Abstract
A rapid and high-throughput quantification method (approximately 300 lipids within 20 min) was established using nanoflow ultrahigh-pressure liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (nUPLC-ESI-MS/MS) with selective reaction monitoring (SRM) and applied to the quantitative profiling of the hepatic lipids of rabbits with different metabolic conditions that stimulate the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Among the metabolic conditions of rabbits in this study [inflammation (I), high-cholesterol diet (HC), and high-cholesterol diet combined with inflammation (HCI)], significant perturbation in hepatic lipidome (>3-fold and p < 0.01) was observed in the HC and HCI groups, while no single lipid showed a significant change in group I. In addition, this study revealed a dramatic increase (>2-fold) in relatively high-abundant monohexosylceramides (MHCs), sphingomyelins (SMs), and triacylglycerols (TGs) in both the HC and HCI groups, especially in MHCs as all 11 MHCs increased by larger than 3- to 12-fold. As the levels of the relatively high-abundant lipids in the above classes increased, the total lipidome level of each class increased significantly by approximately 2-fold to 5-fold. Other classes of lipids also generally increased, which was likely induced by the increase in mitogenic and nonapoptotic MHCs and SMs, as they promote cell proliferation. On the other hand, a slight decrease in the level of apoptotic ceramides (Cers) was observed, which agreed with the general increase in total lipid level. As distinct changes in hepatic lipidome were observed from HC groups, this suggests that HC or HCI is highly associated with NAFLD but not inflammation alone itself.

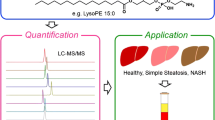
Schematic of lipidomic analysis from hepatic tissue using nanoflow LC-ESI-MS/MS and nUPLC-ESI-MS/MS





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brouwers JFHM, Vernooji EAAN, Tielens AGM, van Golde LMG. J Lipid Res. 1999;40:164.
Wright MM, Howe AG, Zaremberg V. Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;82:18.
Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA, et al. Circulation. 2005;112:2735.
Liu Y-Y, Hill RA, Li Y-T. Anti Cancer Agents Med Chem. 2012;12:340.
Nikolova-Karakashian MN, Rozenova KA. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;688:86.
Cajka T, Fiehn O. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2014;61:192.
Bang DY, Moon MH. J Chromatogr A. 2013;1310:82.
Moon MH. Mass Spectrom Lett. 2014;5:1.
Byeon SK, Lee JY, Lim S, Choi D, Moon MH. J Chromatogr A. 2012;1270:246.
Lee JY, Byeon SK, Moon MH. Anal Chem. 2015;87:1266.
Min HK, Lim S, Chung BC, Moon MH. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011;399:823.
Byeon SK, Lee JY, Lee J-S, Moon MH. J Chromatogr A. 2015;1381:132.
Byeon SK, Kim JY, Lee J-S, Moon MH. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016;408:2265.
Paschos P, Paletas K. Hippokratia. 2009;13:9.
Haga Y, Kanda T, Sasaki R, Nakamura M, Nakamoto S, Yokosuka O. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:12989.
Yu AS, Keeffe EB. Rev Gastroenterol Disord. 2002;2:11.
Yu S, Matsusue K, Kashireddy P, Cao WQ, Yeldandi V, Yeldandi AV, et al. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:498.
Koo SH. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2013;19:210.
James O, Day C. Lancet. 1999;353:1634.
Comhair TM, Garcia Caraballo SC, Dejong CH, Lames WH, Köhler SE. Nutr Metab. 2011;8:4.
Kerr TA, Davison NO. Hepatology. 2012;56:1995.
Donnelly KL, Smith CI, Schwarzenberg SJ, Jessurun J, Boldt MD, Parks EJ. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:1343.
Gordon DL, Ivanova PT, Myers DS, McIntyre JO, VanSaun MN, Wright JK, et al. PLoS One. 2011;6:e22775.
Puri P, Baillie RA, Wiest MM, Mirshahi F, Choudhury J, Cheung O, et al. Hepatology. 2007;46:1081.
Malhi H, Gores GJ. Semin Liver Dis. 2008;28:360.
Byeon SK, Kim JY, Lee JY, Chung BC, Seo HS, Moon MH. J Chromatogr A. 2015;1405:140.
Byeon SK, Lee JY, Moon MH. Analyst. 2012;138:451.
Lim S, Byeon SK, Lee JY, Moon MH. J Mass Spectrom. 2012;47:1004.
Jourayvas FR, Shulman GI. Cell Metab. 2012;15:574.
Qureshi K, Abrams GA. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:3540.
Claus RA, Dorer MJ, Bunck AC, Deigner HP. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16:1978.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant (NRF-2015R1A2A1A01004677) from the National Research Foundation of Korea and in part by a grant (NRF-2013M3A9B6046413) from the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program through the NRF funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT, & Future Planning.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Animal experiments complied with the Korea University Animal Science Rules and the protocols were approved by the Korea University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 493 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Byeon, S.K., Lee, J.C., Chung, B.C. et al. High-throughput and rapid quantification of lipids by nanoflow UPLC-ESI-MS/MS: application to the hepatic lipids of rabbits with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Anal Bioanal Chem 408, 4975–4985 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9592-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9592-y