Abstract
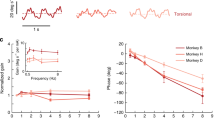
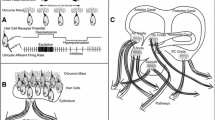
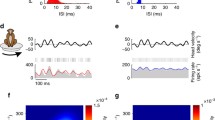
Rotational head motion in vertebrates is detected by the three semicircular canals of the vestibular system whose innervating primary afferent fibers encode movement information in specific head planes. In order to further investigate the nature of vestibular central processing of rotational motion in rhesus monkeys, it was first necessary to quantify afferent information coding in this species. Extracellular recordings were performed to determine the spatial and dynamic properties of semicircular canal afferents to rotational motion in awake rhesus monkeys. We found that the afferents innervating specific semicircular canals had maximum sensitivity vectors that were mutually orthogonal. Similar to other species, afferent response dynamics varied, with regular firing afferents having increased long time constants (t 1), decreased cupula velocity time constants (t v), and decreased fractional order dynamic operator values (s k) as compared to irregular firing afferents.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anastasio TJ, Correia MJ, Perachio AA (1985) Spontaneous and driven responses of semicircular canal primary afferents in the unanesthetized pigeon. J Neurophysiol 54:335–347
Anderson JH, Blanks RHI, Precht W (1978) Response characteristics of semicircular canal and otolith systems in cat. I. Dynamic responses of primary vestibular fibers. Exp Brain Res 32:491–507
Angelaki DE, Dickman JD (2000) Spatiotemporal processing of linear acceleration: primary afferent and central vestibular neuron responses. J Neurophysiol 84:2113–2132
Baird RA, Desmadryl G, Fernandez C, Goldberg JM (1988) The vestibular nerve of the chinchilla. II. Relation between afferent response properties and peripheral innervation patterns in the semicircular canals. J Neurophysiol 60:182–203
Blanks RHI, Precht W (1976) Functional characterization of primary vestibular afferents in the frog. Exp Brain Res 25:369–390
Blanks RHI, Curthoys IS, Markham CH (1972) Planar relationships of semicircular canals in the cat. Am J Physiol 223:55–62
Blanks RHI, Curthoys IS, Markham CH (1975) Planar relationships of semicircular canals in man. Acta Otolaryngol 80:185–196
Blanks RHI, Curthoys IS, Bennett ML, Markham CH (1985) Planar relationships of the semicircular canals in rhesus and squirrel monkeys. Brain Res 340:315–324
Boyle R, Highstein SM (1990) Resting discharge and response dynamics of horizontal semicircular canal afferents of the toadfish, Opsanus tau. J Neurophysiol 10:1557–1569
Brichta AM, Goldberg JM (2000) Morphological identification of physiologically characterized afferents innervating the turtle posterior crista. J Neurophysiol 83:1202–1223
Brichta AM, Acuna DL, Peterson EH (1988) Planar relations of semicircular canals in awake, resting turtles, Pseudemys scripta. Brain Behav Evol 32:236–245
Correia MJ, Perachio AA, Dickman JD et al. (1992) Changes in monkey horizontal semicircular canal afferent responses after space flight. J Appl Physiol 73:112–120
Curthoys IS, Curthoys EJ, Blanks RHI, Markham CH (1975) The orientation of the semicircular canals in the guinea pig. Acta Otolaryngol 80:197–205
Daunicht WJ, Pellionisz AJ (1987) Spatial arrangement of the vestibular and the oculomotor system in the rat. Brain Res 435:48–56
Dickman JD (1996) Spatial orientation of semicircular canals and afferent sensitivity vectors in pigeons. Exp Brain Res 111:8-20
Dickman JD, Angelaki DE (2002) Vestibular convergence patterns in vestibular nuclei neurons of alert primates. J Neurophysiol 88:3518–3533
Dickman JD, Angelaki DE (2003) Dynamics of vestibular neurons during rotational motion in alert rhesus monkeys. Exp Brain Res (in press)
Dickman JD, Correia MJ (1989a) Responses of pigeon horizontal semicircular canal afferent fibers. I. Step, trapezoid, and low-frequency sinusoid mechanical and rotational stimulation. J Neurophysiol 62:1090–1101
Dickman JD, Correia MJ (1989b) Responses of pigeon horizontal semicircular canal afferent fibers. II. High frequency mechanical stimulation. J Neurophysiol 62:1101–1112
Estes MS, Blanks RHI, Markham CH (1975) Physiologic characteristics of vestibular first-order canal neurons in the cat. I. Response plane determination and resting discharge characteristics. J Neurophysiol 38:1232–1249
Ezure K, Graf KW (1984) A quantitative analysis of the spatial organization of the vestibulo-ocular reflexes in lateral- and frontal-eyed animals. I. Orientation of semicircular canals and extraocular muscles. Neuroscience 12:85–94
Fernandez C, Goldberg JM (1971) Physiology of peripheral neurons innervating semicircular canals of the squirrel monkey. II. Response to sinusoidal stimulation and dynamics of peripheral vestibular system. J Neurophysiol 34:661–675
Gacek R, Rasmussen AT (1961) Fiber analysis of the statoacoustic nerve of the guinea pig, cat and monkey. Anat Rec 139:445–463
Ghanem TA, Rabbitt RD, Tresco PA (1998) Three-dimensional reconstruction of the membranous vestibular labyrinth in the toadfish, Opsanus tau. Hearing Res 124:27–43
Goldberg JM, Fernandez C (1971a) Physiology of peripheral neurons innervating semicircular canals of the squirrel monkey. I. Resting discharge and response to constant angular accelerations. J Neurophysiol 34:635–660
Goldberg JM, Fernandez C (1971b) Physiology of peripheral neurons innervating semicircular canals of the squirrel monkey. III. Variations among units in their discharge properties. J Neurophysiol 34:676–683
Goldberg JM, Smith CE, Fernandez C (1984) Relation between discharge regularity and responses to externally applied galvanic currents in vestibular nerve afferents of the squirrel monkey. J Neurophysiol 51:1236–1256
Hartmann R, Klinke R (1980) Discharge properties of afferent fibers of the goldfish semicircular canal with high-frequency stimulation. Pflugers Archiv 388:111–121
Hess BJM (1990) Dual-search coil for measuring 3-dimensional eye movements in experimental animals. Vision Res 30:597–602
Hullar TE, Minor LB (1999) High-frequency dynamics of regularly discharging canal afferents provide a linear signal for angular vestibuloocular reflexes. J Neurophysiol 82:2000–2005
Keller EL (1976) Behavior of horizontal semicircular canal afferents in alert monkey during vestibular and optokinetic stimulation. Exp Brain Res 24:459–471
Landolt JP, Correia MJ (1980) Neurodynamic response analysis of anterior semicircular canal afferents in the pigeon. J Neurophysiol 43:1746–1770
Landolt JP, Topliff EDL, Silverberg JD (1973) Size distribution analysis of myelinated fibers in the vestibular nerve of the pigeon. Brain Res 54:31–42
Louie A, Kimm J (1976) Response of VIII nerve fibers to sinusoidal oscillation in the awake monkey. Exp Brain Res 24:447–457
Lowenstein O, Sand A (1936) The activity of the horizontal semicircular canal of the dogfish, Scyllium canicula. J Exp Biol 13:416–428
O’Leary DP, Honrubia V (1976) Analysis of afferent responses from isolated semicircular canal of the guitarfish using rotational acceleration white-noise inputs. II. Estimation of linear system parameters and gain and phase spectra. J Neurophysiol 39:645–659
Precht W, Llinas R, Clark M (1971) Physiological responses of frog vestibular fibers to horizontal angular rotation. Exp Brain Res 13:378–407
Rabbitt RD (1999) Directional coding of three-dimensional movements by the vestibular semicircular canals. Biol Cybern 80:417–431
Reisine H, Simpson JI, Henn V (1988) A geometric analysis of semicircular canals and induced activity in their peripheral afferents in the rhesus monkey. Ann NY Acad Sci 545:10–20
Robinson DA (1982) The use of matrices in analyzing the three-dimensional behavior of the vestibule-ocular reflex. Biol Cybern 46:53–66
Ross DA (1936) Electrical studies on the frog’s labyrinth. J Physiol (Lond) 86:117–146
Schneider LW, Anderson DJ (1976) Transfer characteristics of first and second order lateral canal vestibular neurons in gerbil. Brain Res 112:61–76
Sirota MG, Babayev BM, Beloozverova IB et al. (1987) Characteristics of vestibular reactions to canal and otolith stimulation at an early stage of exposure to microgravity. Physiologist (Supp. 1) 30:82–84
Steinhausen W (1933) Uber die beobachtung der cupula in den bogengangsampullen des labyrinths des lebenden hechts. Pflugers Arch Ges Physiol 232:500–512
Suzuki Y, Straumann D, Simpson JI et al. (1999) Three-dimensional extraocular motoneuron innervation in the rhesus monkey. Exp Brain Res 126:187–199
Thorson J, Biederman-Thorson M (1974) Distributed relaxation processing sensory adaptation. Science 183:161–172
Tomko DL, Peterka RJ, Schor RH, O’Leary DP (1981) Response dynamics of horizontal canal afferents in barbiturate-anesthetized cats. J Neurophysiol 45:376–396
Van Egmond AAJ, Groen JJ, Jongkess LBW (1949) The mechanics of the semicircular canals. J Physiol (Lond) 110:1-17
Van Egmond AAJ, Groen JJ, Jongkees LBW (1952) The function of the vestibular organ. Pract Otorhinolaryngol (Suppl 2) 14:1–109
Young LR, Oman CR (1969) Model of vestibular adaptation to horizontal rotations. Aerospace Med 40:1076–1080
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Benny Harris and Jesus Loya for their fine technical assistance. The work was supported by grants from NIH (DC04160), and HHMI (57003555). NASA (NAG2-1493).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haque, A., Angelaki, D.E. & Dickman, J.D. Spatial tuning and dynamics of vestibular semicircular canal afferents in rhesus monkeys. Exp Brain Res 155, 81–90 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-003-1693-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-003-1693-0