Abstract
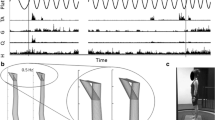
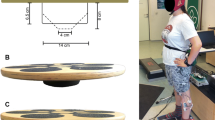
Inferring relations between cognitive processes and postural control is a relatively topical challenge in developmental neurology. This study investigated the effect of a concurrent cognitive task on postural control in a sample of 50 nine-year-old children. Each subject completed two balance trials of 60 s, one with a concurrent cognitive task (cognitive load) and another with no cognitive load. The concurrent cognitive task consisted of mentally counting backwards in steps of 2. Twelve posturographic parameters (PPs) were extracted from the centre of pressure (CoP) trajectory obtained through a load cell force plate. Analysis of variance revealed significant differences in the majority of the extracted PPs. CoP was found to travel faster, farther, and with substantially different features demonstrating an overall broadening of the spectrum in the frequency domain. Nonlinear stability factors revealed significant differences when exposed to a concurrent cognitive task, showing an increase of instability in the intervention rate of the postural control system. By grouping children through selected items from Teachers Ratings and PANESS assessment, specific significant differences were also found both in time and frequency domain PPs, thus confirming the hypothesis of an interaction between cognitive processes (and their development), and postural control.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assaiante C (1998) Development of locomotor balance control in healthy children. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 22:527–532
Assaiante C, Amblard B (1995) An ontogenetic model for the sensorimotor organization of balance control in humans. Hum Mov Sci 14:13–43
Baratto L, Morasso PG, Re C, Spada G (2002) A new look at posturographic analysis in the clinical context: sway-density versus other parameterization techniques. Motor Control 6:246–270
Barela JA, Jeka JJ, Clark JE (2003) Postural control in children. Coupling to dynamic somatosensory information. Exp Brain Res 150:434–442
Barra J, Bray A, Sahni V, Golding JF, Gresty MA (2006) Increasing cognitive load with increasing balance challenge: recipe for catastrophe. Exp Br Res DOI 10.1007/s00221–006–0519–2
Blanchard Y, Carey S, Coffey J, Cohen A, Harris T, Michlik S, Pellecchia GL (2005) The influence of concurrent cognitive tasks on postural sway in children. Pediatr Phys Ther 17:189–193
Blaszczyk JW, Klonowski W (2001) Postural stability and fractal dynamics. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 61:105–112
Chiari L, Cappello A, Lenzi D, Della Croce U (2000) An improved technique for the extraction of stochastic parameters from stabilograms. Gait Posture 12:225–234
Chiari L, Rocchi L, Cappello A (2002) Stabilometric parameters are affected by anthropometry and foot placement. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 17:666–677
Collins JJ, De Luca CJ (1993) Open-loop and closed-loop control of posture: a random-walk analysis of center-of-pressure trajectories. Exp Brain Res 95:308–318
Collins JJ, De Luca CJ (1995) Upright, correlated random walks: a statistical-biomechanics approach to the human postural control system. Chaos 5:57–63
Dault MC, Yardley L, Frank JS (2003) Does articulation contribute to modifications of postural control during dual-task paradigms? Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 16:434–440
Denckla MB (1985) Revised neurological examination for subtle signs (1985). Psychopharmacol Bull 21:773–800
Deutsch F (1952) Analytic posturology. Psychoanal Q 21:196–214
Diener HC, Dichgans J (1988) [Applications and uses of static and dynamic measurement of posture (posturography)]. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr 56:249–258
Fawcett AJ, Nicolson RI (1992) Automatisation deficits in balance for dyslexic children. Percept Mot Skills 75:507–529
Fawcett AJ, Nicolson RI (1999) Performance of dyslexic children on cerebellar and cognitive tests. J Mot Behav 31:68–78
Geuze RH (2003) Static balance and developmental coordination disorder. Hum Mov Sci 22:527–548
Giese MA, Dijkstra TM, Schoner G, Gielen CC (1996) Identification of the nonlinear state-space dynamics of the action-perception cycle for visually induced postural sway. Biol Cybern 74:427–437
Hunter MC, Hoffman MA (2001) Postural control: visual and cognitive manipulations. Gait Posture 13:41–48
Kapteyn TS, de Wit G (1972) Posturography as an auxiliary in vestibular investigation. Acta Otolaryngol 73:104–111
Katoulis EC, Ebdon-Parry M, Hollis S, Harrison AJ, Vileikyte L, Kulkarni J, Boulton AJ (1997) Postural instability in diabetic neuropathic patients at risk of foot ulceration. Diabet Med 14:296–300
Kohen-Raz R (1970) Developmental patterns of static balance ability and their relation to cognitive school readiness. Pediatrics 46:276–285
Liebovitch LS, Yang WM (1997) Transition from persistent to antipersistent correlation in biological systems. Phys Rev E 56:4557–4566
Manckoundia P, Pfitzenmeyer P, d’Athis P, Dubost V, Mourey F (2005) Impact of cognitive task on the posture of elderly subjects with Alzheimer’s disease compared to healthy elderly subjects. Mov Disord 21:236–241
Melzer I, Benjuya N, Kaplanski J (2001) Age related changes of postural control: the effect of cognitive task. Gerontology 47:189–194
Moe-Nilssen R, Helbostad JL, Talcott JB, Toennessen FE (2003) Balance and gait in children with dyslexia. Exp Brain Res 150:237–244
Molloy CA, Dietrich KN, Bhattacharya A (2003) Postural stability in children with autism spectrum disorder. J Autism Dev Disord 33:643–652
Neumann O (1987) Beyond capacity: a functional view of attention. In: Heuer H, Sanders AF (eds) Perspectives on perception and action. Hillsdale, NJ, pp 361–394
Nolan L, Grigorenko A, Thorstensson A (2005) Balance control: sex and age differences in 9- to 16-year-olds. Dev Med Child Neurol 47:449–454
Palus M, Hoyer D (1998) Detecting nonlinearity and phase synchronization with surrogate data. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag 17:40–45
Pellecchia GL (2003) Postural sway increases with attentional demands of concurrent cognitive task. Gait Posture 18:29–34
Poblano A, Ishiwara K, de Lourdes Arias M, Garcia-Pedroza F, Marin H, Trujillo M (2002) Motor control alteration in posturography in learning-disabled children. Arch Med Res 33:485–488
Prieto TE, Myklebust JB, Hoffmann RG, Lovett EG, Myklebust BM (1996) Measures of postural steadiness: differences between healthy young and elderly adults. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 43:956–966
Riach CL, Starkes JL (1993) Stability Limits of Quiet Standing Postural Control in Children and Adults. Gait Posture 1:105–111
Riley MA, Baker AA, Schmit JM (2003) Inverse relation between postural variability and difficulty of a concurrent shortterm memory task. Br Res Bull 63:191–195
Riley MA, Baker AA, Schmit JM, Weaver E (2005) Effects of visual and auditory short-term memory tasks on the spatiotemporal dynamics and variability of postural sway. J Mot Behav 37:311–324
Schmid M, Conforto S, Camomilla V, Cappozzo A, D’Alessio T (2002) The sensitivity of posturographic parameters to acquisition settings. Med Eng Phys 24:623–631
Schmid M, Conforto S, Lopez L, Renzi P, D’Alessio T (2005) The development of postural strategies in children: a factorial design study. Jnl Neuro Eng Rehab 2:29
Seliktar R, Susak Z, Najenson T, Solzi P (1978) Dynamic features of standing and their correlation with neurological disorders. Scand J Rehabil Med 10:59–64
Shumway-Cook A, Woollacott M, Kerns KA, Baldwin M (1997) The effects of two types of cognitive tasks on postural stability in older adults with and without a history of falls. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 52:M232–240
Slobounov SM, Slobounova ES, Newell KM (1997) Virtual time-to-collision and human postural control. J Mot Behav 29:263–281
Soames RW, Atha J (1980) The validity of physique-based inverted pendulum models of postural sway behaviour. Ann Hum Biol 7:145–153
Uimonen S, Laitakari K, Bloigu R, Sorri M (1994) The repeatability of posturographic measurements and the effects of sleep deprivation. J Vestib Res 4:29–36
van Wegen EE, van Emmerik RE, Riccio GE (2002) Postural orientation: age-related changes in variability and time-to-boundary. Hum Mov Sci 21:61–84
Weeks DL, Forget R, Mouchnino L, Gravel D, Bourbonnais D (2003) Interaction between attention demanding motor and cognitive tasks and static postural stability. Gerontology 49:225–232
Woollacott MH, Shumway-Cook A (1990) Changes in posture control across the life span—a systems approach. Phys Ther 70:799–807
Woollacott M, Shumway-Cook A (2002) Attention and the control of posture and gait: a review of an emerging area of research. Gait Posture 16:1–14
Yardley L, Gardner M, Leadbetter A, Lavie N (1999) Effect of articulatory and mental tasks on postural control. Neuroreport 10:215–219
Acknowledgments
The work of the two anonymous reviewers is greatly acknowledged. In particular, the authors wish to thank reviewer 2, for her/his help in substantially improving style. The authors wish also to thank PsyD Annalisa Conte, for her support in PANESS data collection. The help of the class teachers of the “Istituto Comprensivo Indro Montanelli” is greatly acknowledged. Work partially supported by MIUR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmid, M., Conforto, S., Lopez, L. et al. Cognitive load affects postural control in children. Exp Brain Res 179, 375–385 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-006-0795-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-006-0795-x