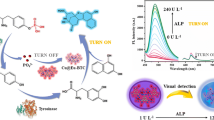
Abstract
Acid phosphatase has become a significant indicator of prognostic and medical diagnosis, and its dysfunction may lead to a series of diseases. A novel dual-signal fluorescence method for acid phosphatase detection based on europium polymer (europium-pyridine dicarboxylicacid-adenine) and pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) was proposed. PLP coordinated with europium polymer via Eu3+ and P–O bonds, and the fluorescence of europium polymer was quenched due to the photoinduced electron transfer (PET) effect between aldehyde and europium polymer. Upon addition of acid phosphatase, the PLP was transformed to phosphate (Pi) and pyridoxal (PL). The PL was released from the surface of europium polymer, and the blue emission was enhanced due to the formation of internal hemiacetal, while the fluorescence of europium polymer recovered. The blue (PL) and red emission (Eu3+) were positively correlated with acid phosphatase activity; thus the sensitive assay of acid phosphatase was effectively achieved. The two signals were applied to determine the acid phosphatase with limits of detection (LOD) of 0.04 mU/mL and 0.38 mU/mL, and the linear ranges were 0.13–5.00 mU/mL and 1.25–20.00 mU/mL, respectively. The probe can be used to trace the acid phosphatase in biological systems and holds promise for use in clinical diagnosis and early prevention.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belfiore F, Napoli E, Vecchio LL, Rabuazzo AM. Serum acid phosphatase activity in diabetes mellitus. Am J Med Sci. 1973;266:139–43.
Bull H, Murray PG, Thomas D, Fraser AM, Nelson PN. Acid phosphatases. J Clin Pathol: Mol Pathol. 2002;55:65–72.
Leman ES, Getzenberg RH. Biomarkers for prostate cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2009;108:3–9.
Xie YH, Tan Y, Liu RX, Zhao R, Tan CY, Jiang YY. Continuous and sensitive acid phosphatase assay based on a conjugated polyelectrolyte. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012;4:3784–7.
Hudson PB, Tsuboi KK, Mittelman A. Prostatic cancer: XII. Extremely elevated serum acid phosphatase associated with altered liver function. Am J Med. 1955;19:895–901.
Yamauchi Y, Ido M, Maeda H. High performance liquid chromatography equipped with a cathodic detector and column-switching device as a high-throughput method for a phosphatase assay with p-nitrophenyl phosphate. J Chromatogr A. 2005;1066:127–32.
Li X, Li B, Hong J, Zhou X. Highly selective determination of acid phosphatase in biological samples using a biomimetic recognition-based SERS sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018;276:421–8.
Kamel AH, Galal HR, Hanna AA. Novel planar chip biosensors for potentiometric immunoassay of acid phosphatase activity based on the use of ion association complexes as novel electroactive materials. Int J Electrochem Sci. 2014;9:5776–87.
Calvo-Marzal P, Rosatto SS, Granjeiro PA, Aoyama H, Kubota LT. Electroanalytical determination of acid phosphatase activity by monitoring p-nitrophenol. Anal Chim Acta. 2001;441:207–14.
Hu Q, Zhou B, Li F, Kong J, Zhang X. Turn-on colorimetric platform for dual activity detection of acid and alkaline phosphatase in human whole blood. Chem Asian J. 2016;11:3040–5.
Deng H, Lin X, Liu Y, Li K, Zhuang Q, Peng H, et al. Chitosan-stabilized platinum nanoparticles as effective oxidase mimics for colorimetric detection of acid phosphatase. Nanoscale. 2017;9:10292–300.
Zheng S, Gu H, Yin D, Zhang J, Li W, Fu Y. Biogenic synthesis of AuPd nanocluster as a peroxidase mimic and its application for colorimetric assay of acid phosphatase. Colloid Surface A. 2020:124444–74.
Jin L, Sun Y, Shi L, Li C, Shen Y. PdPt bimetallic nanowires with efficient oxidase mimic activity for the colorimetric detection of acid phosphatase in acidic media. J Mater Chem B. 2019;7:4561–7.
Na WD, Liu Q, Sui BW, Hu TY, Su XG. Highly sensitive detection of acid phosphatase by using a graphene quantum dots-based förster resonance energy transfer. Talanta. 2016;161:469–75.
Dwivedi AK, Iyer PK. Sensitive detection of acid phosphatase enzyme and screening of inhibitors using an anionic polyfluorene derivative. Anal Methods. 2013;5:2374–8.
Qu Z, Li N, Na W, Su X. A novel fluorescence “turn off–on” nanosensor for sensitivity detection acid phosphatase and inhibitor based on glutathione-functionalized graphene quantum dots. Talanta. 2019;192:61–8.
Xu M, Ma R, Huang C, Shi G, Zhou T, Deng J. Competitive redox reaction of Au-NCs/MnO2 nanocomposite: toward colorimetric and fluorometric detection of acid phosphatase as an indicator of soil cadmium contamination. Anal Chim Acta. 2020;1096:174–83.
Chen CX, Zhao JH, Lu YZ, Sun J, Yang XR. Fluorescence immunoassay based on the phosphate-triggered fluorescence turn-on detection of alkaline phosphatase. Anal Chem. 2018;90:3505–11.
Gao MP, Wu RY, Mei QS, Zhang CL, Ling X, Deng SS, et al. Upconversional nanoprobes with highly efficient energy transfer for ultrasensitive detection of alkaline phosphatase. ACS Sens. 2019;4:2864–8.
Tobey SL, Anslyn EV. Determination of inorganic phosphate in serum and saliva using a synthetic receptor. Org Lett. 2003;12:2029–31.
Enders DB, Rude RK. Mineral and bone metabolism: in Tietz textbook of clinical chemistry. Philadelphia: Saunders Company; 1999.
Zhao CX, Zhang XP, Shu Y, Wang JH. Europium–pyridinedicarboxylate–adenine light-up fluorescence nanoprobes for selective detection of phosphate in biological fluids. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12:22593–600.
Deng HH, Huang KY, He SB, Xue LP, Peng HP, Zha DJ, et al. Rational design of high-performance donor–linker–acceptor hybrids using a Schiff base for enabling photoinduced electron transfer. Anal Chem. 2020;92:2019–26.
Yin HQ, Wang XY, Yin XB. Rotation restricted emission and antenna effect in single metal–organic frameworks. J Am Chem Soc. 2019;141:15166–73.
Yang ZR, Wang MM, Wang XS, Yin XB. Boric-acid-functional lanthanide metal–organic frameworks for selective ratiometric fluorescence detection of fluoride ions. Anal Chem. 2017;89:1930–6.
Wang YM, Tian XT, Zhang H, Yang ZR, Yin XB. Anticounterfeiting quick response code with emission color of invisible metal–organic frameworks as encoding information. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:22445–52.
Achary SN, Bevara S, Tyagi AK. Recent progress on synthesis and structural aspects of rare-earth phosphates. Coord Chem Rev. 2017;340:266–97.
Song X, Ma Y, Ge X, Zhou H, Wang G, Zhang H, et al. Europium-based infinite coordination polymer nanospheres as an effective fluorescence probe for phosphate sensing. RSC Adv. 2017;7:8661–9.
Tan HL, Liu BX, Chen Y. Luminescence nucleotide/Eu3+ coordination polymer based on the inclusion of tetracycline. J Phys Chem C. 2012;116:2292–6.
Hu J, Yang XF, Peng QQ, Wang FY, Zhu Y, Hu X, et al. A highly sensitive visual sensor for tetracycline in food samples by a double signal response fluorescent nanohybrid. Food Control. 2020;108:106832–9.
Gao J, Wang CH, Tan HL. Lanthanide/nucleotide coordination polymers: an excellent host platform for encapsulating enzymes and fluorescent nanoparticles to enhance ratiometric sensing. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5:7692–700.
Wei H, Li BL, Du Y, Dong SJ, Wang E. Nucleobase–metal hybrid materials: preparation of submicrometer-scale, spherical colloidal particles of adenine–gold (III) via a supramolecular hierarchical self-assembly approach. Chem Mater. 2007;19:2987–93.
Liu RT, Chi LN, Wang XZ, Wang Y, Sui YM, Xie TT, et al. Effective and selective adsorption of phosphate from aqueous solution via trivalent-metals-based amino-MIL-101 MOFs. Chem Eng J. 2019;357:159–68.
Tan HL, Liu BX, Chen Y. Lanthanide coordination polymer nanoparticles for sensing of mercury(II) by photoinduced electron transfer. ACS Nano. 2012;6:10505–11.
Nowak MJ, Lapinski L, Kwiatkowski JS, Leszczyński J. Molecular structure and infrared spectra of adenine. Experimental matrix isolation and density functional theory study of adenine 15N isotopomers. J Phys Chem. 1996;100:3527–34.
Yan H, Wang H, He P, Shi J, Gong M. An efficient luminescent bonding-type Eu-containing copolymer as a red-emitting phosphor for fabrication of LED. Synth Met. 2011;161:748–52.
Jiao H, Chen J, Li W, Wang F, Zhou H, Li Y, et al. Nucleic acid-regulated Perylene probe-induced gold nanoparticle aggregation: a new strategy for colorimetric sensing of alkaline phosphatase activity and inhibitor screening. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6:1979–85.
Yang JL, Song NZ, Lv XJ, Jia Q. UV-light-induced synthesis of PEI-CuNCs based on Cu2+-quenchedfluorescence turn-on assay for sensitive detection of biothiols, acetylcholinesterase activity and inhibitor. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2018;259:226–32.
Qian ZS, Chai LJ, Zhou Q, Huang YY, Tang C, Chen JR, et al. Reversible fluorescent nanoswitch based on carbon quantum dots nanoassembly for real-time acid phosphatase activity monitoring. Anal Chem. 2015;87:7332–9.
Zhang J, Yuan Y, Han Z, Li Y, van Zijl PC, Yang X, et al. Detecting acid phosphatase enzymatic activity with phenol as a chemical exchange saturation transfer magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent (PhenolCEST MRI). Biosens Bioelectron. 2019;141:111442–60.
Huang M, Tian J, Zhou C, Bai P, Lu J. Photoelectrochemical determination for acid phosphatase activity based on an electron inhibition strategy. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2020;307:127654–61.
Zhu ZM, Lin XY, Wu L, Zhao CF, Zheng YJ, Liu AL, et al. “Switch-on” fluorescent nanosensor based on nitrogen-doped carbon dots-MnO2 nanocomposites for probing the activity of acid phosphatase. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018;274:609–15.
Shi FP, Zhang JY, Na WD, Zhou H, Zhang XY, Li Y, et al. An organic-inorganic hybrid co-crystal complex as a high-performance solid-state nonlinear optical switch. J Mater Chem C. 2016;4:266–71.
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21575055), the Henan Key Laboratory of Biomolecular Recognition and Sensing (HKLBRSK1901) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 561220006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shuangqin Li: Scheme design, Probe synthesis, Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Writing—original draft. Guoqing Fu: Schematic diagram drawing. Yaya Wang: Formal analysis. Yueci Xiang: Formal analysis. Shuai Mu: Formal analysis. Yixuan Xu: Discussion of experimental mechanism. Xiaoyan Liu: Essay review and grammar revision. Haixia Zhang: Writing—review & editing, Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The fresh serum samples were acquired from healthy individuals in the infirmary of Lanzhou University in accordance with the rules of the local ethical committee.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence their work.
All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOC 14026 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Fu, G., Wang, Y. et al. A dual-signal fluorescent probe for detection of acid phosphatase. Anal Bioanal Chem 413, 3925–3932 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03343-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03343-2