Abstract
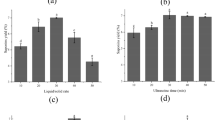
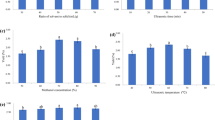
Saponins are triterpenic or steroidal glycosides present in many plants, as juá (Ziziphus joazeiro) and sisal (Agave sisalana), representatives of the Brazilian agrobiodiversity. Due to their properties, saponins are finding application in fine chemistry and pharmaceutical industry. Thus, the study of the extraction of these components from their natural matrixes and their optimization is of interest. The objective of this work is to evaluate the performance of the extraction of saponins from juá and sisal, using cholinium salts and deep eutectic solvents (DES) as adjuvants to aqueous and hydroalcoholic solutions. The goal is to simultaneously optimize the saponin extraction efficiency and the selectivity between saponins and phenolic compounds from these two plant matrixes. For this purpose, 13 cholinium-based ionic liquids and salts and 9 DES were used as adjuvants. It was observed that DES performed better in the proposed extractions and the optimal extraction mixture composition was determined using a mixture-design statistic method. Using this information, other experimental parameters, such as extraction time, raw material/solvent ratio and temperature were also evaluated and optimized. In the end, we show that it is possible to increase the extraction efficiency and selectivity of saponins from juá in 170 % and 18.39 and for sisal 245 % and 10.34, respectively, by the addition of a selected DES.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferro AFP, Bonacelli MBM, Assad ALD (2006) Oportunidades tecnológicas e estratégias concorrenciais de gestão ambiental: O uso sustentável da biodiversidade brasileira. Gest Prod 13:489–501
Rodrigues MG (2009) A pesquisa para a Conservação da Biodiversidade no Brasil: a ecologia a partir de um enfoque interdisciplinar. PhD Thesis. Política Científica e Tecnológica, UNICAMP, Campinas
Barbosa-Filho JM, Trigueiro JA, Cheriyan UO, Bhattacharyya J (1985) Constituents of stem-bark of Zizyphus joazeiro. J Nat Prod 48:152–153
Barbosa-Filho JM (1997) Quimiodiversidade e potencialidade farmacológica da flora paraibana. Cad Farm 13:85–102
Higuchi R, Kubota S, Komori T, Kawasaki T, Pandey VB, Singh JP, Shah AH (1984) Triterpenoid saponins from the bark of Zizyphus joazeiro. Phytochemistry 23:2597–2600
Schühly W, Heilmann J, Çalis I, Sticher O (2000) Novel triterpene saponins from Zizyphus joazeiro. Helv Chim Acta 83:1509–1516
Ding Y, Chen YY, Wang DZ, Yang CR (1989) Steroidal saponins from a cultivated form of Agave sisalana. Phytochemistry 28(10):2787–2791
Ding Y, Tian RH, Yang CR, Chen YY, Nohara T (1993) Two new steroidal saponins from dried fermented residues of leaf-juices of Agave sisalana forma Dong no. 1. Chem Pharm Bull 41(3):5557–5560
Stewart D, Azzini A, Hall AT, Morrison IM (1997) Sisal fibres and their constituent non-cellulosic polymers. Ind Crops Prod 6:17–26
Oashi MCG (1999) Estudo da Cadeia Produtiva como Subsídio para P & D do Agronegócio do Sisal na Paraíba. DSc Thesis. Federal University of Santa Catarina, Florianópolis, Brazil
Pizarro APB, Oliveira Filho AM, Parente JP, Melo MTV, Santos CE, Lima PR (1999) O aproveitamento do resíduo da indústria do sisal no controle de larvas de mosquitos. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 32(1):23–29
Zou P, Fu J, Yu HS, Zhang J, Kang LP, Ma BP, Yan XZ (2006) The NMR studies on two new furostanol saponins from Agave sisalana leaves. Magn Reson Chem 44:1090–1095
Chen PY, Kuo YC, Chen CH, Kuo YH, Lee CK (2009) Isolation and immunomodulatory effect of homoisoflavones and flavones from Agave sisalana Perrine ex Engelm. Molecules 14:1789–1795
Martin AR, Martins MA, Mattoso LHC, Silva ORRF (2009) Caracterização química e estrutural de fibra de sisal da variedade Agave sisalana. Pol Ciênc Tecnol 19(1):40–46
Kalinowska M, Zimowski J, Paczkowski C, Wojciechowski ZA (2005) The formation of sugar chains in triterpenoid saponins and glycoalkaloids. Phytochem Rev 4:237–257
Oleszek WA (2000) Saponins. In: Naidu AS (ed) Natural food antimicrobial systems. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 295–324
Güçlü-Üstündag Ö, Mazza G (2007) Saponins: properties, applications and processing. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 47(3):231–258
Sparg SG, Light ME, Van Staden J (2004) Biological activities and distribution of plant saponins. J Ethnopharmacol 94:219–243
Vincken JP, Heng L, De Groot A, Gruppen H (2007) Saponins, classification and occurrence in plant kingdom. Phytochemistry 68:275–297
Liu J, Henkel T (2002) Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM): are polyphenols and saponins the key ingredients triggering biological activities? Curr Med Chem 9:1483–1485
Wang L, Weller CL (2006) Recent advances in extraction of nutraceuticals from plants. Trends Food Sci Technol 17:300–312
Wassercheid P, Welton T (2008) Ionic liquids in synthesis, 2nd edn. Wiley, Weinheim
Weingärtner H (2008) Understanding ionic liquids at the molecular level: facts, problems, and controversies. Angew Chem Int Ed 47:654–670
Olivier-Bourbigou H, Magna L, Morvan D (2010) Ionic liquids and catalysis: recent progress from knowledge to applications. Appl Catal A Gen 373:1–56
Petkovic M, Seddon KR, Rebelo LPN, Pereira CS (2011) Ionic liquids: a pathway to environmental acceptability. Chem Soc Rev 40:1383–1403
Liu QP, Hou XD, Li N, Zong MH (2012) Ionic liquids from renewable biomaterials: synthesis, characterization and application in the pretreatment of biomass. Green Chem 14:304–307
Fukaya Y, Iizuka Y, Sekikawa K, Ohno H (2007) Bio ionic liquids: room temperature ionic liquids composed wholly of biomaterials. Green Chem 9:1155–1157
Imperato G, König B, Chiappe C (2007) Ionic green solvents from renewable resources. Eur J Org Chem 2007(7):1049–1058
Pernak J, Syguda A, Mirska I, Pernak A, Nawrot J, Pradzynska A, Griffin ST, Rogers RD (2007) Choline-derivative-based ionic liquids. Chem A Eur J 13:6817–6827
Abbott AP, Capper G, Davies DL, Rasheed RK, Tambyrajah V (2003) Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem Commun 2003(1):70–71
Shahbaz K, Mjalli FS, Hashima MA, Al-Nashef IM (2011) Prediction of deep eutectic solvents densities at different temperatures. Thermochim Acta 515:67–72
Maugeri Z, De María PD (2012) Novel choline-chloride-based deep-eutectic-solvents with renewable hydrogen bond donors: levulinic acid and sugar-based polyols. RSC Adv 2:421–425
Petkovic M, Ferguson JL, Gunaratne HQN, Ferreira R, Leitão MC, Seddon KR, Rebelo LPN, Pereira CS (2010) Novel biocompatible cholinium-based ionic liquids—toxicity and biodegradability. Green Chem 12:643–649
Makkar HPS, Siddhuraju P, Becker K (2007) Methods in molecular biology, vol 393: plant secondary metabolites. Humana Press, Totowa
Deng CJ, Nie FH (2008) Extraction of steroidal saponins from sisal hemp by supercritical CO2. Food Res Dev 2:41–44
Waterman PG, Mole S (1994) Analysis of phenolic plant metabolites. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford
Calado V, Montgomery DC (2003) Planejamento de Experimentos usando o Statistica. E-papers Serviços Editoriais, Rio de Janeiro
Rodrigues MI, Iemma AF (2005) Planejamento de Experimentos e Otimização de Processos. Casa do Pão Editora, Campinas
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Brazilian funding agencies, FAPERJ, CAPES and CNPq for financial support and scholarship. I. M. Marrucho acknowledges FCT/MCTES (Portugal) for a contract under Programa Ciência 2007. We also wish to thank the Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia for Project PTDC/EQU-FTT/116015/2009.
Conflict of interest
None.
Compliance with Ethics Requirements
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ribeiro, B.D., Coelho, M.A.Z. & Marrucho, I.M. Extraction of saponins from sisal (Agave sisalana) and juá (Ziziphus joazeiro) with cholinium-based ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents. Eur Food Res Technol 237, 965–975 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-013-2068-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-013-2068-9