS, Frith CD, Perrett DI, Rowland D, Young AW, Calder AJ, Dolan RJ (1996) A differential neural response in the human amygdala to fearful and happy facial expressions. Nature 383:812–815
Morris JS, Friston KJ, Büchel C, Frith CD, Young AW, Calder AJ, Dolan RJ (1998a) A neuromodulatory role for the human amygdala in processing emotional facial expressions. Brain 121:47–57
Morris JS, Öhman A, Dolan RJ (1998b) Conscious and unconscious emotional learning in the human amygdala. Nature 393:467–470
Morris JS, Öhman A, Dolan RJ (1999) A subcortical pathway to the right amygdala mediating “unseen” fear. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:1680–1685
Nomura M, Ohira H, Haneda K, Iidaka T, Sadato N, Okada T, Yonekura Y (2004) Functional association of the amygdala and ventral prefrontal cortex during cognitive evaluation of facial expressions primed by masked angry faces: an event-related fMRI study. Neuroimage 21:352–363
Öhman A, Lunqvist D, Esteves F (2001) The face in the crowd revisited: a threat advantage with schematic stimuli. J Pers Soc Psychol 80:381–396
Purcell DG, Stewart AL, Skov RB (1996) It takes a confounded face to pop out of a crowd. Perception 25:1091–1108
Rauch SL, Whalen PJ, Shin LM, McInerney SC, Macklin ML, Lasko NB, Orr SP, Pitman RK (2000) Exaggerated amygdala response to masked facial stimuli in posttraumatic stress disorder: a functional MRI study. Biol Psychiatry 47:769–776
Schienle A, Schäfer A, Stark R, Walter B, Vaitl D (2005) Relationship between disgust sensitivity, trait anxiety and brain activity during disgust induction. Neuropsychobiology 51:86–92
Spielberger CD, Gorsuch RL, Lushene RE (1970) Manual for the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory. Consulting Psychologists, Palo Alto
Suslow T, Junghanns K, Arolt V (2001) Detection of facial expressions of emotions in depression. Percept Mot Skills 92:857–868
Suslow T, Roestel C, Ohrmann P, Arolt V (2003) Detection of facial expressions of emotions in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 64:137–145
Suslow T, Dannlowski U, Lalee-Mentzel J, Donges US, Arolt V, Kersting A (2004) Spatial processing of facial emotion in patients with unipolar depression: a longitudinal study. J Affect Disord 83:59–63
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N, Mazoyer B, Joliot M (2002) Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage 19:513–531
Vuilleumier P, Armony JL, Driver J, Dolan RJ (2003) Distinct spatial frequency sensitivities for processing faces and emotional expressions. Nat Neurosci 6:624–631
Whalen PJ (1998) Fear, vigilance, and ambiguity: initial neuroimaging studies of the human amygdala. Curr Dir Psychol Sci 7:177–188
Whalen PJ, Rauch SL, Etcoff NL, McInerney SC, Lee MB, Jenike MA (1998) Masked presentations of emotional facial expressions modulate amygdala activity without explicit knowledge. J Neurosci 18:411–418
White M (1995) Preattentive analysis of facial expressions of emotion. Cogn Emot 9:439–460
Williams JMG, Watts FN, MacLeod C, Mathews A (1997) Cognitive psychology and emotional disorders. Wiley, Chichester
Williams MA, Morris AP, McGlone F, Abbott DF, Mattingley JB (2004) Amygdala responses to fearful and happy facial expressions under conditions of binocular suppression. J Neurosci 24:2898–2904
Williams LM, Liddell BJ, Kemp AH, Bryant RA, Meares RA, Peduto AS, Gordon E (2006) Amygdala-prefrontal dissociation of subliminal and supraliminal fear. Hum Brain Mapp 27:652–661
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohrmann, P., Rauch, A.V., Bauer, J. et al. Threat sensitivity as assessed by automatic amygdala response to fearful faces predicts speed of visual search for facial expression. Exp Brain Res 183, 51–59 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-007-1022-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-007-1022-0