Abstract
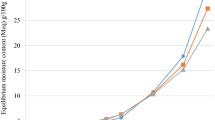
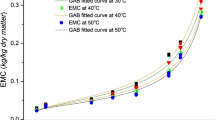
Moisture sorption data are useful in choosing suitable packaging material having a desirable water vapour barrier property in addition to determining the stability of the product. The sorption isotherms of milk burfi, one of the important Indian traditional milk-based sweets, using sugar and sugar substitutes were determined. The product was prepared replacing sugar with sorbitol, maltodextrin (MD)+polydextrose (PD), and PD alone, along with aspartame to give an equi-sweetness level compared to sugar. The isotherms followed typical sigmoidal shape, characteristic of sugar-rich products. The curve for burfi with sorbitol shifted to the left compared to that of sugar, whereas for those prepared with MD+PD or PD, the curves are similar to that of burfi made with sugar. Several models were chosen to fit sorption behaviour and the Guggenheim-Anderson-De Boer model showed a better fit compared to other models.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kilcast D (1999) Food Ingredients Anal Int 21:27–33
Wright N (1990) Manuf Confect 70:65–69
Sen DP, Ramanna BR (1979) Proceedings of the Symposium on The Status and Prospects of the Confectionery Industry in India. Mysore, India, pp 78–83
Arya SS (1990) Indian Food Packer 44:17–38
Hariharakrishnan PS (1979) Proceedings of the Symposium on the Status and Prospects of the Confectionery Industry in India. Mysore, India, pp 104–107
Labuza TP, Tannebaum SR, Karel M (1970) Food Technol 24:543–550
Mizrahi S, Karel MJ (1977) J Food Process Preserv 1:234–255
Venkatesh KVL, Dhanraj S, Mahadeviah B, Anandaswamy B, Govindrajan VS, Sen DP (1984) J Food Sci Technol (India) 21:167–171
Biradar US, Dev DK, Ingle UM (1985) J Food Sci Technol (India) 50:51–55
Rao TSS, Reddy TM, Jayaraman KS (1993) J Food Sci Technol (India) 30:462–464
Ramanna BR, Bhat KK, Mahadeviah B, Dwarkanath CT, Dhanraj S, Potty VH, Sen DP (1983) J Food Sci Technol (India) 20:67–71
Chakraborti S, Bisht HC, Agarwal MB, Saha NK (1980) J Food Sci Technol (India) 22:258–262
Venkatesh KVL, Mahadeviah B, Dhanraj S, Mahadeviah M, Ananthakrishna SM, Anandaswamy B, Govindrajan VS, Sen DP (1983) J Food Sci Technol (India) 20:209–213
Saxena AK, Kulkarni SG, Mannan JK, Berry SK, Beerh OP (1991) J Food Sci Technol (India) 28:352–355
Sharma GK, Madhura CV, Arya SS (1992) J Food Sci Technol (India) 29:289–292
Thakur BR, Arya SS (1990) J Food Sci Technol (India) 27:76–81
Rao TSS, Kaverappa NM, Reddy TH, Jayaraman KS (1990) J Food Sci Technol (India) 27:355–358, 359–361
Bera MB, Das H, Mukherjee RK (1990) Lebesm Wiss Technol 23:221–225
Van den Berg (1984) Description of water activity of foods for engineering purposes by means of the GAB model of sorption. In: BM Mckenna (ed) Engineering and food. Elsevier, London, pp 311–321
Wolf W, Speiss WEL, Jung G, Weisser H, Bizot H, Duckworth RB (1984) Food Eng 3:51–73
Labuza TP, Kaanane A, Chen JY (1985) J Food Sci 50:385–391
AOAC (1995) Official methods of analysis, 17th edn. Methods 96919 and 92504. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington DC
Labuza TP (1968) Food Technol 22:263–272
Caurie MJ (1970) J Food Technol 5:301–307
Chirife J, Iglesias HA (1978) J Food Technol 13:159–174
Weisser H (1985) Influence of temperature on sorption equilibria. In: Simatos D, Multon JL (eds) Properties of water in foods. Martinus Nijhoff, Dordrecht, pp 95–118
Hossain SK, Pal PK, Sarkar PK, Patil GR (2002) Nahrung 463:136–140
Agarwal KK, Clary BL (1971) J Food Sci 36:919–924
Sawhney IK, Patil GR, Kumar B (1991) Lebensm Wiss Technol 24:6–8
Sawhney IK, Kumar B, Patil GR (1991) J Dairy Res 58:329–355
Bandyopadhyay P, Das H, Sharma GP (1987) J Food Sci Technol (India) 24:6–11
Patil GR, Singh S (1998) J Food Sci Technol (India) 35:236–241
Bizot, H (1983) Using the Gab model to construct sorption isotherms. In: Jowitt R, Escher F, Hallstrom B, Meffert HFT, Speiss WEL, Vos G (eds) Physical properties of foods, Applied Science, London, pp 27–41
Caurie M, Lee TC, Salmon M, Chechester CO (1976) J Food Sci 41:448
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. B. R. Lokesh, Head, LSTF department; Dr. R.N. Tharanathan, Scientist, B & N department; and Dr. V. Prakash, Director of the Institute for their keen interest in the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chetana, R., Srinivasa, P.C. & Yella Reddy, S.R. Moisture sorption characteristics of milk burfi, an traditional Indian sweet, using sugar substitutes. Eur Food Res Technol 220, 136–141 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-004-1007-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-004-1007-1