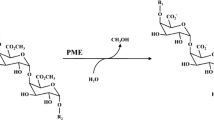
Abstract
Recently, high-pressure–low-temperature (HP-LT) treatments, succeeding a regular freezing unit operation, have been shown to inactivate micro-organisms. In this study, we have evaluated the influence of these treatments on the inactivation of quality-related enzymes. The effect of different pressure/temperature combinations (range 0.1–500 MPa/20 to −26 °C) on the activity of pectinmethylesterase, polygalacturonase, lipoxygenase, peroxidase and polyphenoloxidase in model systems, crude extracts and real-food systems was investigated.
Present results show that under these HP-LT processing conditions, no or limited enzyme inactivation is obtained for all enzyme systems studied, except for lipoxygenase which can be completely inactivated at high pressure in combination with low temperature. These data suggest that HP-LT treatments, although inactivating micro-organisms, fail to inactivate most food quality related enzymes. Therefore, a blanching unit operation (e.g. a conventional thermal blanching process prior to freezing) is required to prevent enzyme related quality degradation during frozen storage and cannot be replaced by an integrated freezing-HP-LT treatment.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fennema O (1978) In: Crowe JH, Clegg JS (eds) Dry biological systems. Academic Press, New York, pp 297–322
Reid DS (1999) In: Roos YH, Leslie RB, Lillford PJ (eds) Water management in the design and distribution of quality foods. Technical Publishing: Lancaster, pp 87–105
Archer DL (2004) Int J Food Microbiol 90:127–138
Cano MP (1996) In: Jeremiah LE (ed) Freezing effects on food quality. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 247–298
Zaritzky NE (2000) In: Kennedy CJ (ed) Managing frozen foods. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, UK, pp 111–135
Kidmose U, Martens HJ (1999) J Sci Food Agric 79:1747–1753
Lisiewska Z, Kmiecik W (2000) Food Chem 70:167–173
Martins RC, Silva CLM (2004) J Food Eng 64:481–488
Van Huystee RB (1987) Annu Rev Plant Physiol 38:205–219
Anthon GE, Barrett DM (2003) Food Chem 81:275–279
Van Buren JP (1979) J Text Stud 10:1–23
Fachin D, Van Loey AM, Ly Nguyen B, Verlent I, Indrawati I, Hendrickx M (2003) Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 4:135–142
Weemaes CA, Ludikhuyze LR, Van den Broeck I, Hendrickx ME, Tobback PP (1998) Lebensm-Wiss Technol 31:44–49
Kaack K (1994) Plant Foods Hum Nutr 46:353–360
Préstamo G, Fuster C, Risueño MC (1998) J Sci Food Agric 77:223–229
Arroqui C, Rumsey TR, Lopez A, Virseda P (2002) J Food Eng 52:25–30
Song J-Y, An G-H, Kim C-J (2003) Food Chem 83:69–74
Gómez FG, Sjöholm I (2004) Trends Food Sci Technol 15:39–43
Kalichevsky MT, Knorr D, Lillford PJ (1995) Trends Food Sci Technol 6:253–259
Li B, Sun D-W (2002) J Food Eng 54:175–182
Benet GU, Schlüter O, Knorr D (2004) Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 5:413–427
LeBail A, Chevalier D, Mussa DM, Ghoul M (2002) Int J Refrigerat 25:504–513
Luscher C, Balasa A, Fröhling A, Ananta E, Knorr D (2004) Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4021–4029
Shen T, Benet GU, Brul S, Knorr D (2005) Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 6:271–278
Anese M, Nicoli MC, Dall'Aglio G, Lerici CR (1995). J Food Biochem 18:285–293
Weemaes C, Ludikhuyze L, Van den Broeck I, Hendrickx M (1998). J Food Sci 63:873–877
Weemaes CA, Ludikhuyze LR, Van den Broeck I, Hendrickx M (1998). Biotechnol Bioeng 60:292–300
Indrawati I, Van Loey A, Ludihuyze LR, Hendrickx M (1999). J Agric Food Chem 47:2468–2474
Ludikhuyze L, Ooms V, Weemaes C, Hendrickx M (1999). J Agric Food Chem 47:1794–1800
Weemaes C, Ludihuyze L, Van den Broek I, Hendrickx M (1999). J Food Sci 64:823–827
Indrawati I, Van Loey A, Ludikhuyze LR, Hendrickx ME (2000). Biotechnol Prog 16:109–115
Indrawati I, Ludikhuyze LR, Van Loey AM, Hendrickx ME (2000). J Agric Food Chem 48:1850–1859
Tangwongchai R, Ledward DA, Ames JM (2000). J Agric Food Chem 48:2896–2902
Van den Broeck I, Ludikhuyze LR, Van Loey AM, Hendrickx ME (2000). J Agric Food Chem 48:1960–1970
Indrawati I, Van Loey AM, Ludikhuyze LR, Hendrickx ME (2001). J Food Sci 66:686–693
Fachin D, Van Loey A, Indrawati I, Ludikhuyze L, Hendrickx M (2002). J Food Sci 67:1610–1615
Ly-Nguyen B, Van Loey AM, Fachin D, Verlent I, Indrawati I, Hendrickx M (2002). J Agric Food Chem 50:5437–5444
Ly-Nguyen B, Van Loey A, Fachin D, Verlent I, Hendrickx M (2002). Biotechnol Bioeng 78:683–691
Ly-Nguyen B, Van Loey AM, Fachin D, Verlent I, Duvetter T, Vu ST, Smout C, Hendrickx ME (2002). Biotechnol Prog 18:1447–1450
Ly-Nguyen B, Van Loey AM, Smout C, Ozcan SE, Fachin D, Verlent I, Vu ST, Duvetter T, Hendrickx ME (2003). J Food Sci 68:1377–1383
Castro SM, Van Loey A, Saraiva JA, Smout C, Hendrickx M (2004). J Agric Food Chem 52:5724–5729
Fachin D, Smout C, Verlent I, Ly-Nguyen B, Van Loey AM, Hendrickx ME (2004). J Agric Food Chem 52:2697–2703
Seyderhelm I, Boguslawski S, Michaelis G, Knorr D (1996). J Food Sci 61:308–310
Goodner JK, Braddock RJ, Parish ME (1998). J Agric Food Sci 46:1997–2000
Shook CM, Shellhammer TH, Schwartz SJ (2001) J Agric Food Chem 49:664–668
Gkinis AM, Fennema OR (1978) J Food Sci 43:527–531
Préstamo G, Palomares L, Sanz P (2005) J Food Sci 70:S22–S27
Otero L, Ousegui A, Guignon B, LeBail A, Sanz P (2005). Food hydrocolloids. in press
Van den Broeck I, Ludikhuyze LR, Weemaes CA, Van Loey AM, Hendrickx ME (1999) J Food Process Preserv 23:391–406
de Araujo BS, de Oliveira JO, Machado SS, Pletsch M (2004) Plant Sci 167:1151–1157
Soysal Ç, Söylemez Z (2004) J Food Eng 68:349–356
Benet GU, Schlüter O, Knorr D (2004). Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 5:413–427
Indrawati I, Van Loey A, Denys S, Hendrickx M (1998) Food Biotechnol 12:263–277
Fachin D, Van Loey AM, Ly-Nguyen B, Verlent I, Indrawati I, Hendrickx ME (2002). Biotechnol Prog 18:739–744
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the European Project SAFE ICE (QLKI-2002–02230) from the Quality of Life and Management Resources Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Buggenhout, S., Messagie, I., Van der Plancken, I. et al. Influence of high-pressure–low-temperature treatments on fruit and vegetable quality related enzymes. Eur Food Res Technol 223, 475–485 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-005-0227-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-005-0227-3