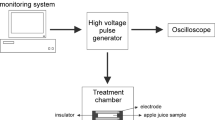
Abstract
The effect of pulsed electric fields (PEF; electric field intensities 15, 25, 35, and 40 kV/cm, and treatments times from 40 to 700 μs) on the carotenoid and vitamin A profile of an orange juice–milk beverage was evaluated and compared with a pasteurization treatment (90 °C, 20 s). Subsequently, the evolution of these parameters during storage of the beverage at 4 and 10 °C was studied. The results obtained indicate that the application of the electric field influenced the concentration of the extracted carotenoids producing a slight increase at 15 kV/cm and a slight decrease at 40 kV/cm. On the other hand, when pasteurization was applied, it was found a reduction in total carotenoid concentration. The reductions in carotenoids with provitamin A activity were very small after pasteurization, the decreases in lutein and zeaxanthin must be taken into account. The degradation kinetics of the carotenoids during storage were similar for the pasteurized and PEF-treated beverages. However, they were less affected initially in the beverages treated by the new technology and were therefore maintained in greater quantities throughout the storage period.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharma R (2005) Austr J Dairy Technol 60:196–199
Wegrzyn TF, Farr JM, Hunter DC, Au J, Wohlers MW, Skinner MA, Stanley RA, Sun-Waterhouse D (2008) Food Chem 109:310–318
Shukla FC, Sharma A, Singh B (2003) Int J Dairy Technol 56:243–246
Mortensen A (2006) Pure Appl Chem 78:1477–1491
Baker R, Günther C (2004) Trends Food Sci Technol 15:484–488
Landrum JT, Bone RA (2001) Arch Biochem Biophys 385:28–40
Calvo MM (2005) Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 45:671
Subagio A, Morita N (2001) Food Res Int 34:183–188
Yeom HW, Streaker CB, Zhang QH, Min DB (2000) J Agric Food Chem 48:4597–4605
Cortés C, Esteve MJ, Frígola A (2008) Food Control 19:151–158
Barsotti L, Cheftel JC (1999) Food Rev Int 15:181–213
Calderón-Miranda ML, Barbosa-Cánovas GV, Swanson BG (1999) Int J Food Microbiol 51:31–38
Kim H, Ye J, Li Y (2001) Institute of food technologists. Annual Meeting, Paper 59H-22
Fernández-Díaz MD, Barsotti L, Dumay E, Cheftel JC (2000) J Agric Food Chem 48:2332–2339
Bendicho S, Barbosa-Canovas GV, Martin O (2002) Trends Food Sci Technol 13:195–204
Bendicho S, Espachs A, Arántegui J, Martín O (2002) J Dairy Res 69:113–123
Cortés C, Esteve MJ, Frígola A, Torregrosa F (2005) Eur Food Res Technol 221:125–131
Michalac S, Alvarez V, Ji T, Zhang QH (2003) J Food Process Preserv 27:137–151
Fernandez-Molina JJ, Barbosa-Canovas GV, Swanson BG (2005) J Food Process Preserv 29:291–306
Torregrosa F, Cortes C, Esteve MJ, Frígola A (2005) J Agric Food Chem 53:9519–9525
Torregrosa F, Esteve MJ, Frígola A, Cortés C (2006) J Food Eng 73:339–345
Rivas A, Rodrigo D, Company B, Sampedro F, Rodrigo M (2007) Food Chem 104:1550–1559
Zulueta A, Esteve MJ, Frasquet I, Frígola A (2007) Food Chem 103:1365–1374
Zulueta A, Esteve MJ, Frígola A (2010) Innovative Food Sci Emerg Technol 11:84–90
A.O.A.C (1997) Official methods of analysis, 17th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington
Rivas A, Sampedro F, Rodrigo D, Martínez A, Rodrigo M (2006) Eur Food Res Technol 223:541–545
Braddock RJ (1999) Single strength orange juices and concentrate. In Wiley J (ed) Handbook of Citrus by products and processing technology. New York, pp 53–83
Cortes C, Esteve MJ, Frigola A, Torregrosa F (2004) J Agric Food Chem 52:2203–2212
Institute of Medicine (IOM) (2001) Dietary Reference Intakes for vitamin A, vitamin K, arsenic, boron, chromium, copper, iodine, iron, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, silicon, vanadium, and zinc. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Trumbo PR, Yates AA, Schlicker-Renfro S, Suitor C (2003) J Food Compos Anal 16:379
Cortés C, Esteve MJ, Rodrigo D, Torregrosa F, Frígola A (2006) Food Chem Toxicol 44:1932–1939
Rodríguez-Amaya DB (1997) Carotenoids and food preparation: the retention of provitamin A carotenoids in prepared, processed and stored foods. OMNI Project, Washington DC, pp 13–51
Lee HS, Coates GA (2003) Food Sci Technol 36:153
Gama JJT, de Sylos CM (2007) Food Chem 100:1686–1690
Sánchez-Moreno C, Plaza L, Élez-Martínez P, De Ancos B, Martín-Belloso O, Cano MP (2005) J Agric Food Chem 53:4403–4409
Bull MK, Zerdin K, Howe E, Goicoechea D, Paramanandhan P, Stockman R, Sellahewa J, Szabo EA, Johnson RL, Stewart CM (2004) Innovative Food Sci Emerging Technol 5:135
Lessin WJ, Catignani GL, Schwartz SJ (1997) J Agric Food Chem 45:3728
Giger A (2003) Pure Appl Chem 74:1383–1390
Acknowledgments
This study was carried out with funds from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Technology and European Regional Development Funds (ERDF; Project AGL2006-13320-C03-03/Ali) and the Generalitat Valenciana’s (Aid for Research Groups 3/147 and CV/2007/048). Ana Zulueta holds an award from this project and F. J. Barba holds an award from the Generalitat Valenciana (Spain). We would like to thank IATA (CSIC) for allowing us to use its installations and equipment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zulueta, A., Barba, F.J., Esteve, M.J. et al. Effects on the carotenoid pattern and vitamin A of a pulsed electric field-treated orange juice–milk beverage and behavior during storage. Eur Food Res Technol 231, 525–534 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-010-1304-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-010-1304-9