Abstract
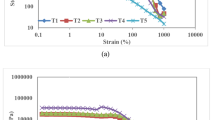
Low fat (17% fat) and full fat (27% fat) Edam cheese manufactured and aged up to 6 months at 5 °C were studies. The objective was to investigate the impact of fat on the physico-chemical and rheological properties of Edam cheese. Total soluble nitrogen in aqueous extract (TNAE), protein nitrogen in aqueous extract (Pro-NAE) and peptide nitrogen in aqueous extract (Pep-NAE) were determined by the Kjeldahl method. Low fat Edam (LFE) had markedly higher Pep-NAE than full fat Edam (FFE). The rheological properties were determined using an Instron Universal Testing Machine. LFE had significantly higher stress values than FFE, indicating hard and rubbery texture. Furthermore, LFE had lower strain values indicating crumbliness.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
McGregor J. U., White C. H. (1990) Effect of enzyme treatment and ultrafiltration on the quality of low fat Cheddar cheese. J Dairy Sci 73:571
Jameson G. W. (1987) Dietary cheeses: low fat, low salt. Food Technol. Aust 38:99
Lawrence R. C., Creamer L. K., Gilles J. 1987. Texture development during cheese ripening. J Dairy Sci 70:1748–1760
Lawrence R. C., Gilles J., Creamer L. K. (1983) The relationship between cheese texture and flavour. N Z J Dairy Sci Technol 18:175
Olson N. F. (1984) Making a marketable low fat cheese. Dairy Record Feb 85:115
Mistry V.V. (2001) Low fat cheese technology. Int Dairy J 11:413–422
Küçüköner E, Haque Z. U. (1995) Comparison of physical and chemical properties of low-fat (5%) and full-fat (32%) cheddar cheese. J Dairy Sci 78(Suppl 1):122 (Abstr.)
Furtado M. M., Partridge J. A. (1988) Characterization of nitrogen fractions during ripening of a soft cheese made from ultrafiltration retentases. J Dairy Sci 71:2877
Graizer C. L., Bodyfelt F. W. , McDaniel M. R., Torres J. A. (1991) Temperature effects on the development of cheddar cheese flavor and aroma. J Dairy Sci 74:3656
Mistry V.V., Kasperson K.M. (1998) Influence of salt on quality of reduced fat cheddar cheese. Journal of Dairy Science 81:1214—1221
Olson N.F.,Johnson M.E. (1990) Light cheese products: characteristics and economics. Food Technology 44(10):9396
Haque Z. U, Küçüköner E., Aryana K. (1997) Aging-induced changes in populations of lactococci, lactobacilli, and aerobic microorganisms in low-fat and full-fat CHEDDAR cheese. J Food Prot 60(9):1095–1098
Küçüköner E., Haque Z. U. (1998) Peptide profile of low fat edam cheese. Tr J Of Veterinary and Animal Sciences 22(5):449–452
Küçüköner E., Martin J. H. (1999) Microbial changes on full and reduced fat edam cheese during maturation. Food Sci Technol Res 5(3):262–264
Kosikowski F. V. (1982) Cheese and fermented milk foods. 2nd edn. F. V. Kosikowski and Assoc. Brooktondale, NY
Marth E. H. (1978) Standard methods for the examination of dairy products. American Public Health Association. 14th edn. Washington, D.C
Anonymous (1990). Association of Official Analytical Chemists International. Official methods of analysis. 15th edn. AOAC, Arlington, VA
Küçüköner E. (1996) Effect of comercial fat replacers on the physico-chemical properties and rheology of lowfat cheddar cheese. Ph.D. thesis, Mississippi State University, MS State, USA
Nielsen S.S. (1994) Introduction to the chemical analysis of Foods. Jones and Barlelt, Boston, MA
Haque Z.U., Mozaffar Z. (1992) Casein hyrolsate: 1. continuous production using immobilized enzyme bieroeactors. Food Hydrocolloids 5:549–559
Lee C.M., Filipi X.Y., Smith D., Regenstein, J., Damodaran S. Ma C.Y., Haque Z.U. (1998) Standardized failure compression test of protein gels from a collaborative study. J Food Sci 62(6):1163–1168
Küçüköner E., Aryana K.J., Haque Z.U. (1998) Rhelogy and microstructure of lowfat (5%) cheddar cheese containing a fat-like perception enhancers and fat replacers. Food Sci Int Tokyo 4 (3):178–183
Richardson G. H. (ed) (1985) Standard methods for the examination of dairy products. 15th edn. Am Publ Health Assoc, Washington, DC
DiLiello L.R. (1982) Methods in food and dairy microbiology. AVI. Westport, Connecticut
Vanderzant C., Splittstoesser D.F. (1992) Compendium of methods for the microbial examination of foods. Am Public Health Assoc, Washington, D.C
SAS User's Guide: Statistics, Version 6.0 Edition. (1990) SAS Inst., Cary, NC
Steele, R. G. D., and J. H. Torrie. 1980. Principles and Producers of Statistics. McGraw-Hill, New York, NY
Park S. S., Kim K. S., Kim . J., Kim Y. K. (1978) Studies on cheese ripening. 6. Variance of water soluble nitrogenous compounds during the ripening of cheddar cheese. Korean J Anim Sci 20:200–207
Litopoulou T.E., Tzanetakis N., Vafopoulou M.A. (1993) Effect of type of lactic starter on microbiological chemical and sensory characteristics of feta cheese. Food Microbiol 10:31–41
Cromie S.J., Giles J.E., Dulley J.R. (1987) Effect of elevated ripening temperatures on the microflora of cheddar cheese. J Dairy Res 54: 69–76
De Yong L. (1976) Protein breakdown in soft cheese and its relation to consistency. 1. proteolysis and consistency of "Noordhollandse Meshanger" cheese. Neth Milk Dairy J 30:242
Creamer L. K, Olson N. F. (1982) Rheological evaluation of maturing cheddar cheese. J Food Sci 47:631
Tunick M. H., Nolan E. J., ShiehJ. J.., Basch J. J., Thompson M. P., Maleeff B. E., Holsinger V. H. (1990) Cheddar and Cheshire cheese rheology. J Dairy Sci 73:1671
Tieleman A.E., Wartesen J.J. (1991) Comparison of three extraction procedures to characterize cheddar cheese proteolysis. J Dairy Sci 74:3686–3694
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Küçüköner, E., Haque, Z.U. Physico-chemical and rheological properties of full fat and low fat edam cheeses. Eur Food Res Technol 217, 281–286 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-003-0752-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-003-0752-x