Abstract
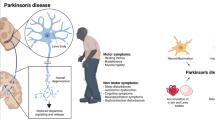
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a multifactorial disease with a complex etiology that results from genetic risk factors, environmental exposures and most likely a combination of both. Rodent models of parkinsonism aim to reproduce key pathogenic features of the syndrome including movement disorder induced by the progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, accompanied by the formation of α-synuclein containing Lewy body inclusions. Despite the creation of many excellent models, both chemically induced and genetically engineered, there is none that accurately demonstrates these features. Recent pathological staging studies in man have also emphasized the significant non-CNS component of PD that has yet to be tackled. Herein, we summarize rodent models of PD and what they offer to the field, and suggest future challenges and opportunities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeliovich A, Schmitz Y, Farinas I, Choi-Lundberg D, Ho WH, Castillo PE, Shinsky N, Verdugo JM, Armanini M, Ryan A, Hynes M, Phillips H, Sulzer D, Rosenthal A (2000) Mice lacking alpha-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron 25:239–252
Andorfer C, Kress Y, Espinoza M, de Silva R, Tucker KL, Barde YA, Duff K, Davies P (2003) Hyperphosphorylation and aggregation of tau in mice expressing normal human tau isoforms. J Neurochem 86:582–590
Betarbet R, Sherer TB, MacKenzie G, Garcia-Osuna M, Panov AV, Greenamyre JT (2000) Chronic systemic pesticide exposure reproduces features of Parkinson’s disease. Nat Neurosci 3:1301–1306
Bonifati V, Rizzu P, van Baren MJ, Schaap O, Breedveld GJ, Krieger E, Dekker MC, Squitieri F, Ibanez P, Joosse M, van Dongen JW, Vanacore N, van Swieten JC, Brice A, Meco G, van Duijn CM, Oostra BA, Heutink P (2003) Mutations in the DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism. Science 299:256–259
Bove J, Prou D, Perier C, Przedborski S (2005) Toxin-induced models of Parkinson’s disease. NeuroRx 2:484–494
Braak H, Ghebremedhin E, Rub U, Bratzke H, Del Tredici K (2004) Stages in the development of Parkinson’s disease-related pathology. Cell Tissue Res 318:121–134
Cabin DE, Shimazu K, Murphy D, Cole NB, Gottschalk W, McIlwain KL, Orrison B, Chen A, Ellis CE, Paylor R, Lu B, Nussbaum RL (2002) Synaptic vesicle depletion correlates with attenuated synaptic responses to prolonged repetitive stimulation in mice lacking alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci 22:8797–8807
Cabin DE, Gispert-Sanchez S, Murphy D, Auburger G, Myers RR, Nussbaum RL (2005) Exacerbated synucleinopathy in mice expressing A53T SNCA on a SNCA null background. Neurobiol Aging 26:25–35
Chandra S, Fornai F, Kwon HB, Yazdani U, Atasoy D, Liu X, Hammer RE, Battaglia G, German DC, Castillo PE, Sudhof TC (2004) Double-knockout mice for alpha- and beta-synucleins: effect on synaptic functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:14966–14971
Chen L, Feany MB (2005) Alpha-synuclein phosphorylation controls neurotoxicity and inclusion formation in a Drosophila model of Parkinson disease. Nat Neurosci 8:657–663
Chen L, Cagniard B, Mathews T, Jones S, Koh HC, Ding Y, Carvey PM, Ling Z, Kang UJ, Zhuang X (2005) Age-dependent motor deficits and dopaminergic dysfunction in DJ-1 null mice. J Biol Chem 280:21418–21426
Cory-Slechta DA, Thiruchelvam M, Barlow BK, Richfield EK (2005) Developmental pesticide models of the Parkinson disease phenotype. Environ Health Perspect 113:1263–1270
Dauer W, Kholodilov N, Vila M, Trillat AC, Goodchild R, Larsen KE, Staal R, Tieu K, Schmitz Y, Yuan CA, Rocha M, Jackson-Lewis V, Hersch S, Sulzer D, Przedborski S, Burke R, Hen R (2002) Resistance of alpha-synuclein null mice to the parkinsonian neurotoxin MPTP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:14524–14529
Drolet RE, Behrouz B, Lookingland KJ, Goudreau JL (2004) Mice lacking alpha-synuclein have an attenuated loss of striatal dopamine following prolonged chronic MPTP administration. Neurotoxicology 25:761–769
Duff K, Knight H, Refolo LM, Sanders S, Yu X, Picciano M, Malester B, Hutton M, Adamson J, Goedert M, Burki K, Davies P (2000) Characterization of pathology in transgenic mice over-expressing human genomic and cDNA tau transgenes. Neurobiol Dis 7:87–98
Fahn S (2003) Description of Parkinson’s disease as a clinical syndrome. Ann NY Acad Sci 991:1–14
Fernagut PO, Chesselet MF (2004) Alpha-synuclein and transgenic mouse models. Neurobiol Dis 17:123–130
Fleming SM, Salcedo J, Fernagut PO, Rockenstein E, Masliah E, Levine MS, Chesselet MF (2004) Early and progressive sensorimotor anomalies in mice overexpressing wild-type human alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci 24:9434–9440
Frasier M, Walzer M, McCarthy L, Magnuson D, Lee JM, Haas C, Kahle P, Wolozin B (2005) Tau phosphorylation increases in symptomatic mice overexpressing A30P alpha-synuclein. Exp Neurol 192:274–287
Giasson BI, Duda JE, Quinn SM, Zhang B, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2002) Neuronal alpha-synucleinopathy with severe movement disorder in mice expressing A53T human alpha-synuclein. Neuron 34:521–533
Gispert S, Del Turco D, Garrett L, Chen A, Bernard DJ, Hamm-Clement J, Korf HW, Deller T, Braak H, Auburger G, Nussbaum RL (2003) Transgenic mice expressing mutant A53T human alpha-synuclein show neuronal dysfunction in the absence of aggregate formation. Mol Cell Neurosci 24:419–429
Gloeckner CJ, Kinkl N, Schumacher A, Braun RJ, O’Neill E, Meitinger T, Kolch W, Prokisch H, Ueffing M (2005) The Parkinson disease causing LRRK2 mutation I2020T is associated with increased kinase activity. Hum Mol Genet 15:223–232
Goldberg MS, Fleming SM, Palacino JJ, Cepeda C, Lam HA, Bhatnagar A, Meloni EG, Wu N, Ackerson LC, Klapstein GJ, Gajendiran M, Roth BL, Chesselet MF, Maidment NT, Levine MS, Shen J (2003) Parkin-deficient mice exhibit nigrostriatal deficits but not loss of dopaminergic neurons. J Biol Chem 278:43628–43635
Goldberg MS, Pisani A, Haburcak M, Vortherms TA, Kitada T, Costa C, Tong Y, Martella G, Tscherter A, Martins A, Bernardi G, Roth BL, Pothos EN, Calabresi P, Shen J (2005) Nigrostriatal dopaminergic deficits and hypokinesia caused by inactivation of the familial Parkinsonism-linked gene DJ-1. Neuron 45:489–496
Gomez-Isla T, Irizarry MC, Mariash A, Cheung B, Soto O, Schrump S, Sondel J, Kotilinek L, Day J, Schwarzschild MA, Cha JH, Newell K, Miller DW, Ueda K, Young AB, Hyman BT, Ashe KH (2003) Motor dysfunction and gliosis with preserved dopaminergic markers in human alpha-synuclein A30P transgenic mice. Neurobiol Aging 24:245–258
Hashimoto M, Rockenstein E, Mante M, Mallory M, Masliah E (2001) beta-Synuclein inhibits alpha-synuclein aggregation: a possible role as an anti-parkinsonian factor. Neuron 32:213–223
Hope A, Farrer M (2004) Genetics of α-synucleinopathy. In: Philipp K, Haass C (eds) Molecular mechanisms in Parkinson’s disease. Landes Bioscience, Georgetown
Itier JM, Ibanez P, Mena MA, Abbas N, Cohen-Salmon C, Bohme GA, Laville M, Pratt J, Corti O, Pradier L, Ret G, Joubert C, Periquet M, Araujo F, Negroni J, Casarejos MJ, Canals S, Solano R, Serrano A, Gallego E, Sanchez M, Denefle P, Benavides J, Tremp G, Rooney TA, Brice A, Garcia de Yebenes J (2003) Parkin gene inactivation alters behaviour and dopamine neurotransmission in the mouse. Hum Mol Genet 12:2277–2291
Jensen PH, Nielsen MS, Jakes R, Dotti CG, Goedert M (1998) Binding of alpha-synuclein to brain vesicles is abolished by familial Parkinson’s disease mutation. J Biol Chem 273:26292–26294
Jeon BS, Jackson-Lewis V, Burke RE (1995) 6-Hydroxydopamine lesion of the rat substantia nigra: time course and morphology of cell death. Neurodegeneration 4:131–137
Kachergus J, Mata IF, Hulihan M, Taylor JP, Lincoln S, Aasly J, Gibson JM, Ross OA, Lynch T, Wiley J, Payami H, Nutt J, Maraganore DM, Czyzewski K, Styczynska M, Wszolek ZK, Farrer MJ, Toft M (2005) Identification of a novel LRRK2 mutation linked to autosomal dominant parkinsonism: evidence of a common founder across European populations. Am J Hum Genet 76:672–680
Kahle PJ, Neumann M, Ozmen L, Muller V, Jacobsen H, Schindzielorz A, Okochi M, Leimer U, van Der Putten H, Probst A, Kremmer E, Kretzschmar HA, Haass C (2000) Subcellular localization of wild-type and Parkinson’s disease-associated mutant alpha -synuclein in human and transgenic mouse brain. J Neurosci 20:6365–6373
Kahle PJ, Neumann M, Ozmen L, Muller V, Odoy S, Okamoto N, Jacobsen H, Iwatsubo T, Trojanowski JQ, Takahashi H, Wakabayashi K, Bogdanovic N, Riederer P, Kretzschmar HA, Haass C (2001) Selective insolubility of alpha-synuclein in human Lewy body diseases is recapitulated in a transgenic mouse model. Am J Pathol 159:2215–2225
Kay DM, Kramer P, Higgins D, Zabetian CP, Payami H (2005) Escaping Parkinson’s disease: a neurologically healthy octogenarian with the LRRK2 G2019S mutation. Mov Disord 20:1077–1078
Khan NL, Brooks DJ, Pavese N, Sweeney MG, Wood NW, Lees AJ, Piccini P (2002) Progression of nigrostriatal dysfunction in a parkin kindred: an [18F]dopa PET and clinical study. Brain 125:2248–2256
Khan NL, Scherfler C, Graham E, Bhatia KP, Quinn N, Lees AJ, Brooks DJ, Wood NW, Piccini P (2005) Dopaminergic dysfunction in unrelated, asymptomatic carriers of a single parkin mutation. Neurology 64:134–136
Kholodilov NG, Oo TF, Burke RE (1999) Synuclein expression is decreased in rat substantia nigra following induction of apoptosis by intrastriatal 6-hydroxydopamine. Neurosci Lett 275:105–108
Kim RH, Smith PD, Aleyasin H, Hayley S, Mount MP, Pownall S, Wakeham A, You-Ten AJ, Kalia SK, Horne P, Westaway D, Lozano AM, Anisman H, Park DS, Mak TW (2005) Hypersensitivity of DJ-1-deficient mice to 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyrindine (MPTP) and oxidative stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:5215–5220
Kirik D, Rosenblad C, Burger C, Lundberg C, Johansen TE, Muzyczka N, Mandel RJ, Bjorklund A (2002) Parkinson-like neurodegeneration induced by targeted overexpression of alpha-synuclein in the nigrostriatal system. J Neurosci 22:2780–2791
Kirik D, Annett LE, Burger C, Muzyczka N, Mandel RJ, Bjorklund A (2003) Nigrostriatal alpha-synucleinopathy induced by viral vector-mediated overexpression of human alpha-synuclein: a new primate model of Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:2884–2889
Kitada T, Asakawa S, Hattori N, Matsumine H, Yamamura Y, Minoshima S, Yokochi M, Mizuno Y, Shimizu N (1998) Mutations in the parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature 392:605–608
Klein RL, King MA, Hamby ME, Meyer EM (2002) Dopaminergic cell loss induced by human A30P alpha-synuclein gene transfer to the rat substantia nigra. Hum Gene Ther 13:605–612
Klivenyi P, Siwek D, Gardian G, Yang L, Starkov A, Cleren C, Ferrante RJ, Kowall NW, Abeliovich A, Beal MF (2005) Mice lacking alpha-synuclein are resistant to mitochondrial toxins. Neurobiol Dis 21:541–548. DOI 10.1016/j.nbd.2005.08.018
Kopin IJ, Markey SP (1988) MPTP toxicity: implications for research in Parkinson’s disease. Annu Rev Neurosci 11:81–96
Langston JW, Ballard P, Tetrud JW, Irwin I (1983) Chronic Parkinsonism in humans due to a product of meperidine-analog synthesis. Science 219:979–980
Lauwers E, Debyser Z, Van Dorpe J, De Strooper B, Nuttin B, Baekelandt V (2003) Neuropathology and neurodegeneration in rodent brain induced by lentiviral vector-mediated overexpression of alpha-synuclein. Brain Pathol. 13:364–372
Lee MK, Stirling W, Xu Y, Xu X, Qui D, Mandir AS, Dawson TM, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Price DL (2002) Human alpha-synuclein-harboring familial Parkinson’s disease-linked Ala-53 –> Thr mutation causes neurodegenerative disease with alpha-synuclein aggregation in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8968–8973
Lincoln S, Wiley J, Lynch T, Langston JW, Chen R, Lang A, Rogaeva E, Sa DS, Munhoz RP, Harris J, Marder K, Klein C, Bisceglio G, Hussey J, West A, Hulihan M, Hardy J, Farrer M (2003) Parkin-proven disease: common founders but divergent phenotypes. Neurology 60:1605–1610
Lo Bianco C, Ridet JL, Schneider BL, Deglon N, Aebischer P (2002) alpha -Synucleinopathy and selective dopaminergic neuron loss in a rat lentiviral-based model of Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:10813–10818
Lockhart PJ, O’Farrell CA, Farrer MJ (2004) It’s a double knock-out! The quaking mouse is a spontaneous deletion of parkin and parkin co-regulated gene (PACRG). Mov Disord 19:101–104
Lorenzetti D, Antalffy B, Vogel H, Noveroske J, Armstrong D, Justice M (2004) The neurological mutant quaking(viable) is Parkin deficient. Mamm Genome. 15:210–217
Lo Bioanco C, Schneider BL, Bauer M, Sajadi A, Brice A, Iwatsubo T, Aebischer P (2004) Lentiviral vector delivery of parkin prevents dopaminergic degeneration in an alpha-synuclein rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:17510–17515
Manning-Bog AB, McCormack AL, Li J, Uversky VN, Fink AL, Di Monte DA (2002) The herbicide paraquat causes up-regulation and aggregation of alpha-synuclein in mice: paraquat and alpha-synuclein. J Biol Chem 277:1641–1644
Martin LJ, Pan Y, Price AC, Sterling W, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Price DL, Lee MK (2006) Parkinson’s disease alpha-synuclein transgenic mice develop neuronal mitochondrial degeneration and cell death. J Neurosci 26:41–50
Masliah E, Rockenstein E, Veinbergs I, Mallory M, Hashimoto M, Takeda A, Sagara Y, Sisk A, Mucke L (2000) Dopaminergic loss and inclusion body formation in alpha-synuclein mice: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Science 287:1265–1269
Masliah E, Rockenstein E, Veinbergs I, Sagara Y, Mallory M, Hashimoto M, Mucke L (2001) Beta-amyloid peptides enhance alpha-synuclein accumulation and neuronal deficits in a transgenic mouse model linking Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12245–12250
Mata IF, Kachergus JM, Taylor JP, Lincoln S, Aasly J, Lynch T, Hulihan MM, Cobb SA, Wu RM, Lu CS, Lahoz C, Wszolek ZK, Farrer MJ (2005) LRRK2 pathogenic substitutions in Parkinson’s disease. Neurogenetics 6:171–177
Mata IF, Lockhart PJ, Farrer MJ (2004) Parkin genetics: one model for Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 13(1):R127–R133
Matsuoka Y, Vila M, Lincoln S, McCormack A, Picciano M, LaFrancois J, Yu X, Dickson D, Langston WJ, McGowan E, Farrer M, Hardy J, Duff K, Przedborski S, Di Monte DA (2001) Lack of nigral pathology in transgenic mice expressing human alpha-synuclein driven by the tyrosine hydroxylase promoter. Neurobiol Dis 8:535–539
McNaught KS, Perl DP, Brownell AL, Olanow CW (2004) Systemic exposure to proteasome inhibitors causes a progressive model of Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 56:149–162
Melrose HL, Lincoln S, Tyndall G, Dickson D, Farrer M (2006) Anatomical localization of LRRK2 in mouse brain. Neuroscience (in press)
Moore DJ, West AB, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2005) Molecular pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease. Annu Rev Neurosci 28:57–87
Nieto M, Gil-Bea FJ, Dalfo E, Cuadrado M, Cabodevilla F, Sanchez B, Catena S, Sesma T, Ribe E, Ferrer I, Ramirez MJ, Gomez-Isla T (2005) Increased sensitivity to MPTP in human alpha-synuclein A30P transgenic mice. Neurobiol Aging 7:7. DOI 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.04.010
Parkkinen L, Kauppinen T, Pirttila T, Autere JM, Alafuzoff I (2005) Alpha-synuclein pathology does not predict extrapyramidal symptoms or dementia. Ann Neurol 57:82–91
Perez FA, Palmiter RD (2005) Parkin-deficient mice are not a robust model of parkinsonism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:2174–2179
Perez FA, Curtis WR, Palmiter RD (2005) Parkin-deficient mice are not more sensitive to 6-hydroxydopamine or methamphetamine neurotoxicity. BMC Neurosci 6:71
Periquet M, Corti O, Jacquier S, Brice A (2005) Proteomic analysis of parkin knockout mice: alterations in energy metabolism, protein handling and synaptic function. J Neurochem 95:1259–1276
Pramstaller PP, Schlossmacher MG, Jacques TS, Scaravilli F, Eskelson C, Pepivani I, Hedrich K, Adel S, Gonzales-McNeal M, Hilker R, Kramer PL, Klein C (2005) Lewy body Parkinson’s disease in a large pedigree with 77 Parkin mutation carriers. Ann Neurol 58:411–422
Purisai MG, McCormack AL, Langston WJ, Johnston LC, Di Monte DA (2005) Alpha-synuclein expression in the substantia nigra of MPTP-lesioned non-human primates. Neurobiol Dis 20:898–906
van der Putten H, Wiederhold KH, Probst A, Barbieri S, Mistl C, Danner S, Kauffmann S., Hofele K, Spooren WP, Ruegg MA, Lin S, Caroni P, Sommer B, Tolnay M, Bilbe G (2000) Neuropathology in mice expressing human alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci 20:6021–6029
Richardson JR, Quan Y, Sherer TB, Greenamyre JT, Miller GW (2005) Paraquat neurotoxicity is distinct from that of MPTP and rotenone. Toxicol Sci 88:193–201
Richfield EK, Thiruchelvam MJ, Cory-Slechta DA, Wuertzer C, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG, Di Monte DA, Federoff HJ (2002) Behavioral and neurochemical effects of wild-type and mutated human alpha-synuclein in transgenic mice. Exp Neurol 175:35–48
Robertson DC, Schmidt O, Ninkina N, Jones PA, Sharkey J, Buchman VL (2004) Developmental loss and resistance to MPTP toxicity of dopaminergic neurones in substantia nigra pars compacta of gamma-synuclein, alpha-synuclein and double alpha/gamma-synuclein null mutant mice. J Neurochem 89:1126–1136
Rockenstein E, Mallory M, Hashimoto M, Song D, Shults CW, Lang I, Masliah E (2002). Differential neuropathological alterations in transgenic mice expressing alpha-synuclein from the platelet-derived growth factor and Thy-1 promoters. J Neurosci Res 68:568–578
Ross OA, Farrer MJ (2005) Pathophysiology, pleiotrophy and paradigm shifts: genetic lessons from Parkinson’s disease. Biochem Soc Trans 33:586–590
Ross OA, Toft M, Whittle AJ, Johnson JL, Papapetropoulos S, Mash DC, Litvan I, Gordon MF, Wszolek ZK, Farrer MJ, Dickson DW (2006) LRRK2 and Lewy body disease. Ann Neurol 59:388–393
Schluter OM, Fornai F, Alessandri MG, Takamori S, Geppert M, Jahn R, Sudhof TC (2003) Role of alpha-synuclein in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced parkinsonism in mice. Neuroscience 118:985–1002
Schober A (2004) Classic toxin-induced animal models of Parkinson’s disease: 6-OHDA and MPTP. Cell Tissue Res 318:215–224
Sedelis M, Schwarting RK, Huston JP (2001) Behavioral phenotyping of the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Behav Brain Res 125:109–125
Sherer TB, Betarbet R, Greenamyre JT (2002) Environment, mitochondria, and Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscientist 8:192–197
Sherer TB, Kim JH, Betarbet R, Greenamyre JT (2003) Subcutaneous rotenone exposure causes highly selective dopaminergic degeneration and alpha-synuclein aggregation. Exp Neurol 179:9–16
Simon-Sanchez J, Herranz-Perez V, Olucha-Bordonau F, Perez-Tur J (2006) LRRK2 is expressed in areas affected by Parkinson’s disease in the adult mouse brain. Eur J Neurosci 23:659–666
Song DD, Shults CW, Sisk A, Rockenstein E, Masliah E (2004) Enhanced substantia nigra mitochondrial pathology in human alpha-synuclein transgenic mice after treatment with MPTP. Exp Neurol 186:158–172
Sopher BL, La Spada AR (2006) Efficient recombination-based methods for bacterial artificial chromosome fusion and mutagenesis. Gene 15:15
Specht CG, Schoepfer R (2001) Deletion of the alpha-synuclein locus in a subpopulation of C57BL/6J inbred mice. BMC Neurosci 2:24
Speciale SG (2002) MPTP: insights into parkinsonian neurodegeneration. Neurotoxicol Teratol 24:607–620
Steidl JV, Gomez-Isla T, Mariash A, Ashe KH, Boland LM (2003) Altered short-term hippocampal synaptic plasticity in mutant alpha-synuclein transgenic mice. Neuroreport 14:219–223
Tao X, Tong L (2003) Crystal structure of human DJ-1, a protein associated with early onset Parkinson’s disease. J Biol Chem 278:31372–31379
Twelves D, Perkins KS, Counsell C (2003) Systematic review of incidence studies of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 18:19–31
Vila M, Vukosavic S, Jackson-Lewis V, Neystat M, Jakowec M, Przedborski S (2000) Alpha-synuclein up-regulation in substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons following administration of the parkinsonian toxin MPTP. J Neurochem 74:721–729
Von Coelln R, Thomas B, Savitt JM, Lim KL, Sasaki M, Hess EJ, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2004) Loss of locus coeruleus neurons and reduced startle in parkin null mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:10744–10749
Watanabe Y, Himeda T, Araki T (2005) Mechanisms of MPTP toxicity and their implications for therapy of Parkinson’s disease. Med Sci Monit 11:RA17–RA23
West A, Periquet M, Lincoln S, Lucking CB, Nicholl D, Bonifati V, Rawal N, Gasser T, Lohmann E, Deleuze JF, Maraganore D, Levey A, Wood N, Durr A, Hardy J, Brice A, Farrer M (2002) Complex relationship between Parkin mutations and Parkinson disease. Am J Med Genet 114:584–591
West AB, Moore DJ, Biskup S, Bugayenko A, Smith WW, Ross CA, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2005) Parkinson’s disease-associated mutations in leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 augment kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:16842–16847
Yamada M, Iwatsubo T, Mizuno Y, Mochizuki H (2004) Overexpression of alpha-synuclein in rat substantia nigra results in loss of dopaminergic neurons, phosphorylation of alpha-synuclein and activation of caspase-9: resemblance to pathogenetic changes in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 91:451–461
Yamada M, Mizuno Y, Mochizuki H (2005) Parkin gene therapy for alpha-synucleinopathy: a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Hum Gene Ther 16:262–270
Zeng BY, Dass B, Owen A, Rose S, Cannizzaro C, Tel BC, Jenner P, Kholodilov NG, Oo TF, Burke RE (2002) 6-Hydroxydopamine lesioning differentially affects alpha-synuclein mRNA expression in the nucleus accumbens, striatum and substantia nigra of adult rats
Zhang L, Shimoji M, Thomas B, Moore DJ, Yu SW, Marupudi NI, Torp R, Torgner IA, Ottersen OP, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2005) Mitochondrial localization of the Parkinson’s disease related protein DJ-1: implications for pathogenesis. Hum Mol Genet 14:2063–2073
Zimprich A, Biskup S, Leitner P, Lichtner P, Farrer M, Lincoln S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Uitti RJ, Calne DB, Stoessl AJ, Pfeiffer RF, Patenge N, Carbajal IC, Vieregge P, Asmus F, Muller-Myhsok B, Dickson DW, Meitinger T, Strom TM, Wszolek ZK, Gasser T (2004) Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron 44:601–607
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Michael J Fox Fellowship to Dr. Heather Melrose and by research grants from the National Parkinson’s Foundation and the National Institute for Neurological Disease and Stroke (P01 NS40256).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Melrose, H.L., Lincoln, S.J., Tyndall, G.M. et al. Parkinson’s disease: a rethink of rodent models. Exp Brain Res 173, 196–204 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-006-0461-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-006-0461-3