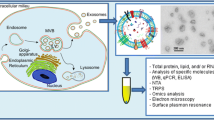
Abstract
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are secreted by all cells into bodily fluids and play an important role in intercellular communication through the transfer of proteins and RNA. There is evidence that EVs specifically released from mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) are potent cell-free regenerative agents. However, for MSC EVs to be used in therapeutic practices, there must be a standardized and reproducible method for their characterization. The detection and characterization of EVs are a challenge due to their nanoscale size as well as their molecular heterogeneity. To address this challenge, we have fabricated gold nanohole arrays of varying sizes and shapes by electron beam lithography. These platforms have the dual purpose of trapping single EVs and enhancing their vibrational signature in surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). In this paper, we report SERS spectra for MSC EVs derived from pancreatic tissue (Panc-MSC) and bone marrow (BM-MSC). Using principal component analysis (PCA), we determined that the main compositional differences between these two groups are found at 1236, 761, and 1528 cm−1, corresponding to amide III, tryptophan, and an in-plane -C=C- vibration, respectively. We additionally explored several machine learning approaches to distinguish between BM- and Panc-MSC EVs and achieved 89 % accuracy, 89 % sensitivity, and 88 % specificity using logistic regression.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lawson C, Vicencio JM, Yellon DM, Davidson SM. Microvesicles and exosomes: new players in metabolic and cardiovascular disease. J Endocrinol. 2016;228(2):R57–71.
Veziroglu EM, Mias GI. Characterizing extracellular vesicles and their diverse RNA contents. Front Genet. 2020;11:700.
Shpacovitch V, Hergenröder R. Optical and surface plasmonic approaches to characterize extracellular vesicles. A review Anal Chim Acta. 2018;1005:1–15.
Ståhl A-L, Johansson K, Mossberg M, Kahn R, Karpman D. Exosomes and microvesicles in normal physiology, pathophysiology, and renal diseases. Pediatr Nephrol. 2019;34(1):11–30.
Raposo G, Stoorvogel W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 2013;200(4):373–83.
Margolis L, Sadovsky Y. The biology of extracellular vesicles: the known unknowns. PLoS Biol. 2019;17(7):e3000363.
Pang B, Zhu Y, Ni J, Thompson J, Malouf D, Bucci J, et al. Extracellular vesicles: the next generation of biomarkers for liquid biopsy-based prostate cancer diagnosis. Theranostics. 2020;10(5):2309–26.
Mathew M, Zade M, Mezghani N, Patel R, Wang Y, Momen-Heravi F. Extracellular vesicles as biomarkers in cancer immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(10):2825.
De Jong OG, Van Balkom BWM, Schiffelers RM, Bouten CVC, Verhaar MC. Extracellular vesicles: potential roles in regenerative medicine. Front Immunol. 2014;5:608.
Marote A, Teixeira FG, Mendes-Pinheiro B, Salgado AJ. MSCs-derived exosomes: cell-secreted nanovesicles with regenerative potential. Front Pharmacol. 2016;7:231.
Jing H, He X, Zheng J. Exosomes and regenerative medicine: state of the art and perspectives. Transl Res. 2018;196:1–16.
Xin H, Li Y, Buller B, Katakowski M, Zhang Y, Wang X, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of miR-133b from multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells to neural cells contributes to neurite outgrowth. Stem Cells. 2012;30(7):1556–64.
Takeda YS, Xu Q. Neuronal differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells using exosomes derived from differentiating neuronal cells. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0135111.
El Bassit G, Patel RS, Carter G, Shibu V, Patel AA, Song S, et al. E MALAT1 in human adipose stem cells modulates survival and alternative splicing of PKCdII in HT22 cells. Endocrinology. 2017;158(1):183–95.
Ibrahim Ahmed G-E, Cheng K, Marbán E. Exosomes as critical agents of cardiac regeneration triggered by cell therapy. Stem Cell Rep. 2014;2(5):606–19.
Zhao Y, Sun X, Cao W, Ma J, Sun L, Qian H, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells relieve acute myocardial ischemic injury. Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:761643.
Agarwal U, George A, Bhutani S, Ghosh-Choudhary S, Maxwell JT, Brown ME, et al. Experimental, systems, and computational approaches to understanding the microRNA-mediated reparative potential of cardiac progenitor cell-derived exosomes from pediatric patients. Circ Res. 2017;120(4):701–12.
Tan CY, Lai RC, Wong W, Dan YY, Lim SK, Ho HK. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote hepatic regeneration in drug-induced liver injury models. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(3):76.
Nojima H, Freeman CM, Schuster RM, Japtok L, Kleuser B, Edwards MJ, et al. Hepatocyte exosomes mediate liver repair and regeneration via sphingosine-1-phosphate. J Hepatol. 2016;64(1):60–8.
Borges FT, Melo SA, Özdemir BC, Kato N, Revuelta I, Miller CA, et al. TGF-β1-containing exosomes from injured epithelial cells activate fibroblasts to initiate tissue regenerative responses and fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013;24(3):385–92.
Zhou Y, Xu H, Xu W, Wang B, Wu H, Tao Y, et al. Exosomes released by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells protect against cisplatin-induced renal oxidative stress and apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(2):34.
Jiang ZZ, Liu YM, Niu X, Yin JY, Hu B, Guo SC, et al. Exosomes secreted by human urine-derived stem cells could prevent kidney complications from type I diabetes in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7:24.
Zhang J, Chen C, Hu B, Niu X, Liu X, Zhang G, et al. Exosomes derived from human endothelial progenitor cells accelerate cutaneous wound healing by promoting angiogenesis through erk1/2 signaling. Int J Biol Sci. 2016;12(12):1472–87.
Li X, Liu L, Yang J, Yu Y, Chai J, Wang L, et al. Exosome derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell mediates miR-181c attenuating burn-induced excessive inflammation. EBioMedicine. 2016;8:72–82.
Zhao B, Zhang Y, Han S, Zhang W, Zhou Q, Guan H, et al. Exosomes derived from human amniotic epithelial cells accelerate wound healing and inhibit scar formation. J Mol Histol. 2017;48(2):121–32.
Furuta T, Miyaki S, Ishitobi H, Ogura T, Kato Y, Kamei N, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote fracture healing in a mouse model. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(12):1620–30.
Qi X, Zhang J, Yuan H, Xu Z, Li Q, Niu X, et al. Exosomes secreted by human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells repair critical-sized bone defects through enhanced angiogenesis and osteogenesis in osteoporotic rats. Int J Biol Sci. 2016;12(7):836–49.
Zhang S, Chu WC, Lai RC, Lim SK, Hui JHP, Toh WS. Exosomes derived from human embryonic mesenchymal stem cells promote osteochondral regeneration. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2016;24(12):2135–40.
Zhu Y, Wang Y, Zhao B, Niu X, Hu B, Li Q, et al. Comparison of exosomes secreted by induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells and synovial membrane-derived mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):64.
Nakamura Y, Miyaki S, Ishitobi H, Matsuyama S, Nakasa T, Kamei N, et al. Mesenchymal-stem-cell-derived exosomes accelerate skeletal muscle regeneration. FEBS Lett. 2015;589(11):1257–65.
Choi JS, Yoon HI, Lee KS, Choi YC, Yang SH, Kim I-S, et al. Exosomes from differentiating human skeletal muscle cells trigger myogenesis of stem cells and provide biochemical cues for skeletal muscle regeneration. J Control Release. 2016;222:107–15.
Zhang Y, Chopp M, Zhang ZG, Katakowski M, Xin H, Qu C, et al. Systemic administration of cell-free exosomes generated by human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured under 2D and 3D conditions improves functional recovery in rats after traumatic brain injury. Neurochem Int. 2017;111:69–81.
Mead B, Tomarev S. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes promote survival of retinal ganglion cells through miRNA-dependent mechanisms. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(4):1273–85.
Teng X, Chen L, Chen W, Yang J, Yang Z, Shen Z. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes improve the microenvironment of infarcted myocardium contributing to angiogenesis and anti-inflammation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;37(6):2415–24.
Tomasoni S, Longaretti L, Rota C, Morigi M, Conti S, Gotti E, et al. Transfer of growth factor receptor mRNA via exosomes unravels the regenerative effect of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(5):772–80.
van Niel G, D’Angelo G, Raposo G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(4):213–28.
Möller A, Lobb RJ. The evolving translational potential of small extracellular vesicles in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020;20(12):697–709.
Moskovits M. Persistent misconceptions regarding SERS. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2013;15(15):5301–11.
Rojalin T, Phong B, Koster HJ, Carney RP. Nanoplasmonic approaches for sensitive detection and molecular characterization of extracellular vesicles. Front Chem. 2019;7:279.
Iliescu FS, Vrtačnik D, Neuzil P, Iliescu C. Microfluidic technology for clinical applications of exosomes. Micromachines. 2019;10(6):392.
Zong S, Wang L, Chen C, Lu J, Zhu D, Zhang Y, et al. Facile detection of tumor-derived exosomes using magnetic nanobeads and SERS nanoprobes. Anal Methods. 2016;8(25):5001–8.
Tian YF, Ning CF, He F, Yin BC, Ye BC. Highly sensitive detection of exosomes by SERS using gold nanostar@Raman reporter@nanoshell structures modified with a bivalent cholesterol-labeled DNA anchor. Analyst. 2018;143(20):4915–22.
Beekman P, Enciso-Martinez A, Rho HS, Pujari SP, Lenferink A, Zuilhof H, et al. Immuno-capture of extracellular vesicles for individual multi-modal characterization using AFM, SEM and Raman spectroscopy Lab Chip. 2019;19(15):2526–36.
Kwizera EA, O’Connor R, Vinduska V, Williams M, Butch ER, Snyder SE, et al. Molecular detection and analysis of exosomes using surface-enhanced Raman scattering gold nanorods and a miniaturized device. Theranostics. 2018;8(10):2722–38.
Kim N, Thomas MR, Bergholt MS, Pence IJ, Seong H, Charchar P, et al. Surface enhanced Raman scattering artificial nose for high dimensionality fingerprinting. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):207.
Lee C, Carney RP, Hazari S, Smith ZJ, Knudson A, Robertson CS, et al. 3D plasmonic nanobowl platform for the study of exosomes in solution. Nanoscale. 2015;7(20):9290–7.
Sivashanmugan K, Huang W-L, Lin C-H, Liao J-D, Lin C-C, Su W-C, et al. Bimetallic nanoplasmonic gap-mode SERS substrate for lung normal and cancer-derived exosomes detection. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2017;80:149–55.
Yan Z, Dutta S, Liu Z, Yu X, Mesgarzadeh N, Ji F, et al. A label-free platform for identification of exosomes from different sources. ACS Sens. 2019;4(2):488–97.
Gualerzi A, Niada S, Giannasi C, Picciolini S, Morasso C, Vanna R, et al. Raman spectroscopy uncovers biochemical tissue-related features of extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stromal cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):9820.
Gualerzi A, Kooijmans SAA, Niada S, Picciolini S, Brini AT, Camussi G, et al. Raman spectroscopy as a quick tool to assess purity of extracellular vesicle preparations and predict their functionality. J Extracell Vesicles. 2019;8(1):1568780.
Kaufman L, Cooper T, Wallace G, Hawke D, Betts D, Hess D, et al. Trapping and SERS identification of extracellular vesicles using nanohole arrays. Proc SPIE 10894: Plasmonics in Biology and Medicine XVI, 108940B; 2019.
Sherman SE, Kuljanin M, Cooper TT, Putman DM, Lajoie GA, Hess DA. High aldehyde dehydrogenase activity identifies a subset of human mesenchymal stromal cells with vascular regenerative potential. Stem Cells. 2017;35(6):1542–53.
Cooper TT, Sherman SE, Bell GI, Ma J, Kuljanin M, Jose SE, et al. Characterization of a vimentinhigh/nestinhigh proteome and tissue regenerative secretome generated by human pancreas-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cells. 2020;38(5):666–82.
Cooper TT, Sherman SE, Bell GI, Dayarathna T, McRae DM, Ma J, et al. Ultrafiltration and injection of islet regenerative stimuli secreted by pancreatic mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2021;30(5):247–64.
Haynes CL, McFarland AD, Van Duyne RP. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 2005;77(17):338 A-46 A.
Sur UK. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Resonance. 2010;15(2):154–64.
Guo L, Jackman JA, Yang H-H, Chen P, Cho N-J, Kim D-H. Strategies for enhancing the sensitivity of plasmonic nanosensors. Nano Today. 2015;10(2):213–39.
Talari ACS, Movasaghi Z, Rehman S, Rehman IU. Raman spectroscopy of biological tissues. Appl Spectrosc Rev. 2015;50(1):46–111.
Rehman IU, Movasaghi Z, Rehman. FTIR and Raman characteristic peak frequencies in biological studies. Vibrational spectroscopy for tissue analysis. Boca Raton: CRC Press. 2012;1:213–94.
Stremersch S, Marro M, Pinchasik B-E, Baatsen P, Hendrix A, De Smedt SC, et al. Identification of individual exosome-like vesicles by surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Small. 2016;12(24):3292–301.
Huang Z, McWilliams A, Lui H, McLean DI, Lam S, Zeng H. Near-infrared Raman spectroscopy for optical diagnosis of lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 2003;107(6):1047–52.
Rau KR, Guerra A, Vogel A, Venugopalan V. Investigation of laser-induced cell lysis using time-resolved imaging. Appl Phys Lett. 2004;84(15):2940–2.
Gazor M, Talesh SSA, Kavianpour A, Khatami M, Javidanbardan A, Hosseini SN. A novel cell disruption approach: effectiveness of laser-induced cell lysis of pichia pastoris in the continuous system. Biotechnol Bioproc E. 2018;23(1):49–54.
Shin H, Oh S, Hong S, Kang M, Kang D. Ji Y-g, et al. Early-stage lung cancer diagnosis by deep learning-based spectroscopic analysis of circulating exosomes. ACS Nano. 2020;14(5):5435–44.
Howley T, Madden MG, O’Connell M-L, Ryder AG. The effect of principal component analysis on machine learning accuracy with high dimensional spectral data. Proc AI-2005: Applications and Innovcations in Intelligent Systems XII; 2005. p. 209-22.
Qi Y. Random forest for bioinformatics. In: Zhang C, Ma Y, editors. Ensemble machine learning: Methods and applications. Boston, MA: Springer US; 2012. p. 307–23.
Binkhonain M, Zhao L. A review of machine learning algorithms for identification and classification of non-functional requirements. Expert Syst Appl. 2019;1:100001.
Swe SM, Sett KM. Approaching rules induction CN2 algorithm in categorizing of biodiversity. Int J Trend Sci Res Dev. 2019;3(4):1581–4.
Dreiseitl S, Ohno-Machado L. Logistic regression and artificial neural network classification models: a methodology review. J Biomed Inform. 2002;35(5):352–9.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to gratefully thank the Nanofabrication Facility at the University of Western Ontario (Western University) for their assistance with the preparation of the platforms by electron-beam lithography.
Availability of data and material
The data sets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable
Funding
This research was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada (DG RGPIN-2020-06676).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Nina M. Ćulum: writing (original draft); investigation (nanofabrication and sample characterization); formal analysis; conceptualization.
Tyler T. Cooper: investigation (sample isolation and collection).
Gillian I. Bell: investigation (sample isolation and collection).
David A. Hess: supervision; conceptualization.
François Lagugné-Labarthet: supervision; writing (review and editing); conceptualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Ethics approval for the collection of human bone marrow was provided by the Western University Research Ethics Board (REB#12394).
Consent to participate
Informed written consent was acquired from all human bone marrow donors.
Consent for publication
All authors have given approval of the final version of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 241 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ćulum, N.M., Cooper, T.T., Bell, G.I. et al. Characterization of extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stromal cells by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Anal Bioanal Chem 413, 5013–5024 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03464-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03464-8